The Differences Between Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes
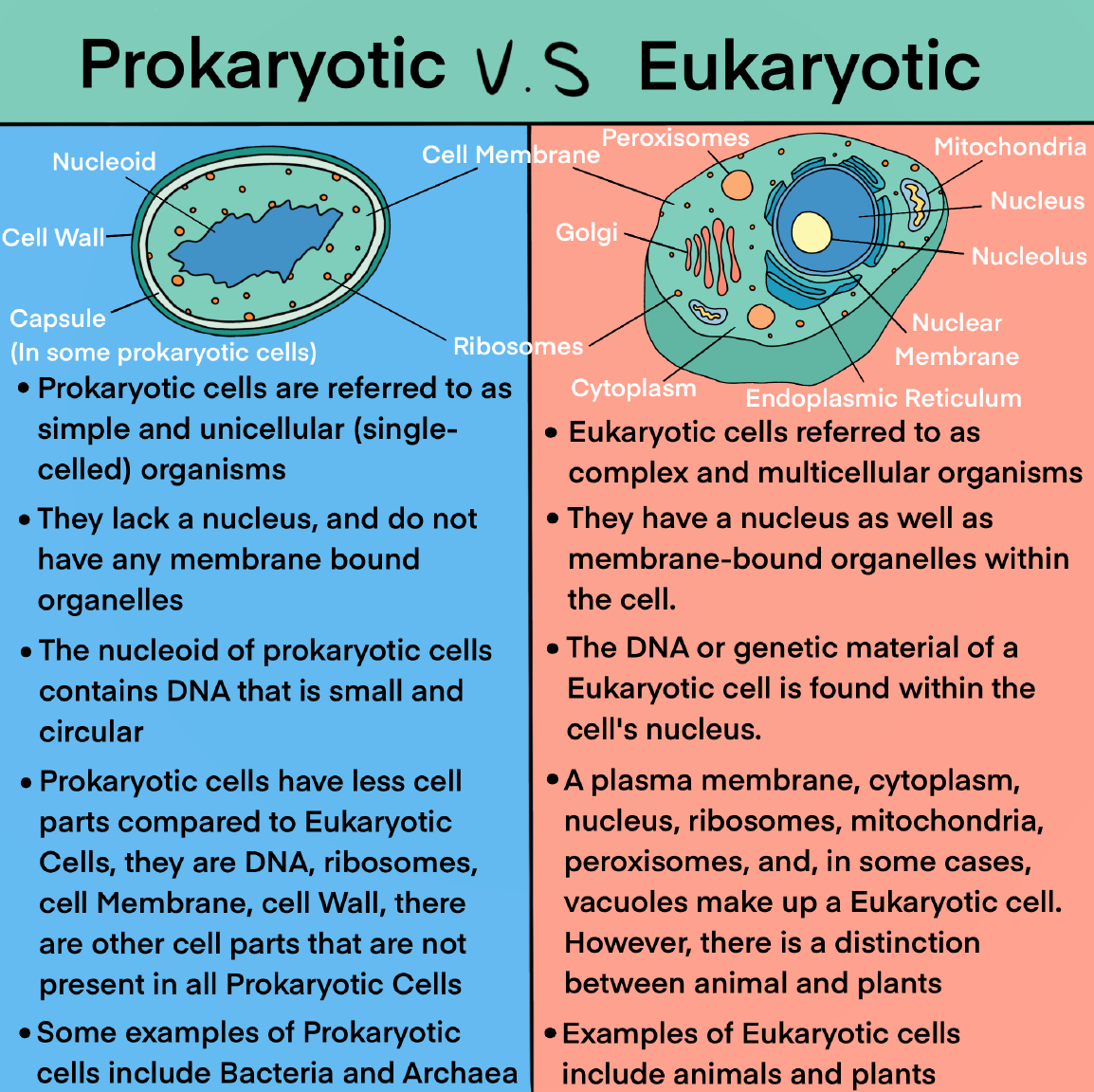
Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes What Are The Key Differences Images Prokaryotic cells are unicellular, while eukaryotic cells may be multicellular. a prokaryotic cell has a single haploid (n) chromosome, while eukaryotes have multiple, paired, diploid (2n) chromosomes. both types of cells have ribosomes, but eukaryotic ribosomes are larger. prokaryotic chromosomes are circular or linear. Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and there are several structural differences between the two. eukaryotes are complex cells storage of dna. the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes contain membrane bound organelles, and prokaryotes do not.
