Sum Of Angles In Triangle Theorem

Triangle Sum Theorem вђ Definition Proof Examples The triangle sum theorem states that the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. in a euclidean space, the sum of the measure of the interior angles of a triangle sum up to 180 degrees, be it an acute, obtuse, or a right triangle which is the direct result of the triangle sum theorem, also known as the angle sum theorem of. A, b and c are the three vertices and ∠abc, ∠bca and ∠cab are three interior angles of ∆abc. theorem 1: angle sum property of triangle states that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°. proof: consider a ∆abc, as shown in the figure below. to prove the above property of triangles, draw a line pq parallel to the side bc of.

Angle Sum In A Triangle Passy S World Of Mathematics Hypothesis: from the triangle sum theorem, the sum of all three angles equals 180°. again, from the definition of an equilateral triangle, all angles are of equal measure. adding up all the angles, we get, ⇒ x x x = 180°. ⇒ 3x = 180°. ⇒ x = 60°. conclusion: each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60°. what is the triangle. The angle sum property of a triangle theorem states that the sum of all three internal angles of a triangle is 180 ∘. it is also known as the angle sum theorem or triangle sum theorem. according to the angle sum theorem, in the above abc, m ∠ a m ∠ b m ∠ c = 180 ∘. example: in pqr, ∠ p = 60 ∘, ∠ q = 70 ∘. The triangle sum theorem says that the three interior angles of any triangle add up to 180∘ 180 ∘. figure 4.17.1 4.17. 1. m∠1 m∠2 m∠3 = 180∘ m ∠ 1 m ∠ 2 m ∠ 3 = 180 ∘. here is one proof of the triangle sum theorem. figure 4.17.2 4.17. 2. The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°.
