Terminal And Coterminal Angles
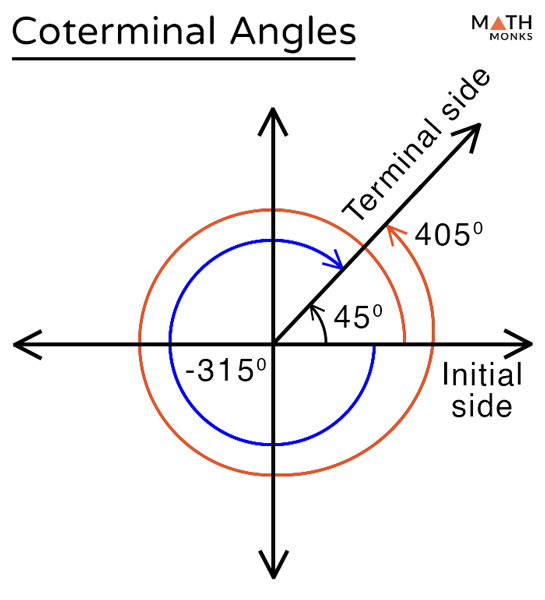
Coterminal Angles вђ Definition Formula With Examples The coterminal angles are the angles that have the same initial side and the same terminal sides. we determine the coterminal angle of a given angle by adding or subtracting 360° or 2π to it. in trigonometry, the coterminal angles have the same values for the functions of sin, cos, and tan. Coterminal angles are those angles that share the terminal side of an angle occupying the standard position. the standard position means that one side of the angle is fixed along the positive x axis, and the vertex is located at the origin.
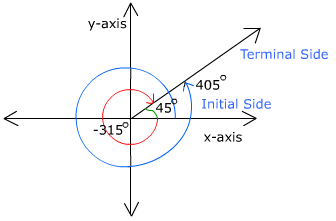
Coterminal Angles 2. add or subtract 360° when working with degrees. to find a coterminal angle, you must rotate the terminal side in a complete circle. simply take your original angle and add or subtract 360°. [3] the formula can be written as θ±360°, where θ is your original angle. for example, if your original angle was 30°, you may write 30° 360°. In the above figure, 45°, 405° and 315° are coterminal angles having the same initial side (x axis) and the same terminal side but with different amount of rotations. other examples : similarly, 30°, 330°, 390° and 57°, 417°, 303° are also coterminal angles. A negative coterminal angle will be one that is measured clockwise, and a positive coterminal angle will be one that is measured more than once around the unit circle. using the formulas above, a negative coterminal angle is $ (360 60) = 300$ degrees. a positive coterminal angle is $360(2) 60 = 720 60 = 780$ degrees. An angle’s reference angle is the size of the smallest acute angle, [latex]{t}^{\prime }[ latex], formed by the terminal side of the angle [latex]t[ latex] and the horizontal axis. how to: given an angle greater than 360°, find a coterminal angle between 0° and 360°.
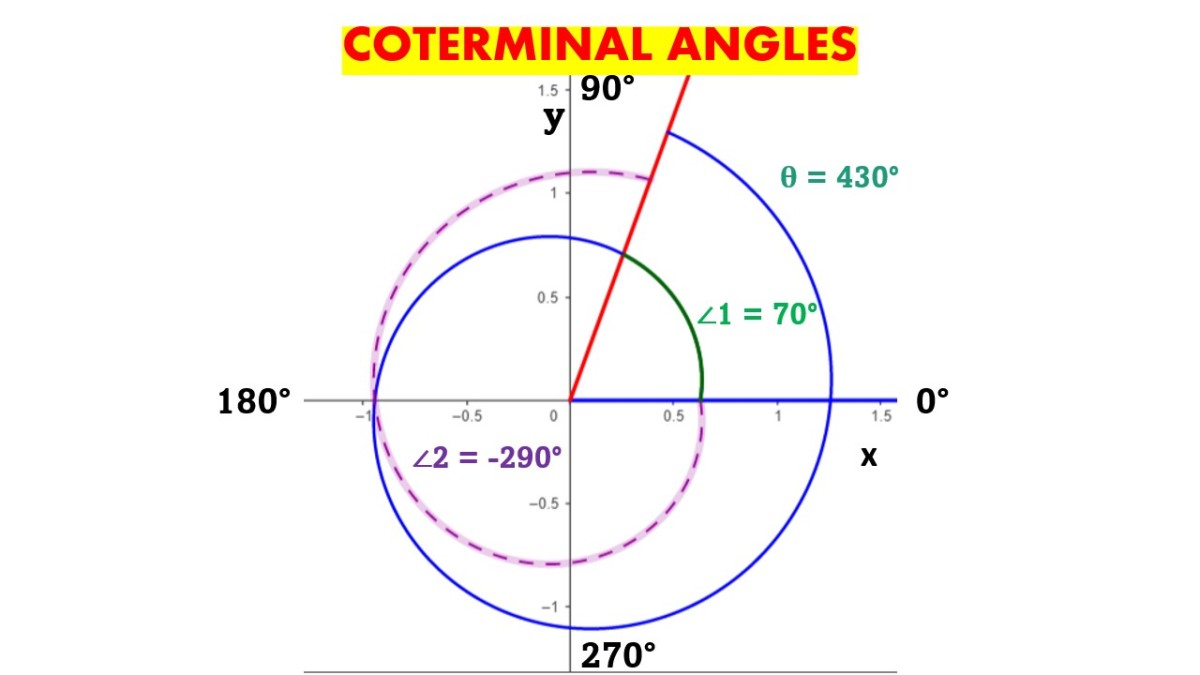
Coterminal Angles How To Find Coterminal Angles In Radians And Degrees A negative coterminal angle will be one that is measured clockwise, and a positive coterminal angle will be one that is measured more than once around the unit circle. using the formulas above, a negative coterminal angle is $ (360 60) = 300$ degrees. a positive coterminal angle is $360(2) 60 = 720 60 = 780$ degrees. An angle’s reference angle is the size of the smallest acute angle, [latex]{t}^{\prime }[ latex], formed by the terminal side of the angle [latex]t[ latex] and the horizontal axis. how to: given an angle greater than 360°, find a coterminal angle between 0° and 360°. The terminal side of an angle is the ray where the measurement of an angle ends. co terminal angles are angles which when drawn at standard position share a terminal side . for example, 30°, 330°, 390° are all coterminal. Figure 2.3.4.3 2.3.4. 3. notice that 390∘ 390 ∘ looks the same as 30∘ 30 ∘. formally, we say that the angles share the same terminal side. therefore we call the angles co terminal. not only are these two angles co terminal, but there are infinitely many angles that are co terminal with these two angles. for example, if we rotate another.

Comments are closed.