Solved Use An Eigenvalue Eigenfunction Expansion To Solve Chegg
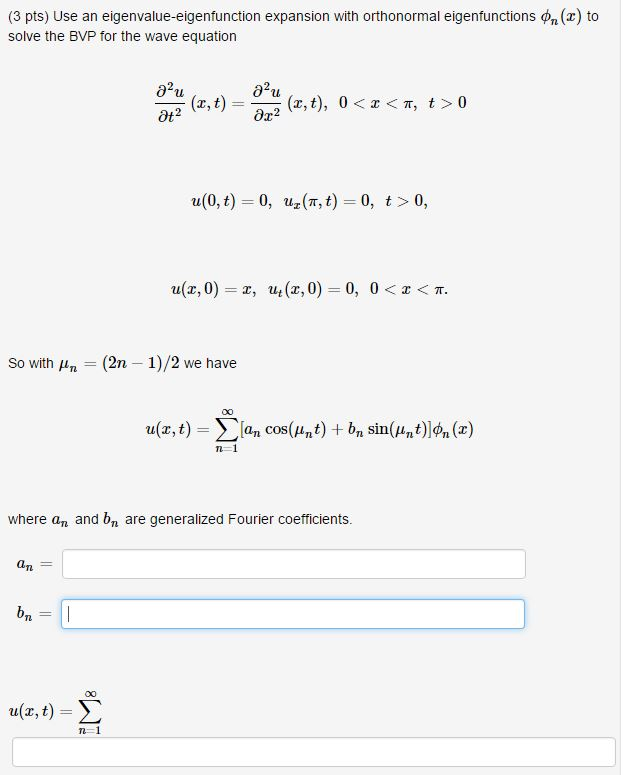
Solved Use An Eigenvalue Eigenfunction Expansion With Chegg Advanced math questions and answers. (4 points) use an eigenvalue eigenfunction expansion to solve the bvp for the wave equation so here an = bn = j²u j²u (x, t) = x2 (x,t), 00 at² u (x,t) = Σ n=1 u (0,t) = 0, u (1, t) = 0, t> 0, u (x, 0) = 0, u (x,0) = x, 0. Answer to use an eigenvalue eigenfunction expansion to solve. use an eigenvalue eigenfunction expansion to solve the bvp for the wave equation ∂2u∂t2(x,t)=∂.
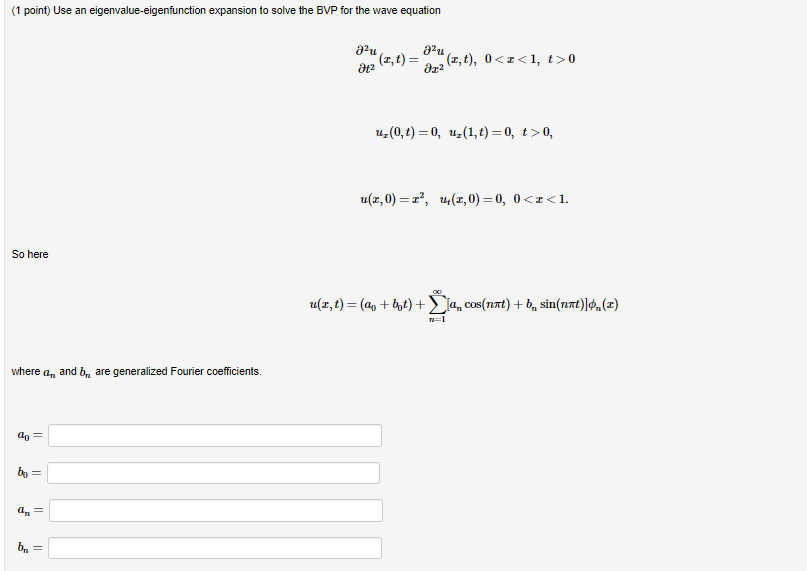
Solved 1 Point Use An Eigenvalue Eigenfunction Expansion Chegg Step 1. to solve the boundary value problem (bvp) for the wave equation using eigenvalue eigenfunction expan view the full answer step 2. unlock. step 3. unlock. step 4. unlock. answer. The eigenfunctions and eigenvalues are given by. ϕn(x) = sinnπx l, λn = (nπ l)2, n = 1, 2, 3, …. we can use these eigenfunctions to obtain a solution of the nonhomogeneous problem (7.6.1). we begin by assuming the solution is given by the eigenfunction expansion. u(x, t) = ∞ ∑ n = 1an(t)ϕn(x). We seek a solution in terms of the eigenfunction basis u(x;t) = x n c n(t)˚ n(x) by nding simple odes to solve for the coe cients c n(t):this form of the solution is called an eigenfunction expansion for u(or ‘eigenfunction series’) and each term c n˚ n(x) is a mode (or ‘fourier mode’ or ‘eigenmode’). part 1: nd the eigenfunction. The eigenfunction expansion technique requires that the problem be linear; for all functions. and w satisfying the boundary conditions and all scalar values α, l(y w) = l(y) l(w) l(αy) = αl(y) (y w) and αy satisfy the boundary conditions. we assume that there is a complete set of orthogonal eigenfunctions.

Comments are closed.