Supply Demand In Equilibrium
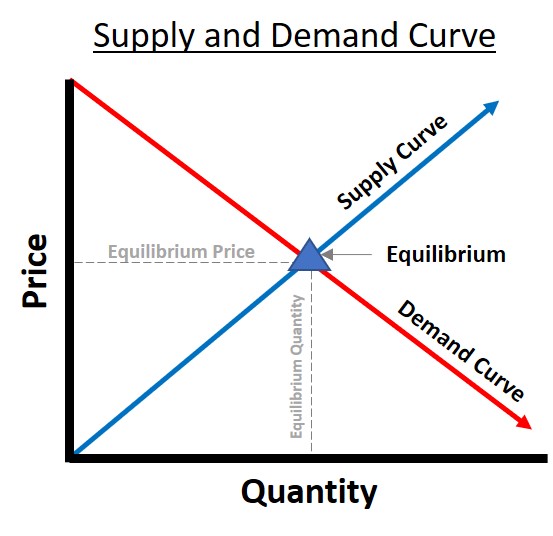
рџњ How Do You Find The Equilibrium Price And Quantity How To Calculate Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. it is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. a surplus exists if the quantity of a good or service supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current price; it causes downward pressure on price.

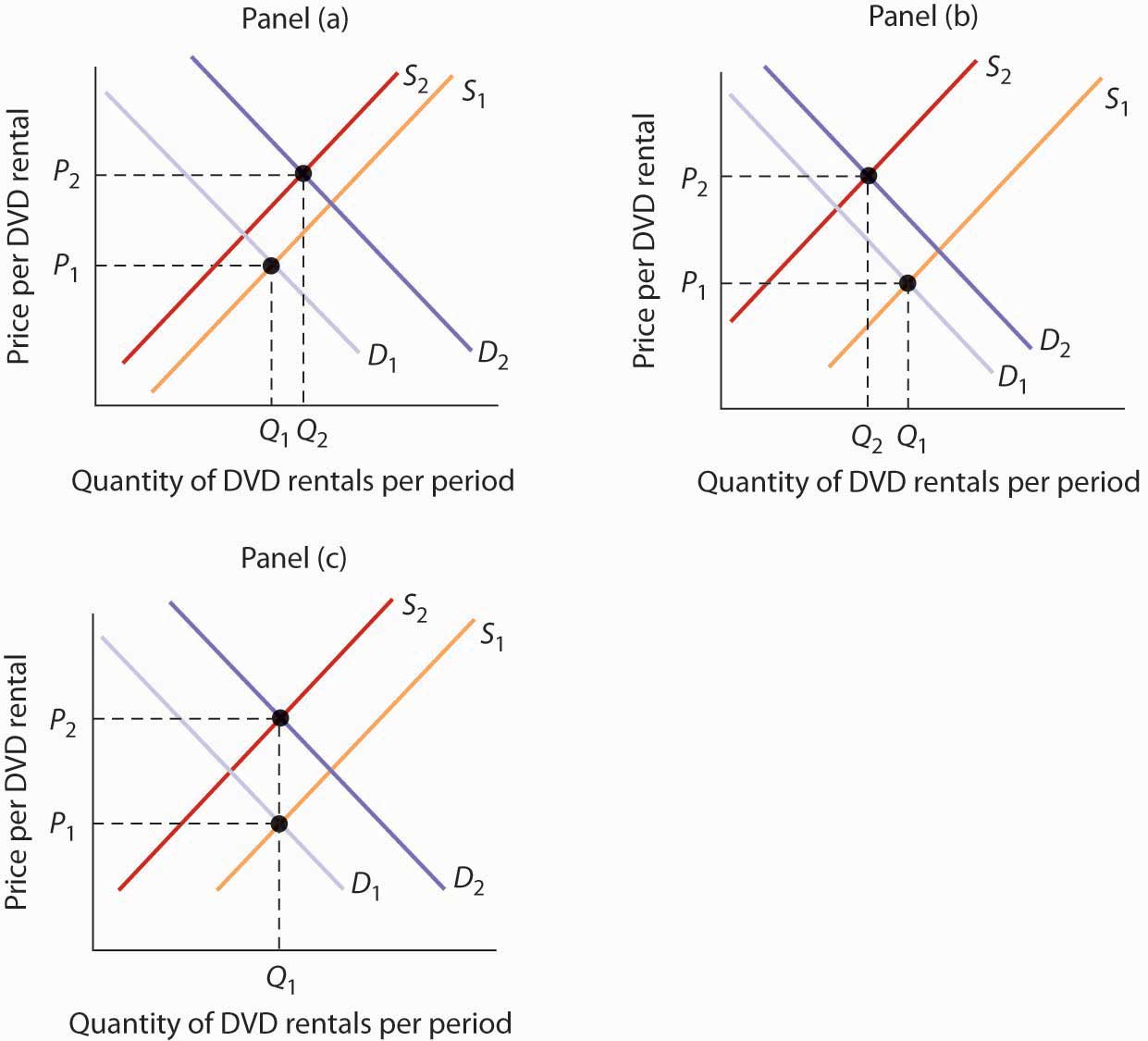
Explain What Equilibrium Is In A Demand And Supply Curve Homework A decrease in demand. panel (b) of figure 3.10 “changes in demand and supply” shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. the equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. as the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity demanded and supplied at the equilibrium price. figure 3.14 the determination of equilibrium price and quantity when we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. The price at which demand matches supply is the equilibrium, the point at which the market clears. the law of supply and demand is critical in helping all players within a market understand and. Equilibrium is the state in which market supply and demand balance each other, and as a result prices become stable. generally, an over supply of goods or services causes prices to go down, which.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g367-5c79c858c9e77c0001d19d1d.jpg)
Illustrated Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium The price at which demand matches supply is the equilibrium, the point at which the market clears. the law of supply and demand is critical in helping all players within a market understand and. Equilibrium is the state in which market supply and demand balance each other, and as a result prices become stable. generally, an over supply of goods or services causes prices to go down, which. Supply and demand model. the equilibrium is located at the intersection of the curves. dallas.epperson cc by sa 3.0 creative commons. even though the concepts of supply and demand are introduced separately, it's the combination of these forces that determine how much of a good or service is produced and consumed in an economy and at what price. Introduction to demand and supply; 3.1 demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets for goods and services; 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process; 3.4 price ceilings and price floors; 3.5 demand, supply, and efficiency; key terms; key concepts and summary; self.
Demand Supply And Equilibrium вђ Microeconomics For Managers Supply and demand model. the equilibrium is located at the intersection of the curves. dallas.epperson cc by sa 3.0 creative commons. even though the concepts of supply and demand are introduced separately, it's the combination of these forces that determine how much of a good or service is produced and consumed in an economy and at what price. Introduction to demand and supply; 3.1 demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets for goods and services; 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process; 3.4 price ceilings and price floors; 3.5 demand, supply, and efficiency; key terms; key concepts and summary; self.

Comments are closed.