T Cell Structure
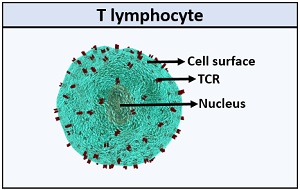
What Is T Cell Definition Types Receptors Maturation Biology Reader T cell. t cells are one of the important types of white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. t cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a t cell receptor (tcr) on their cell surface. t cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, [1] found in the bone marrow. T cell, type of leukocyte (white blood cell) that is an essential part of the immune system. t cells are one of two primary types of lymphocytes — b cells being the second type—that determine the specificity of immune response to antigens (foreign substances) in the body. t cells originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus.
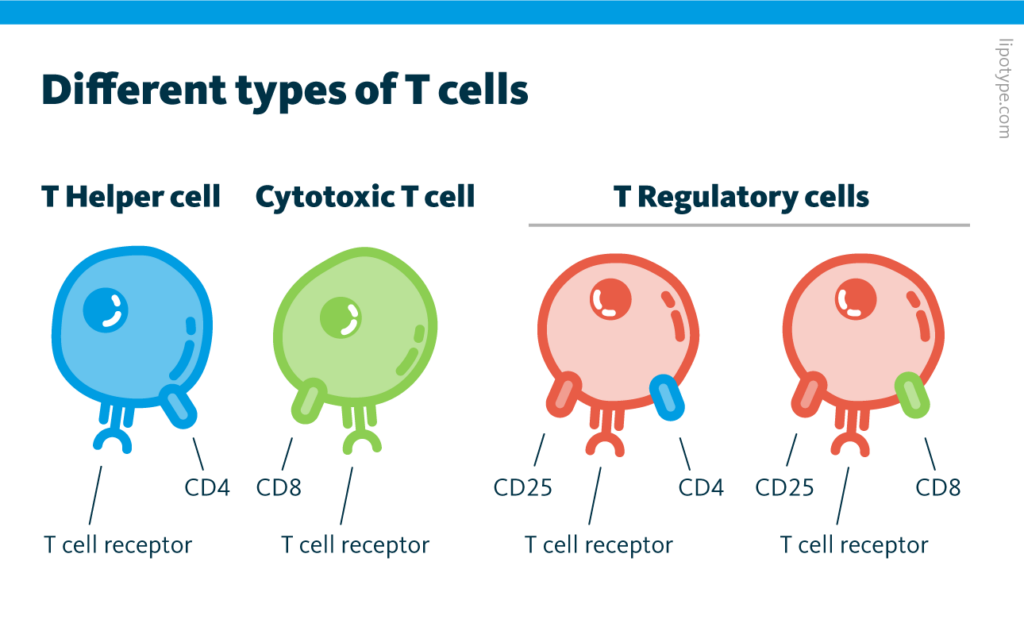
Types Of T Cells And Their Functions T cells are a type of white blood cell called lymphocytes. they’re also called t lymphocytes. lymphocytes play an essential role in your immune system. your immune system fights infection causing pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites) and harmful cells, like cancer cells. your lymphocytes include t cells and b cells. Summary. t cells coordinate multiple aspects of adaptive immunity throughout life, including responses to pathogens, allergens, and tumors. in mouse models, the role of t cells is studied in the context of a specific type of pathogen, antigen, or disease condition over a limited timeframe, while in humans, t cells control multiple insults. T cells are a diverse and important group of lymphocytes that mature and undergo a positive and negative selection processes in the thymus. these cells play a vital role in both components of active immunity, including cell mediated and to some extent humoral immunity. there are several types of t cells; the most common and well known are the cd4 t cells (helper t cells) and cd8 t cells. An αβ t cell receptor structure at 2.5 a and its orientation in the tcr mhc complex. science 274: 209–219 [google scholar] garrity d, call me, feng j, wucherpfennig kw 2005. the activating nkg2d receptor assembles in the membrane with two signaling dimers into a hexameric structure.
