Structure Of Antibodies
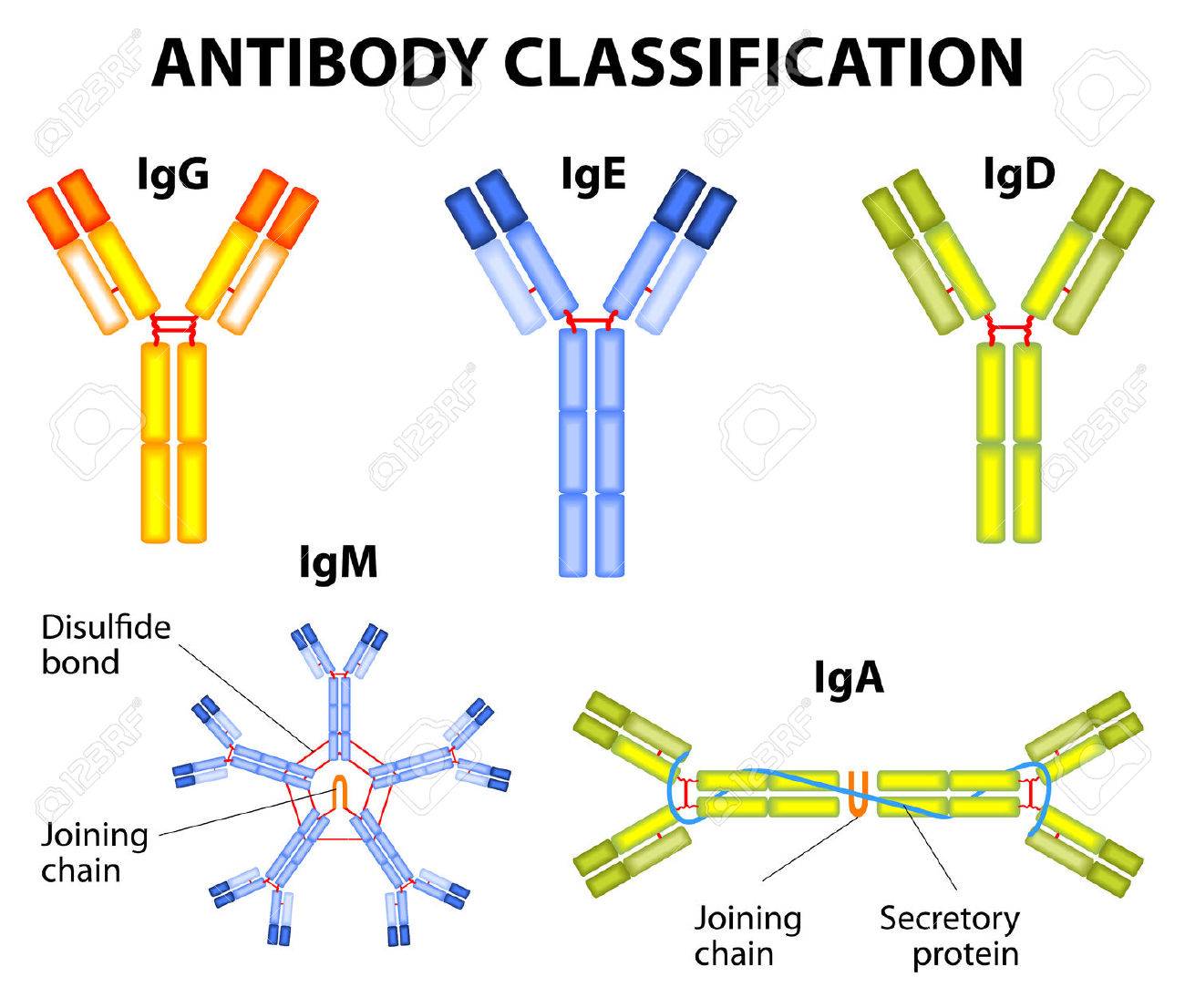
Antibody Structure Classes And Functions Online Biology Notes Learn about the structure and functions of antibodies, the protein molecules produced by b lymphocytes that recognize and bind antigens. find out the different forms, isotypes, and domains of antibodies, and how they interact with antigens and other immune cells. Antibodies are y shaped proteins that bind to specific antigens and trigger immune responses. learn about their structure, function, classes, subclasses, and how they are produced and regulated by b cells.

Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica Antibodies are protective proteins produced by b cells in response to antigens. learn how antibodies work, how they are structured, and how they differ in function and type. The structure of a typical antibody molecule. antibodies are the secreted form of the b cell receptor. an antibody is identical to the b cell receptor of the cell that secretes it except for a small portion of the c terminus of the heavy chain constant region. in the case of the b cell receptor the c terminus is a hydrophobic membrane anchoring. Learn how antibodies are y shaped proteins that bind to specific antigens and neutralize or tag them for removal by the immune system. explore the five isotypes of antibodies and their roles in different parts of the body. Learn how antibodies are composed of two pairs of polypeptide chains that form a y shape and have two antigen binding sites. find out the five classes of antibodies and their functions in medicine and research.
