The Phoenician Expansion C 11th To 6th Centuries Bce By Simeon

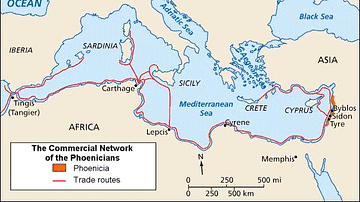
The Phoenician Expansion C 11th To 6th Centuries Bce By Simeon The geographical proximity of cyprus probably meant it was one of the first places to be colonized by the phoenicians, perhaps as early as the 11th century bce. resources on the island which motivated phoenician expansion included timber and copper. the most important city was kition but others included golgoi, idalion, tamassos, marion, and. Published on 09 november 2021. subscribe to author. download full size image. a map illustrating the expansion of the phoenicians, including the trade routes and process of phoenician colonization, from its origins in the levant region of the eastern mediterranean, until its height when it spanned from cyprus to the iberian peninsula and beyond.

The Phoenician Expansion C 11th To 6th Centuries Bce Illus The phoenician expansion c. 11th to 6th centuries bce simeon netchev (cc by nc nd) it is estimated that over 30,000 citizens of tyre were massacred or sold into slavery and only those wealthy enough to properly bribe alexander were allowed to escape with their lives (besides those who found a way to escape by stealth). There is therefore much continuity in phoenician traditions from the late bronze age until the hellenistic period around 300 b.c. by the late eighth century b.c., the phoenicians, alongside the greeks, had founded trading posts around the entire mediterranean and excavations of many of these centers have added significantly to our understanding. 29 israel and judah from the coming of assyrian domination until the fall of samaria, and the struggle for independence in judah (c. 750–700 b.c.) 30 judah until the fall of jerusalem (c. 700–586 b.c.) 31 the babylonian exile and the restoration of the jews in palestine (586–c. 500 b.c.) 32 phoenicia and phoenician colonization; 33. At byblos, commercial and religious connections with egypt are attested from the egyptian 4th dynasty (c. 2613–c. 2494); extensive trade was certainly carried on by the 16th century, and the egyptians soon established suzerainty over much of phoenicia. the 14th century, however, was one of much political unrest, and egypt eventually lost its.
The Phoenician Expansion C 11th To 6th Centuries Bce Illus 29 israel and judah from the coming of assyrian domination until the fall of samaria, and the struggle for independence in judah (c. 750–700 b.c.) 30 judah until the fall of jerusalem (c. 700–586 b.c.) 31 the babylonian exile and the restoration of the jews in palestine (586–c. 500 b.c.) 32 phoenicia and phoenician colonization; 33. At byblos, commercial and religious connections with egypt are attested from the egyptian 4th dynasty (c. 2613–c. 2494); extensive trade was certainly carried on by the 16th century, and the egyptians soon established suzerainty over much of phoenicia. the 14th century, however, was one of much political unrest, and egypt eventually lost its. Iron age (11th to 6th centuries bce) silver objects and hoards are known from the southern levant, including abundant finds that specifically date to the postulated precolonization epoch (refs. 32 and 33). today, lead isotope (li) analysis is the main method used to associate between silver items and their original ore source (for. Delgado hervás, a., and m. ferrer. 2012. life and death in ancient colonies: domesticity, material culture and sexual politics in the western phoenician world, eighth to sixth centuries bce. in the archaeology of colonialism: intimate encounters and sexual effects, ed. b. voss and e.c. casella, 195–213. new york: cambridge university press.

Comments are closed.