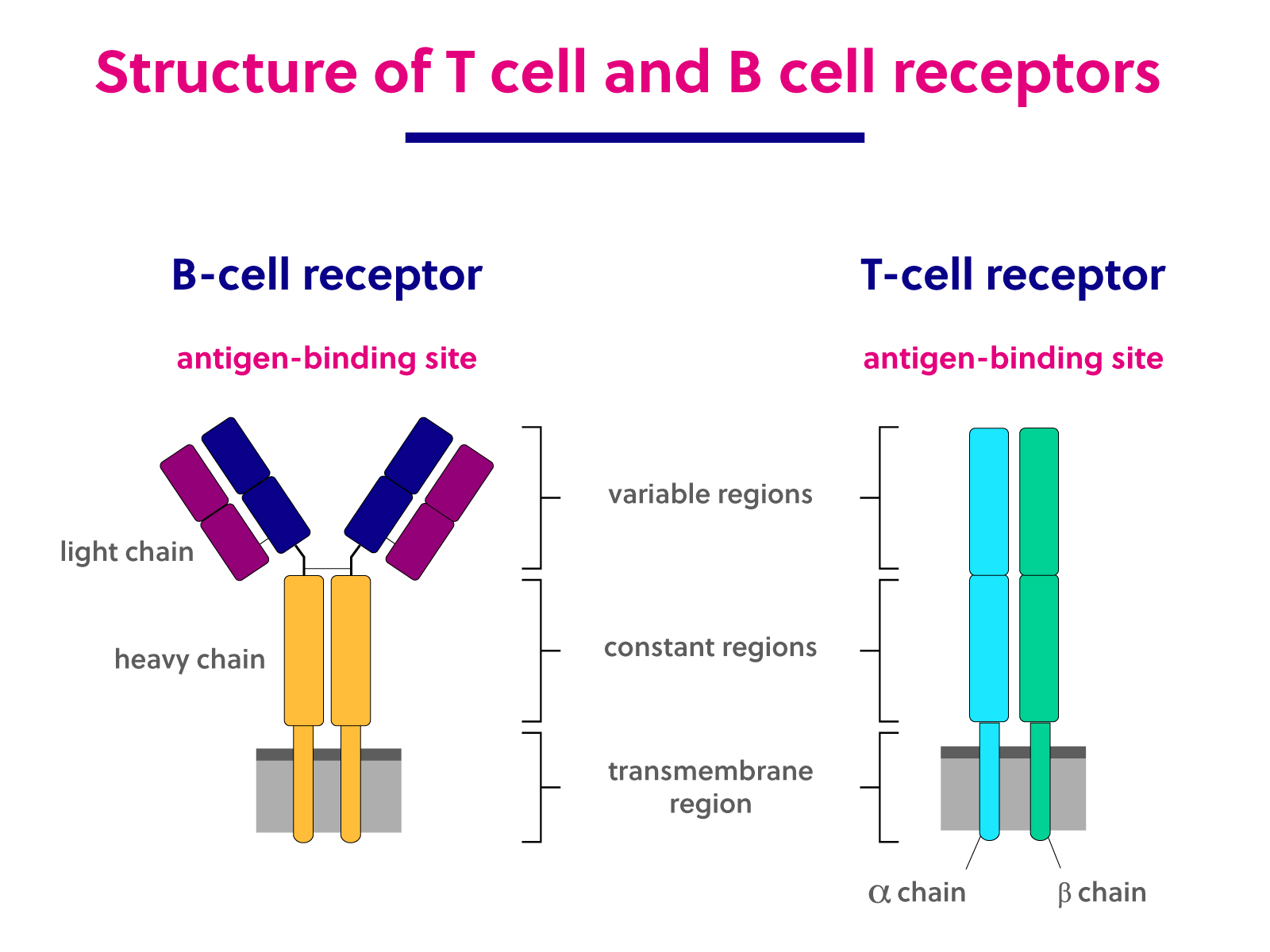
B Cell And T Cell Structure And Function Immunology T cells are a diverse and important group of lymphocytes that mature and undergo a positive and negative selection processes in the thymus. these cells play a vital role in both components of active immunity, including cell mediated and to some extent humoral immunity. there are several types of t cells; the most common and well known are the cd4 t cells (helper t cells) and cd8 t cells. An αβ t cell receptor structure at 2.5 a and its orientation in the tcr mhc complex. science 274: 209–219 [google scholar] garrity d, call me, feng j, wucherpfennig kw 2005. the activating nkg2d receptor assembles in the membrane with two signaling dimers into a hexameric structure. A high resolution cryo electron microscopy structure of the human octameric t cell receptor–cd3 complex, including the complete extracellular and transmembrane domains, reveals the structural. Abstract. throughout life, t cells coordinate multiple aspects of adaptive immunity, including responses to pathogens, allergens, and tumors. in mouse models, the role of t cells is studied in the context of a specific type of pathogen, antigen, or disease condition over a limited time frame, whereas in humans, t cells control multiple insults.
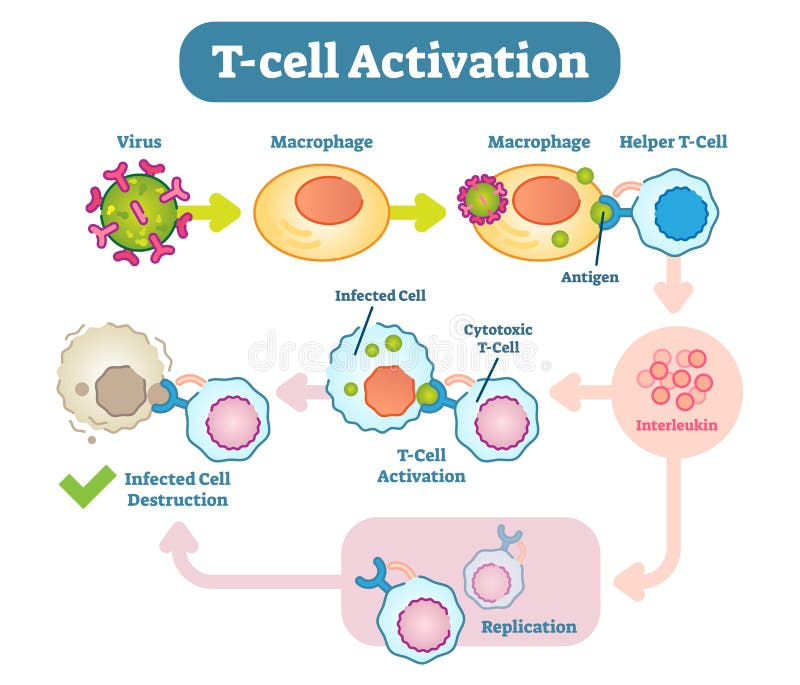
T Cell Activation Diagram Vector Scheme Illustration Stock Vector A high resolution cryo electron microscopy structure of the human octameric t cell receptor–cd3 complex, including the complete extracellular and transmembrane domains, reveals the structural. Abstract. throughout life, t cells coordinate multiple aspects of adaptive immunity, including responses to pathogens, allergens, and tumors. in mouse models, the role of t cells is studied in the context of a specific type of pathogen, antigen, or disease condition over a limited time frame, whereas in humans, t cells control multiple insults.

Comments are closed.