Solved 2 1 Use The Laplace Transform Method To Solve Th

Laplace Transform Table Formula Examples Properties Now we need to find the inverse laplace transform. namely, we need to figure out what function has a laplace transform of the above form. we will use the tables of laplace transform pairs. later we will show that there are other methods for carrying out the laplace transform inversion. the inverse transform of the first term is \(e^{ 3 t}\). The laplace transform method from sections 5.2 and 5.3: applying the laplace transform to the ivp y00 ay0 by = f(t) with initial conditions y(0) = y 0, y0(0) = y 1 leads to an algebraic equation for y = lfyg, where y(t) is the solution of the ivp. the algebraic equation can be solved for y = lfyg.
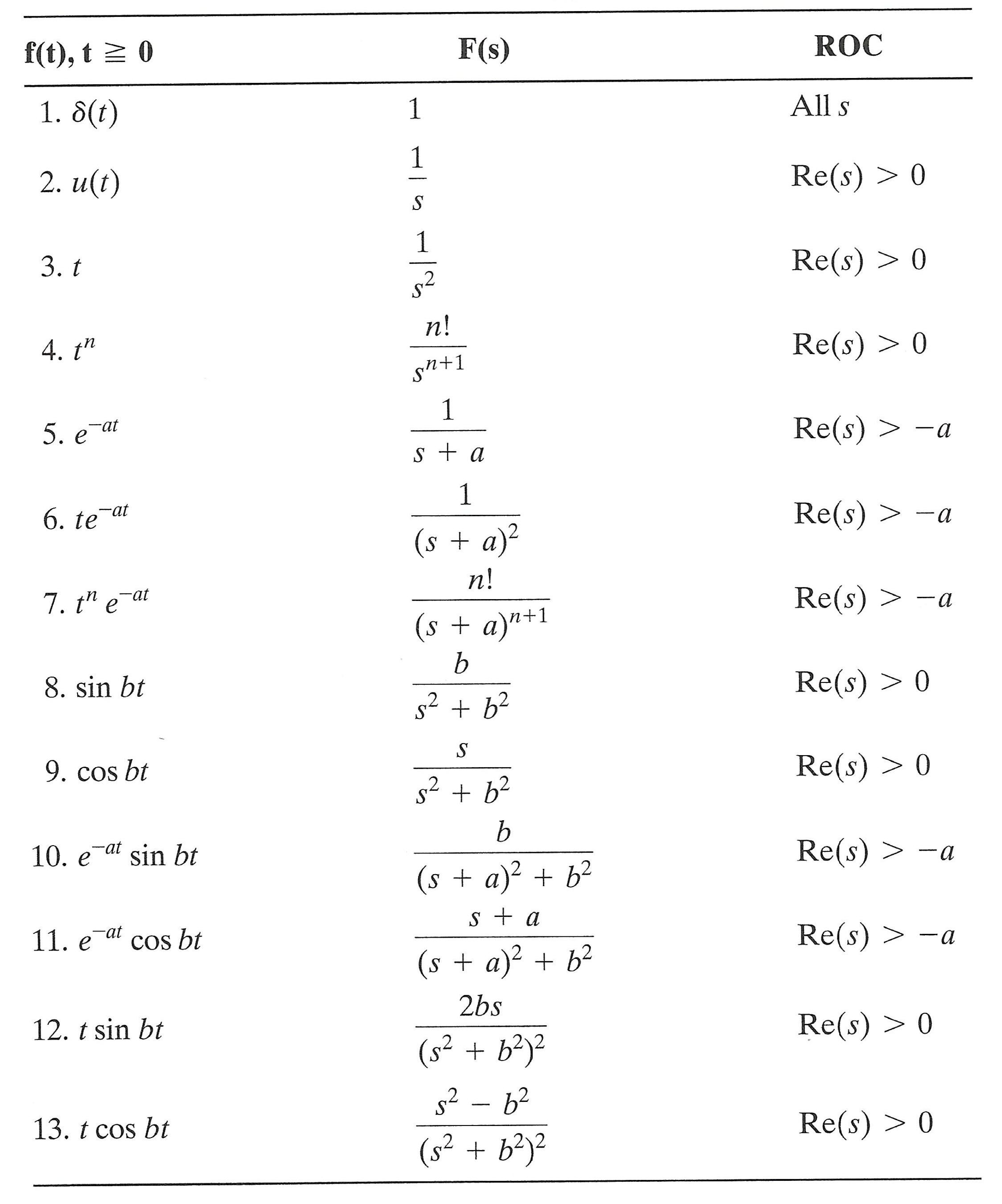
Solved Use Laplace Transforms To Solve The Initial Value Chegg While laplace transforms are particularly useful for nonhomogeneous differential equations which have heaviside functions in the forcing function we’ll start off with a couple of fairly simple problems to illustrate how the process works. example 1 solve the following ivp. y′′ −10y′ 9y =5t, y(0) = −1 y′(0) = 2. show solution. Use laplace transform to solve the differential equation y ″ 2y ′ 2y = 0 with the initial conditions y(0) = − 1 and y ′ (0) = 2 and y is a function of time t. solution to example 3. let y(s) be the laplace transform of y(t) take the laplace transform of both sides of the given differential equation. Solving ivps using laplace transforms real • solve the equation with initial conditions y(0)=1, y’(0)=0 using laplace transforms. 1. does the denominator have real or complex roots? 2. factor the denominator (factor directly, complete the square or qf). 3. partial fraction decomposition. 4. invert. I 1 = i 2 i 3 l di 1 dt i 1 r 1 i 2 r 2 = 0 e (t) i 2 r 2 q c i 3 r 3 = 0. substitute the relation i 3 = d q d t (which is the rate of the capacitor being charged) to the above equations to get the differential equations for the rlc circuit. di 1 dt r 2 l dq dt = r 1 r 2 l i 1 dq dt = 1 r 2 r 3 (e (t) q c) r 2 r 2 r.