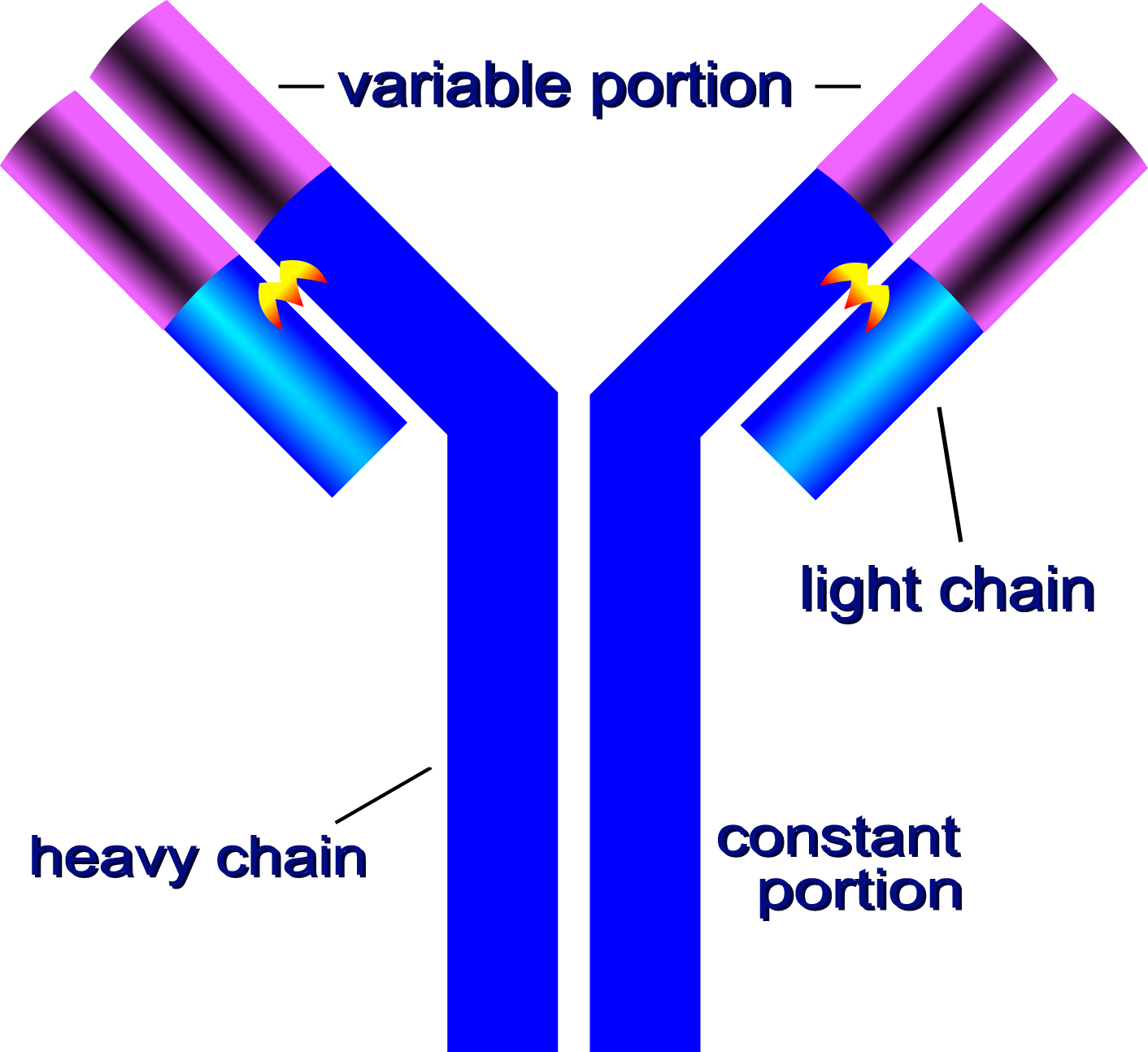
Label The Diagram Of An Antibody Structure Learn how antibodies are y shaped proteins that bind to specific antigens and neutralize or tag them for removal by the immune system. explore the five isotypes of antibodies and their roles in different parts of the body. Learn how antibodies are composed of two pairs of polypeptide chains that form a y shape and have two antigen binding sites. find out the five classes of antibodies and their functions in medicine and research. 42.3: antibodies. an antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin (ig), is a protein that is produced by plasma cells after stimulation by an antigen. antibodies are the functional basis of humoral immunity. antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk. The general features of antibodies described below will focus on the igg1 framework. our knowledge of how antibody structure relates to function is being exploited to create antibodies and antibody related biologics with the appropriate functional and biophysical properties to address specific therapeutic needs.