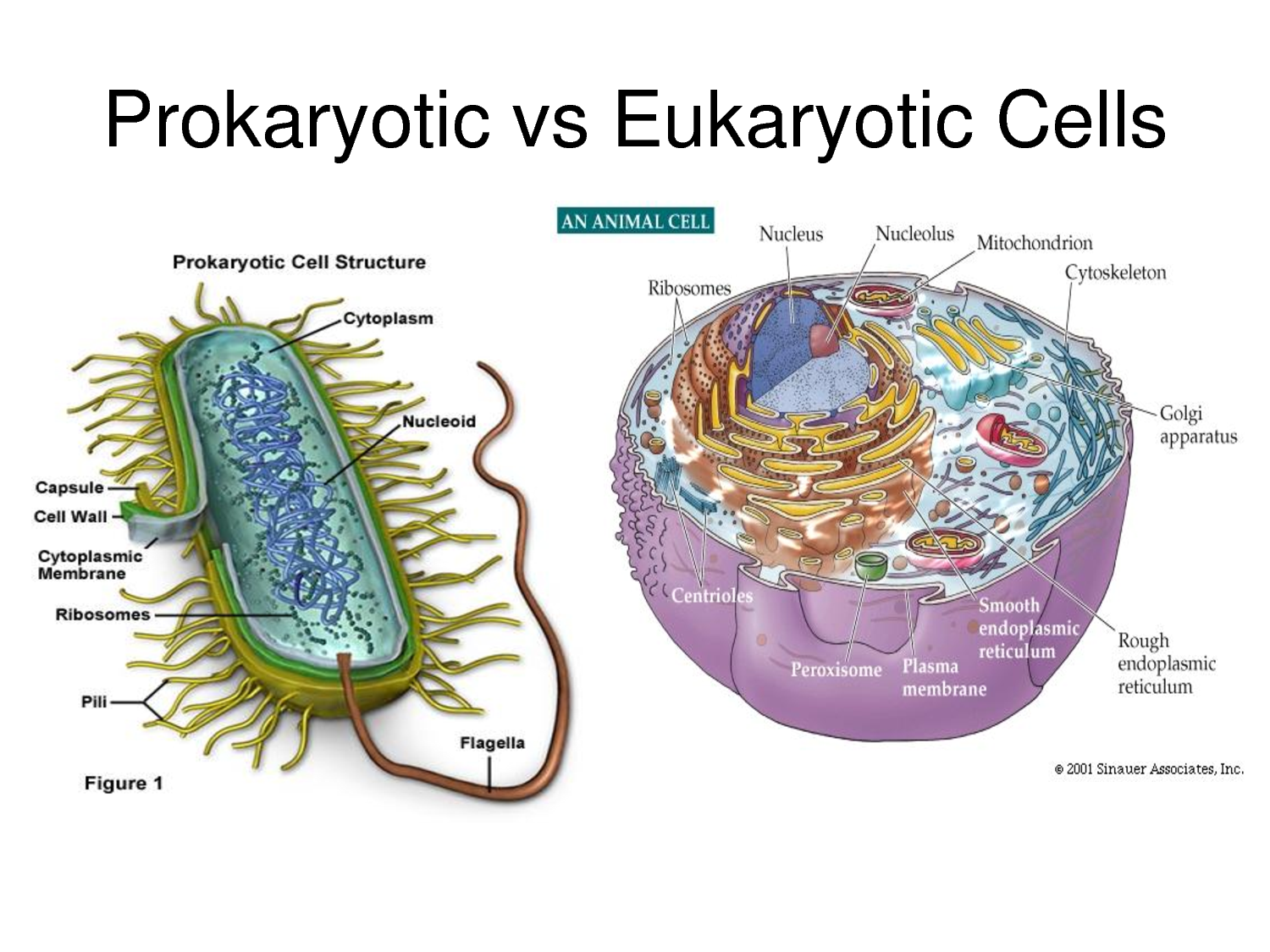
Differences Between Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Biochemanics Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane encased organelles. this means the genetic material dna in prokaryotes is not bound within a nucleus. in addition, the dna is less structured in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes: in prokaryotes, dna is a single loop while in eukaryotes dna is organized into chromosomes. The general characteristics of prokaryotic cells are listed below: in general, prokaryotes range in size from 0.1 to 5.0 µm and are considerably smaller than eukaryotic cells. the shape of prokaryotes ranges from cocci, bacilli, spirilla, and vibrio. however, prokaryotic cells with modifications of these shapes are also found in nature. The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells has to do with the little stuff doing parts of the cell, called organelles. prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's dna. though more primitive than eukaryotes, prokaryotic bacteria are the most diverse and. The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. the nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. in prokaryotes, dna is bundled together in the nucleoid region, but it is not stored within a membrane bound nucleus.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)
The Differences Between Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells has to do with the little stuff doing parts of the cell, called organelles. prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's dna. though more primitive than eukaryotes, prokaryotic bacteria are the most diverse and. The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. the nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. in prokaryotes, dna is bundled together in the nucleoid region, but it is not stored within a membrane bound nucleus. At 0.1–5.0 µm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10–100 µm (figure 3.2.2 3.2. 2). the small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. similarly, any wastes produced within a prokaryotic. 02 17 2011. prokaryotic cell. a eukaryotic cell (left) has membrane enclosed dna, which forms a structure called the nucleus (located at center of the eukaryotic cell; note the purple dna enclosed.