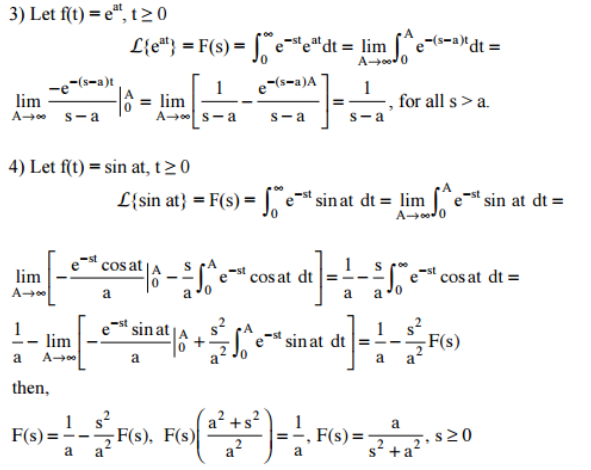
Laplace Transform Definition Formula Properties And Examples Solving ivps using laplace transforms real • solve the equation with initial conditions y(0)=1, y’(0)=0 using laplace transforms. 1. does the denominator have real or complex roots? 2. factor the denominator (factor directly, complete the square or qf). 3. partial fraction decomposition. 4. invert. I 1 = i 2 i 3 l di 1 dt i 1 r 1 i 2 r 2 = 0 e (t) i 2 r 2 q c i 3 r 3 = 0. substitute the relation i 3 = d q d t (which is the rate of the capacitor being charged) to the above equations to get the differential equations for the rlc circuit. di 1 dt r 2 l dq dt = r 1 r 2 l i 1 dq dt = 1 r 2 r 3 (e (t) q c) r 2 r 2 r. Theorem 2. 1 example (laplace method) solve by laplace’s method the initial value problem y0 = 5 2t, y(0) = 1. solution: laplace’s method is outlined in tables 2 and 3. the l notation of table 3 will be used to nd the solution y(t) = 1 5t t2. This is a linear homogeneous ode and can be solved using standard methods. let