The Mohs Hardness Scale вђ J Brooks
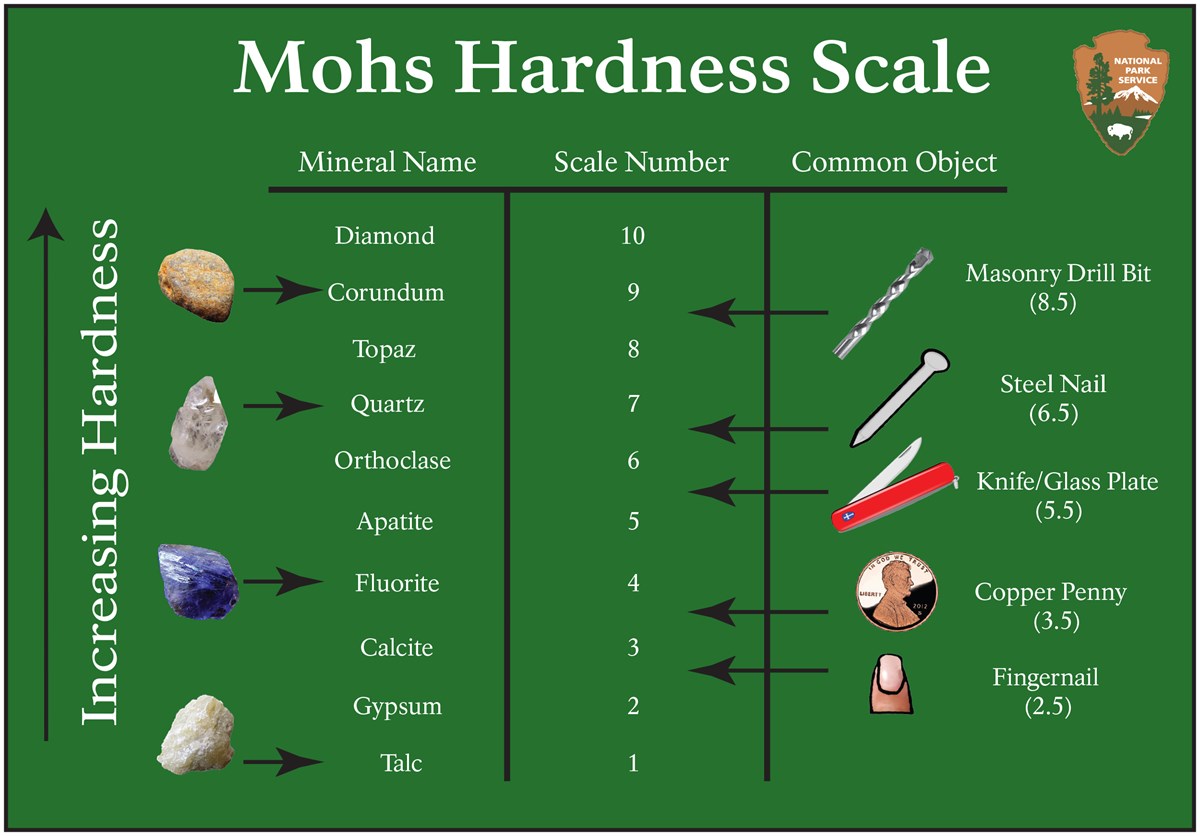
Mohs Hardness Scale U S National Park Service The mohs hardness scale was created by friedrick mohs in 1812 and it is “a measure of how difficult (or easy) it is to scratch the surface of the gemstone” (gem select). diamonds are at the top of the scale being the only one with a rating of 10. the ratings continue down to a 1 with some of the softest gems which can be seen on the scale. The mohs hardness scale is a qualitative test that measures the hardness of a mineral by its ability to visibly scratch softer minerals. the scale isn’t perfect, but it’s a great tool for quick identification of rocks in the field. here a look at the scale, how ordinary minerals and objects rank, and how to perform the mohs test.

Printable Mohs Hardness Scale The mohs scale ( moʊz mohz) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. the scale was introduced in 1812 by the german geologist and mineralogist friedrich mohs, in his book versuch einer elementar methode. The mohs hardness scale is a set of ten reference minerals (numbered 1 through 10) that are used to determine the relative hardness of minerals and other objects. in this test the hardness of a mineral is defined as its "resistance to being scratched". a list of the mohs hardness scale minerals is shown in the table below. The hardness scale is as follows: talc 1 (softest), gypsum 2, calcite 3, fluorite 4, apatite 5, orthoclase (also known as feldspar or periclase) 6, quartz 7, topaz 8, corundum 9, diamond 10 (hardest). mohs hardness is also used to express the hardness of other solid materials. level. minerals. T he mohs scale was introduced almost 200 yrs ago as a simple way to rank mineral hardness.1since then, multi ple scientific papers from mathematical physicists,2physical chemists,3 civil engineers,4 and materials scientists5 have debated the role of plasticity and fracture on scratch hard ness and ultimately the mohs ranking.

Mohs Hardness Scale U S Geological Survey The hardness scale is as follows: talc 1 (softest), gypsum 2, calcite 3, fluorite 4, apatite 5, orthoclase (also known as feldspar or periclase) 6, quartz 7, topaz 8, corundum 9, diamond 10 (hardest). mohs hardness is also used to express the hardness of other solid materials. level. minerals. T he mohs scale was introduced almost 200 yrs ago as a simple way to rank mineral hardness.1since then, multi ple scientific papers from mathematical physicists,2physical chemists,3 civil engineers,4 and materials scientists5 have debated the role of plasticity and fracture on scratch hard ness and ultimately the mohs ranking. The mohs scale is set forth in table 1, talc being the softest mineral. the standard for hardness 2 is specified to be “of imperfect cleavage, and not perfectly transparent. varieties perfectly transparent and crystallized, are commonly too soft.”. calcite is not an ideal choice for 3, as the hardness varies by about half a unit between the. The minerals contained in the scale are shown in the table; also shown are other materials that approximate the hardness of some of the minerals. as is indicated by the ranking in the scale, if a mineral is scratched by orthoclase but not by apatite, its mohs hardness is between 5 and 6. in the determination procedure it is necessary to be.

Mohs Hardness Scale Geology Page The mohs scale is set forth in table 1, talc being the softest mineral. the standard for hardness 2 is specified to be “of imperfect cleavage, and not perfectly transparent. varieties perfectly transparent and crystallized, are commonly too soft.”. calcite is not an ideal choice for 3, as the hardness varies by about half a unit between the. The minerals contained in the scale are shown in the table; also shown are other materials that approximate the hardness of some of the minerals. as is indicated by the ranking in the scale, if a mineral is scratched by orthoclase but not by apatite, its mohs hardness is between 5 and 6. in the determination procedure it is necessary to be.

Comments are closed.