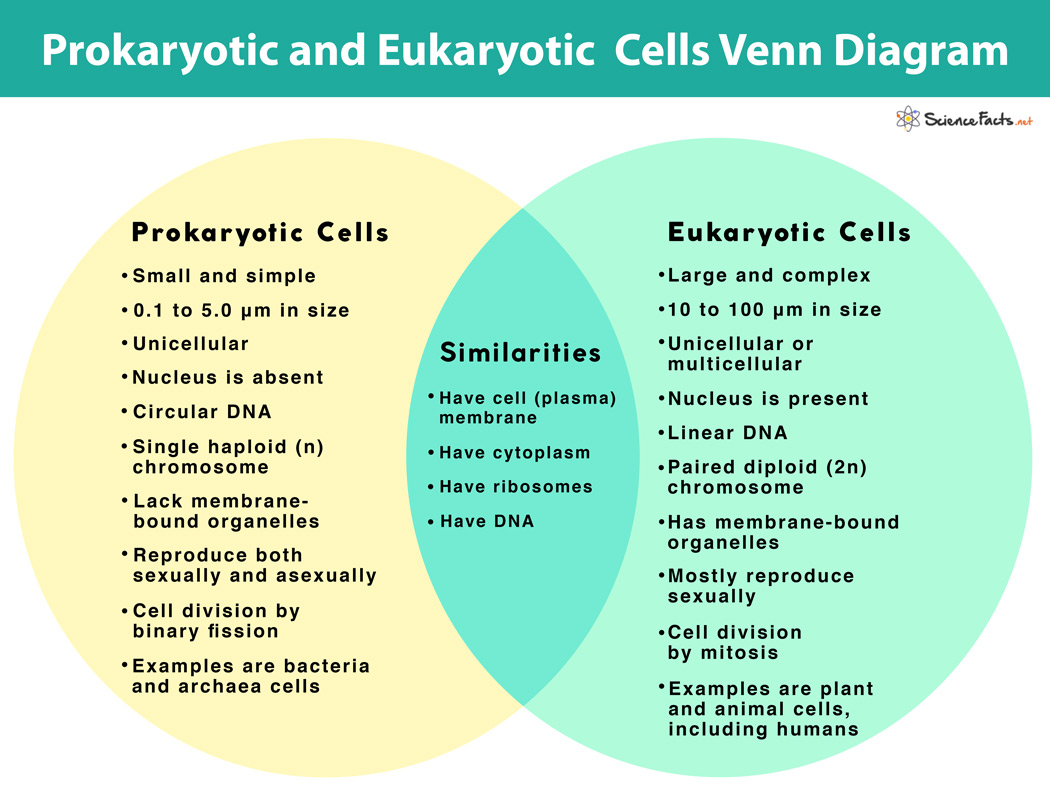
Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Definition And Characteristics At 0.1–5.0 µm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10–100 µm (figure 3.2.2 3.2. 2). the small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. similarly, any wastes produced within a prokaryotic. 02 17 2011. prokaryotic cell. a eukaryotic cell (left) has membrane enclosed dna, which forms a structure called the nucleus (located at center of the eukaryotic cell; note the purple dna enclosed.
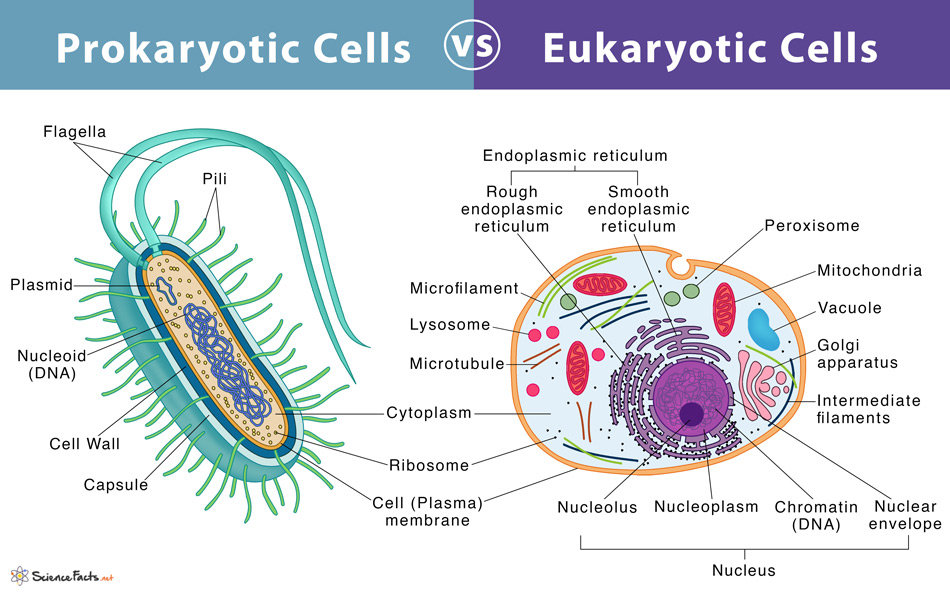
Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Definition And Characteristics

Comments are closed.