y (s)=l [y (t)] (s). instead of solving directly for y (t), we derive a new equation for y (s). once we find y (s), we inverse transform to determine y (t). the first step is to take the laplace transform of both sides of the original differential equation.
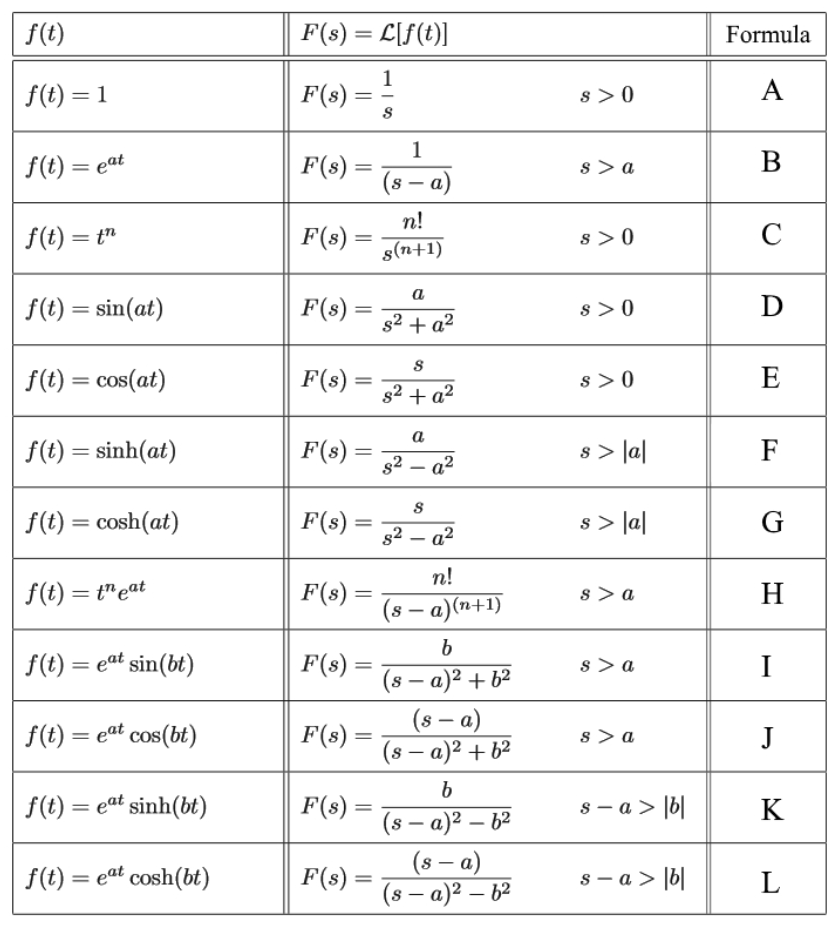
Calculating Laplace Transforms Studypug Theorem 2. 1 example (laplace method) solve by laplace’s method the initial value problem y0 = 5 2t, y(0) = 1. solution: laplace’s method is outlined in tables 2 and 3. the l notation of table 3 will be used to nd the solution y(t) = 1 5t t2. This is a linear homogeneous ode and can be solved using standard methods. let y (s)=l [y (t)] (s). instead of solving directly for y (t), we derive a new equation for y (s). once we find y (s), we inverse transform to determine y (t). the first step is to take the laplace transform of both sides of the original differential equation.
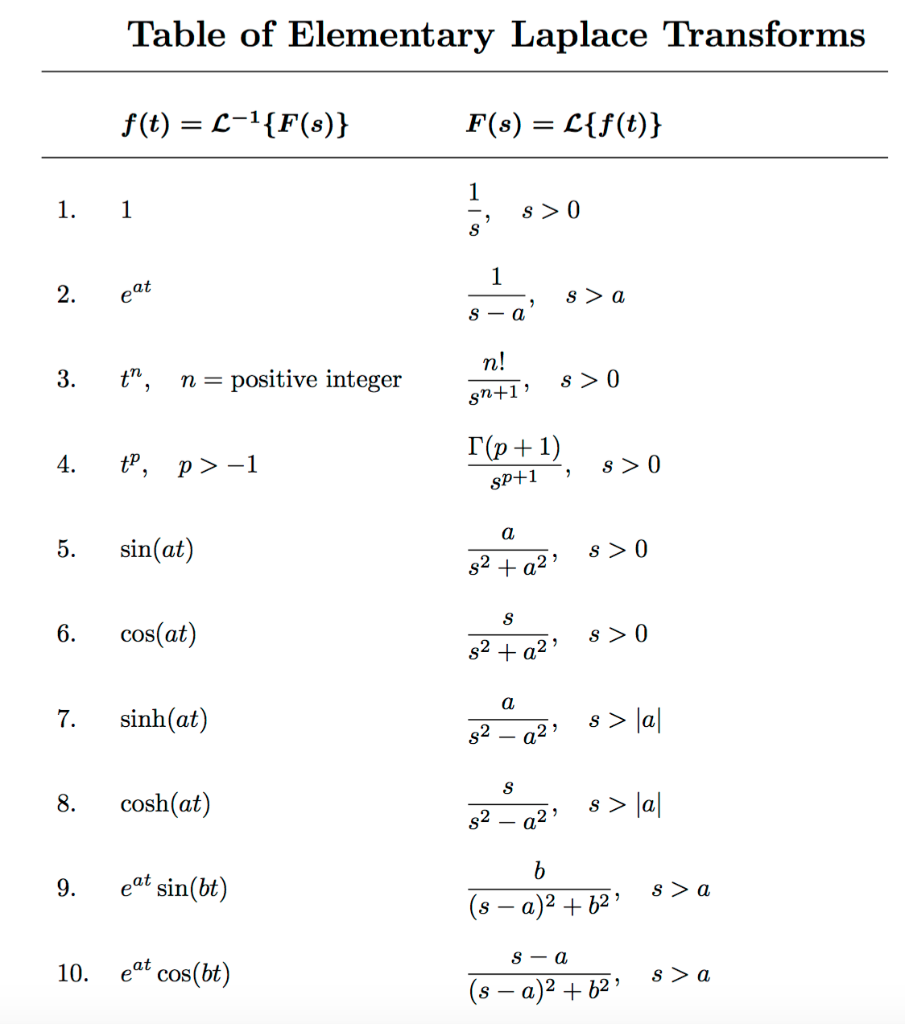
Solved Use Laplace Method To Solve The Following Chegg

Comments are closed.