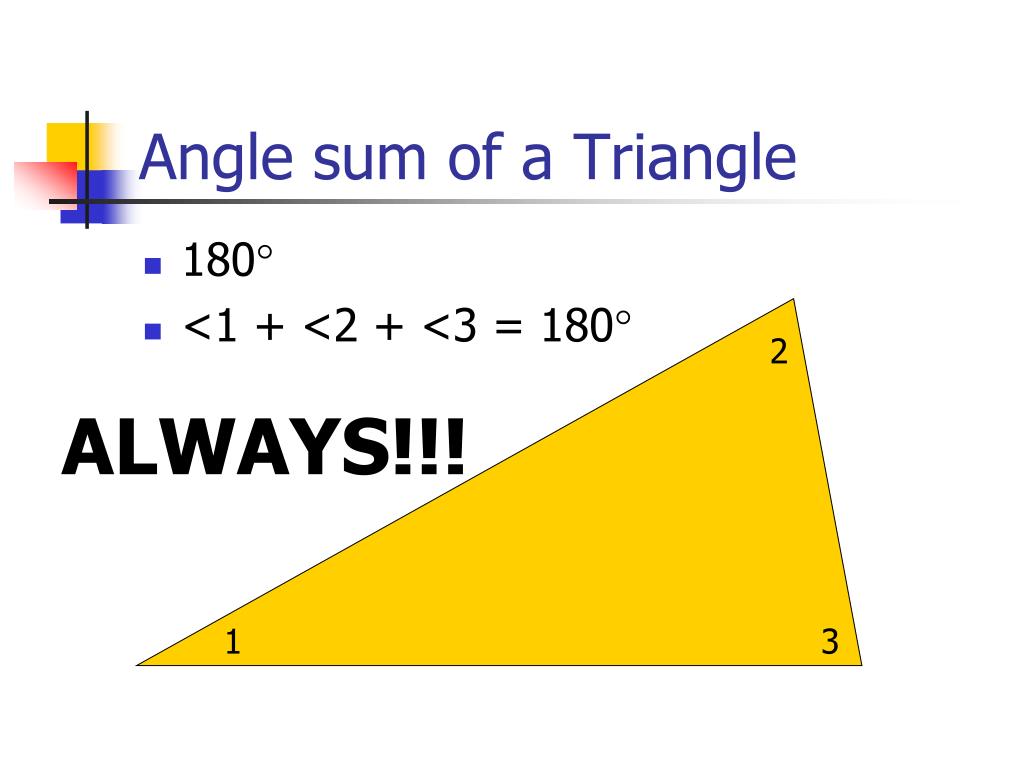
Ppt Triangle Sum Theorem Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id The triangle sum theorem says that the three interior angles of any triangle add up to 180∘ 180 ∘. figure 4.17.1 4.17. 1. m∠1 m∠2 m∠3 = 180∘ m ∠ 1 m ∠ 2 m ∠ 3 = 180 ∘. here is one proof of the triangle sum theorem. figure 4.17.2 4.17. 2. The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°. The angle sum property of a triangle states that the sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to 180º. a triangle has three sides and three angles, one at each vertex. whether a triangle is an acute, obtuse, or a right triangle, the sum of its interior angles is always 180º. Exterior angles can be also defined, and the euclidean triangle postulate can be formulated as the exterior angle theorem. one can also consider the sum of all three exterior angles, that equals to 360° [8] in the euclidean case (as for any convex polygon), is less than 360° in the spherical case, and is greater than 360° in the hyperbolic case.
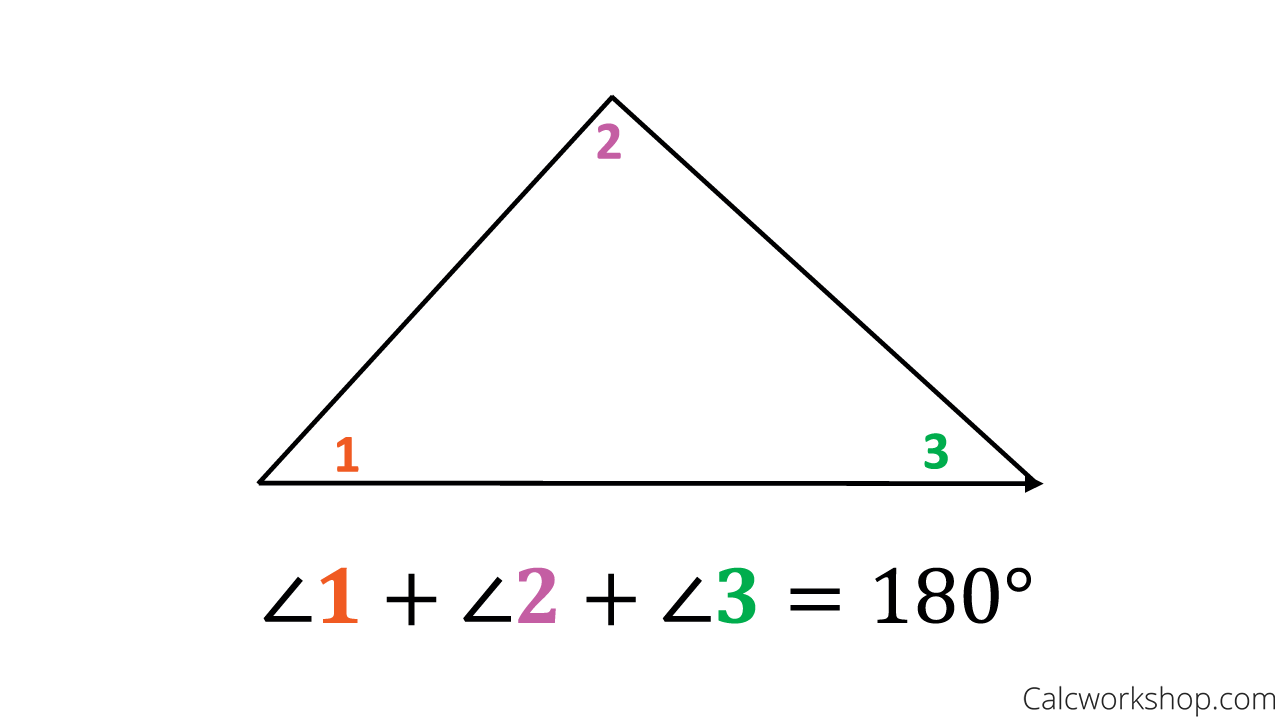
Classifying Triangles 15 Step By Step Examples The angle sum property of a triangle states that the sum of the angles of a triangle is equal to 180º. a triangle has three sides and three angles, one at each vertex. whether a triangle is an acute, obtuse, or a right triangle, the sum of its interior angles is always 180º. Exterior angles can be also defined, and the euclidean triangle postulate can be formulated as the exterior angle theorem. one can also consider the sum of all three exterior angles, that equals to 360° [8] in the euclidean case (as for any convex polygon), is less than 360° in the spherical case, and is greater than 360° in the hyperbolic case.

Comments are closed.