Spontaneous Gamma Activity In Schizophrenia Psychiatry And Behavioral

Spontaneous Gamma Activity In Schizophrenia Psychiatry And Behavioral This dissociation may have been found because cortical gamma activity is increased during wakefulness compared with rest, an effect that involves activation of the mesencephalic reticular formation and cholinergic input to the cortex from the basal forebrain. 30,31 increased spontaneous gamma activity in sz may require this cholinergic input to. R01mh093450 mh nimh nih hhs united states. spontaneous gamma activity is increased during auditory steady state stimulation in sz, reflecting a disruption in the normal balance of excitation and inhibition. this phenomenon interacts with evoked oscillations, possibly contributing to the gamma assr deficit found in sz. the similarity of incre ….

Spontaneous Gamma Activity In Schizophrenia Psychiatry And Behavioral Hirano y, oribe n, kanba s, et al. spontaneous gamma activity in schizophrenia. jama psychiatry. 2015; 72:813–821. the study examined both spontaneous gbo and evoked gbo activity in the auditory cortex of schizophrenia patients. compared to healthy controls, spontaneous (induced) gbo activity was increased during 40 hz auditory state. Background: spontaneous gamma (30 100 hz) activity (sg) in the eeg may reflect the balance of cortical excitation and inhibition (e i balance), which is disrupted in schizophrenia. i will review new work from our laboratory concerning sg and its implications for understanding cortical circuit abnormalities in schizophrenia. Spontaneous gamma (sg; 30 100 hz) activity has been related to cortical excitation inhibition balance. we previously reported that sg power was increased in individuals with schizophrenia (sz) compared to healthy controls (hc) during auditory steady state stimulation, consistent with evidence of increased cortical excitability in schizophrenia. increased spontaneous eeg activity has also been. The similarity of this induced gamma effect to the findings of increased spontaneous gamma activity in animal models of nmdar hypofunction suggests that induced gamma activity could serve as a biomarker for the integrity of nmdars on pvbcs in humans and in animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders (although other mechanisms could be involved.

Spontaneous Gamma Activity In Schizophrenia Psychiatry And Behavioral Spontaneous gamma (sg; 30 100 hz) activity has been related to cortical excitation inhibition balance. we previously reported that sg power was increased in individuals with schizophrenia (sz) compared to healthy controls (hc) during auditory steady state stimulation, consistent with evidence of increased cortical excitability in schizophrenia. increased spontaneous eeg activity has also been. The similarity of this induced gamma effect to the findings of increased spontaneous gamma activity in animal models of nmdar hypofunction suggests that induced gamma activity could serve as a biomarker for the integrity of nmdars on pvbcs in humans and in animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders (although other mechanisms could be involved. Abstract. increased spontaneous gamma (30–100 hz) activity (sga) has been reported in the auditory cortex in schizophrenia. this phenomenon has been correlated with psychotic symptoms such as auditory hallucinations and could reflect the dysfunction of nmda receptors on parvalbumin expressing inhibitory interneurons. Conclusions and relevance: spontaneous gamma activity is increased during auditory steady state stimulation in sz, reflecting a disruption in the normal balance of excitation and inhibition. this.
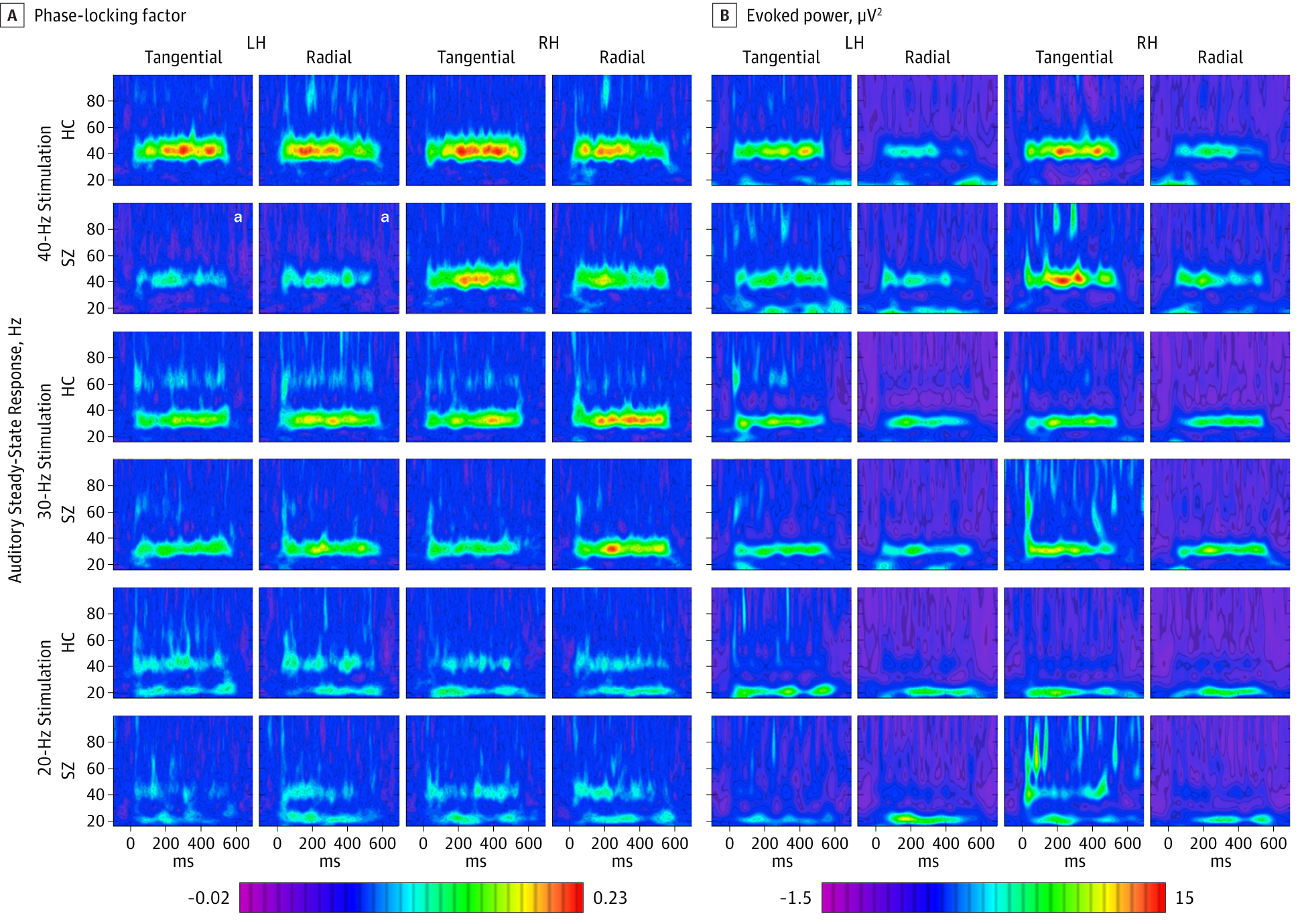
Spontaneous Gamma Activity In Schizophrenia Psychiatry And Behavioral Abstract. increased spontaneous gamma (30–100 hz) activity (sga) has been reported in the auditory cortex in schizophrenia. this phenomenon has been correlated with psychotic symptoms such as auditory hallucinations and could reflect the dysfunction of nmda receptors on parvalbumin expressing inhibitory interneurons. Conclusions and relevance: spontaneous gamma activity is increased during auditory steady state stimulation in sz, reflecting a disruption in the normal balance of excitation and inhibition. this.

Pdf The Contribution Of Gamma Bursting To Spontaneous Gamma Activity

Comments are closed.