Supply And Demand Pdf Economic Equilibrium Supply And Demand
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g367-5c79c858c9e77c0001d19d1d.jpg)
Illustrated Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium Introduction. supply and demand are mechanisms by which our market economy functions. changes in supply and demand affect prices and quantities produced, which in turn affect profit, employment, wages, and government revenue. chapter 3 introduces models explaining the behavior of consumers and producers in markets, as well as the effects of. Anges between peo. place.ii. supply and demand. emandthe buying side of the market.there is a negative relationship between the quan. ty demanded of a good and its price.the relationship reflects optimizi. d. sprice (p)dquantity (q) pplythe selling side of the market.there is a positive relationship between the quan.

Law Of Supply And Demand Pdf Economic Equilibrium Supply And Demand The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. it is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. a surplus exists if the quantity of a good or service supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current price; it causes downward pressure on price. Rental prices fell because the demand for office space fell. figure 2.10 describes the market for office space in downtown manhattan. the supply and demand curves before 9 11 appear as saug and daug. the equilib rium price and quantity of downtown manhattan office space were $45.34 psf and 76.4 msf, respectively. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. 10. in general, an increase in demand tends to increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity. 11. if both supply and demand increase, the price of the good will also increase. 12. if demand increases and supply decreases, the price of the good will increase. 13. the more precise a model is, the more likely it is to be accurate.
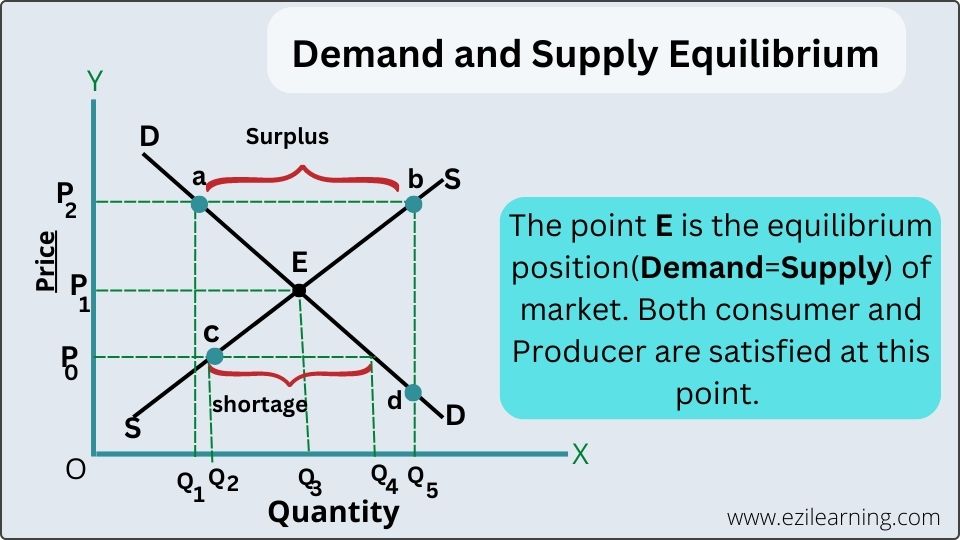
Explain The Law Of Supply And Demand Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. 10. in general, an increase in demand tends to increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity. 11. if both supply and demand increase, the price of the good will also increase. 12. if demand increases and supply decreases, the price of the good will increase. 13. the more precise a model is, the more likely it is to be accurate. B. explain the principles of demand and supply; c. describe causes of shifts in and movements along demand and supply curves; d. describe the process of aggregating demand and supply curves; e. describe the concept of equilibrium (partial and general), and mechanisms by which markets achieve equilibrium; f. Ø 2. implies buyers and sellers are price takers. undifferentiated products: consumers perceive the product to be identical so don’t care who they buy it from. perfect information about price: consumers know the price of all sellers. equal access to resources: everyone has access to the same technology and inputs.

Demand And Supply Pdf Supply And Demand Economic Equilibriumо B. explain the principles of demand and supply; c. describe causes of shifts in and movements along demand and supply curves; d. describe the process of aggregating demand and supply curves; e. describe the concept of equilibrium (partial and general), and mechanisms by which markets achieve equilibrium; f. Ø 2. implies buyers and sellers are price takers. undifferentiated products: consumers perceive the product to be identical so don’t care who they buy it from. perfect information about price: consumers know the price of all sellers. equal access to resources: everyone has access to the same technology and inputs.

Equilibrium Of Demand And Supply Pdf Supply And Demand Econom

Comments are closed.