Structure Of The Cell Membrane Active And Passive Transport
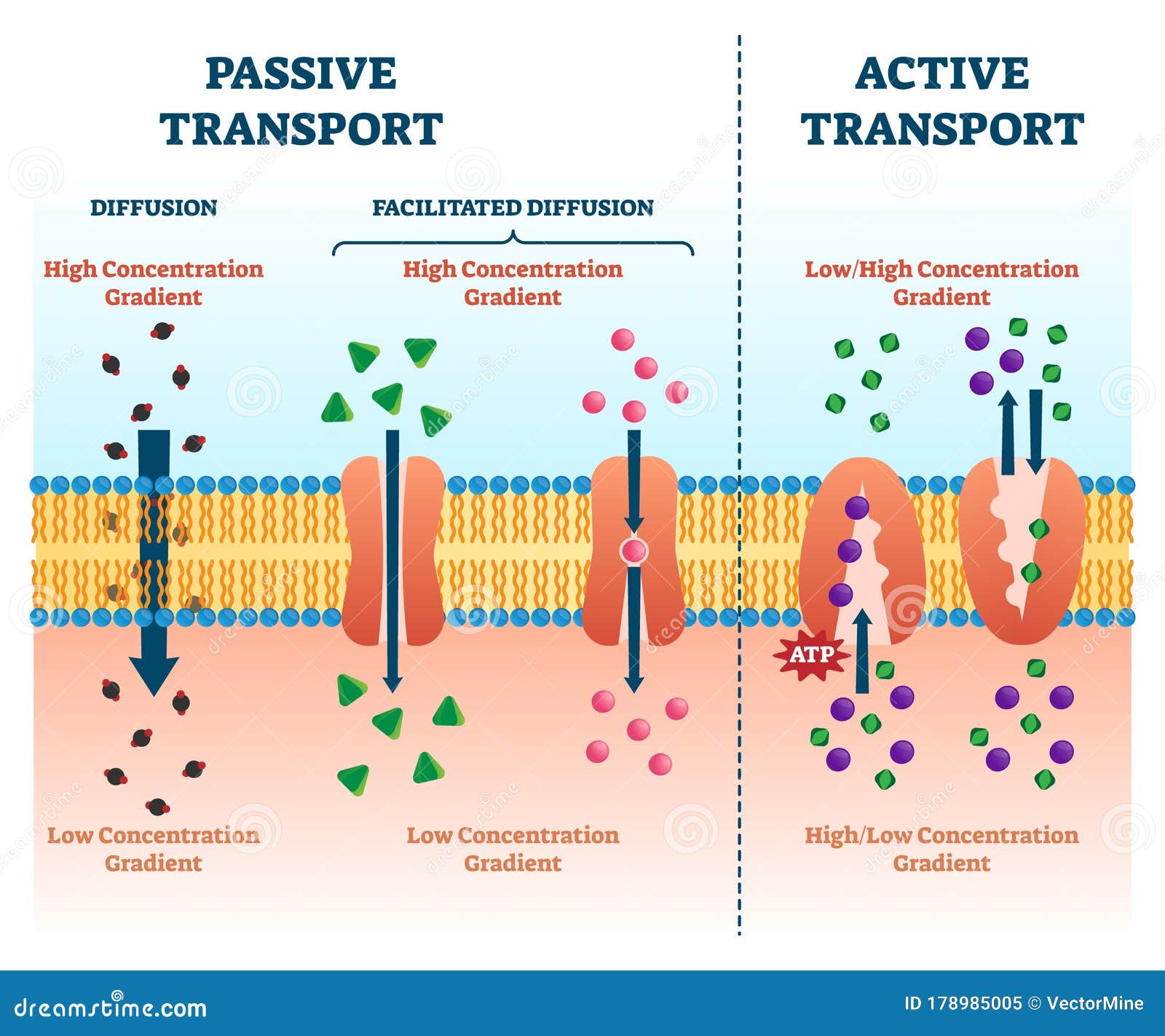
Cell Membrane Transport Diagram Simple Functions And Diagram What is it that separates what's inside a cell from what's outside of a cell? why, that's the cell membrane. what's it made out of? how does it work? how do. There are two major methods for moving molecules across a membrane, and it is related to whether or not cell energy is used. passive mechanisms, such as diffusion, require no energy to function, whereas active transport does. in passive transport, an ion or molecule crosses the membrane and moves down its concentration or electrochemical gradient.
.PNG)
Membranes Structure And Function Presentation Biology The cell membrane is selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival. the movement of substances across the membrane can be either "passive", occurring without the input of cellular energy, or "active", requiring the cell to expend energy in transporting. While passive transport is the simple option for moving molecules across the membrane, active transport is no less essential to cell function and survival. now, as explained above, passive transport involves moving molecules “down” the concentration gradient, from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Molecules move in and out of cells in one of three ways: passive diffusion, facilitated transport and active transport. only a few small, relatively uncharged molecules can cross a membrane unassisted (i.e., by passive diffusion). hydrophilic molecules that must enter or leave cells do so with help, i.e., by facilitated transport. Other forms of membrane transport. other forms of active transport do not involve membrane carriers. endocytosis (bringing “into the cell”) is the process of a cell ingesting material by enveloping it in a portion of its cell membrane, and then pinching off that portion of membrane (figure 3.1.8). once pinched off, the portion of membrane.

Comments are closed.