The Life Cycle Of A Bed Bug

Bed Bugs And College Avoiding An Infestation The life cycle of a bed bug is shown in the photograph below. during its lifetime, a bed bug will go through the following stages (starting from the top left, moving counterclockwise): eggs (1mm). 1 st stage nymph (1.5 mm). 2 nd stage nymph (2 mm). 3 rd stage nymph (2.5 mm). 4 th stage nymph (3 mm). The bed bug life cycle. here is an introduction to a bed bug’s life cycle — a process that takes less than 40 days to complete. egg stage. about the size of a speck of dust, a bed bug egg looks like a grain of salt. once a female lays her eggs, they hatch into nymphs in less than a week, depending on the room’s temperature.
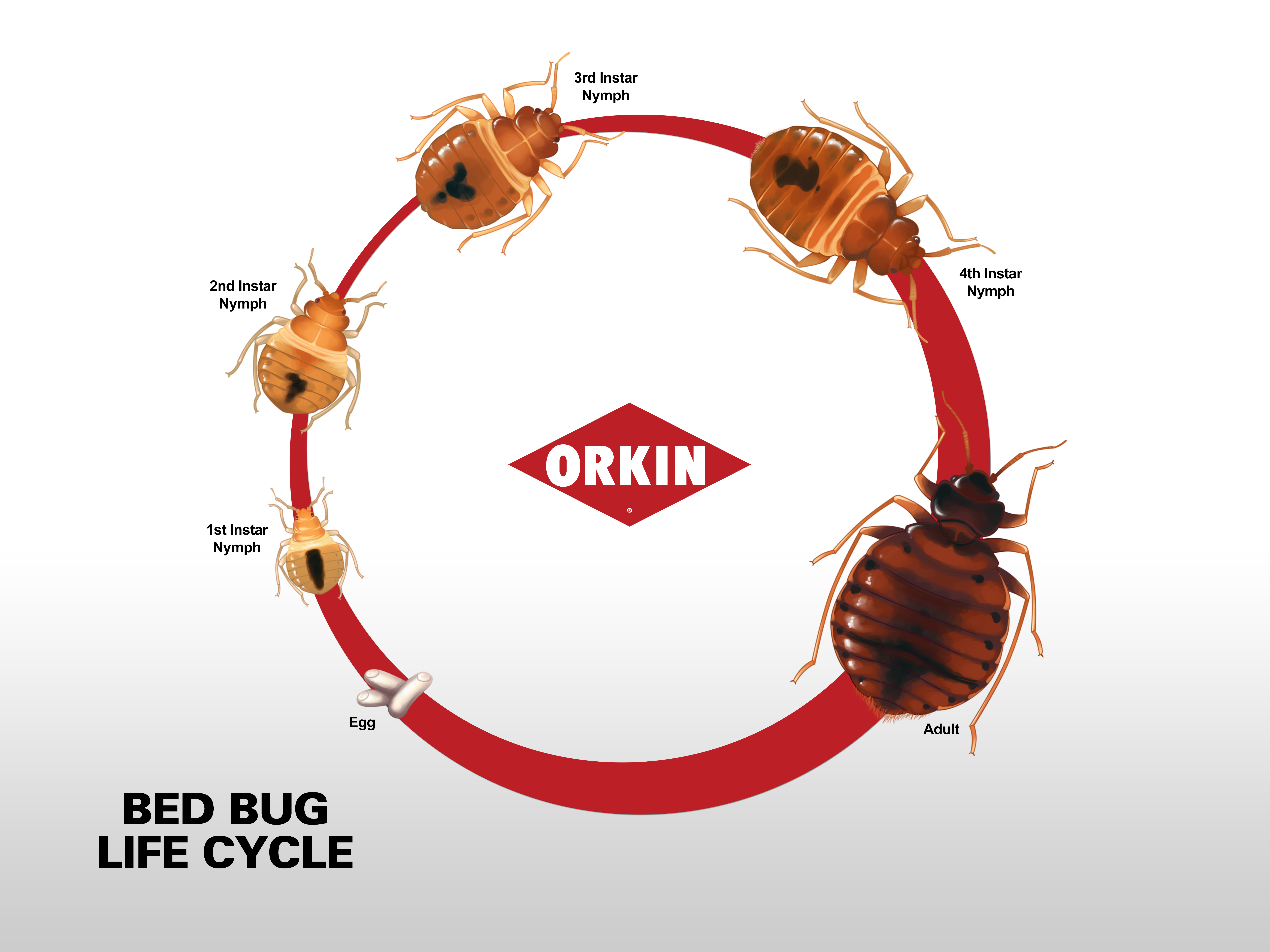
Bedbug Life Stages Bedbug Life Cycle Bed bug life cycle. bed bugs feed entirely on blood. their “blood meal” usually takes about 5 10 minutes, which is why they tend to feed on sleeping humans at night. adult bed bugs can live without feeding for around a year depending on temperatures. one female bed bug can lay 200 250 eggs in her lifetime. The bed bug life cycle comprises seven key stages, starting with the egg stage, evolving through five nymphal or ‘instar’ stages and culminating in the adult stage. an instar is a developmental stage of arthropods, like insects, between each molt until sexual maturity is reached. The bedbug life cycle can be as short as 21 days under ideal conditions, but in most environments, this process will take from 5 to 8 weeks this assumes the availability of a warm blooded host such as a human or pet, and temperatures at 86f (30c). from egg to adulthood a bedbug will pass through 5 instars or stages with the last or sixth. This cycle includes several distinct bed bug stages. the bed bug life cycle starts as eggs, which are about 1mm in size [1]. shortly after hatching, bed bugs progress through 5 nymph stages. each stage of nymph development requires a blood meal to progress, with each blood meal resulting in a molt. after the molting process finishes, a larger.

Comments are closed.