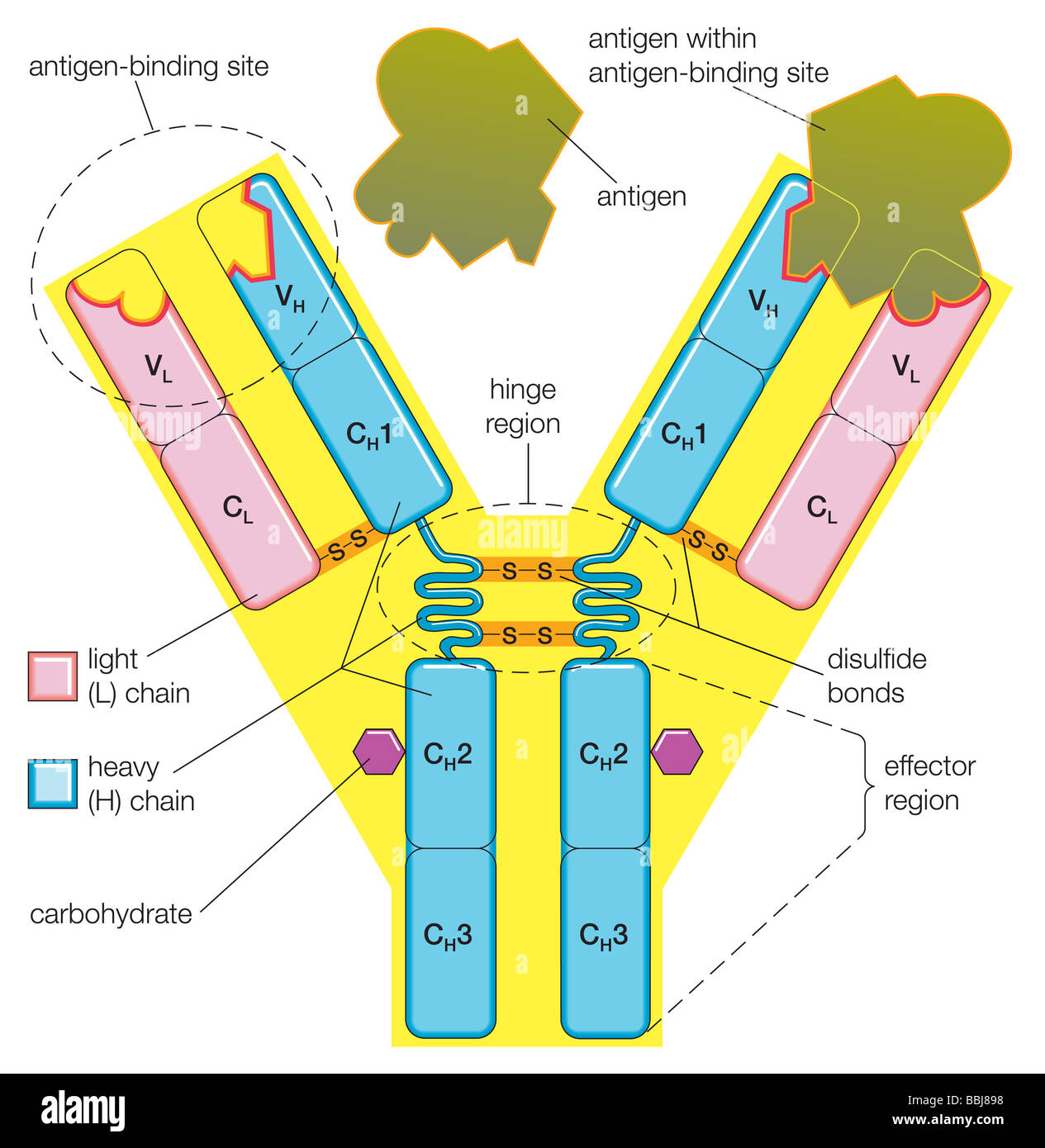
The Structure Of An Antibody Molecule Represents The Dramatic 42.3: antibodies. an antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin (ig), is a protein that is produced by plasma cells after stimulation by an antigen. antibodies are the functional basis of humoral immunity. antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk. The general features of antibodies described below will focus on the igg1 framework. our knowledge of how antibody structure relates to function is being exploited to create antibodies and antibody related biologics with the appropriate functional and biophysical properties to address specific therapeutic needs.

Comments are closed.