The Physics Of Damped Harmonic Oscillations Simplified Equations Of Motion Beyond

Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Dampe When we place an ideal harmonic oscillator in a medium that introduces friction, we get a damped harmonic oscillations. under light damping, we observe oscil. Figure 15.6.4 15.6. 4: the position versus time for three systems consisting of a mass and a spring in a viscous fluid. (a) if the damping is small (b < 4mk− −−−√ 4 m k), the mass oscillates, slowly losing amplitude as the energy is dissipated by the non conservative force (s). the limiting case is (b) where the damping is (b = 4mk−.
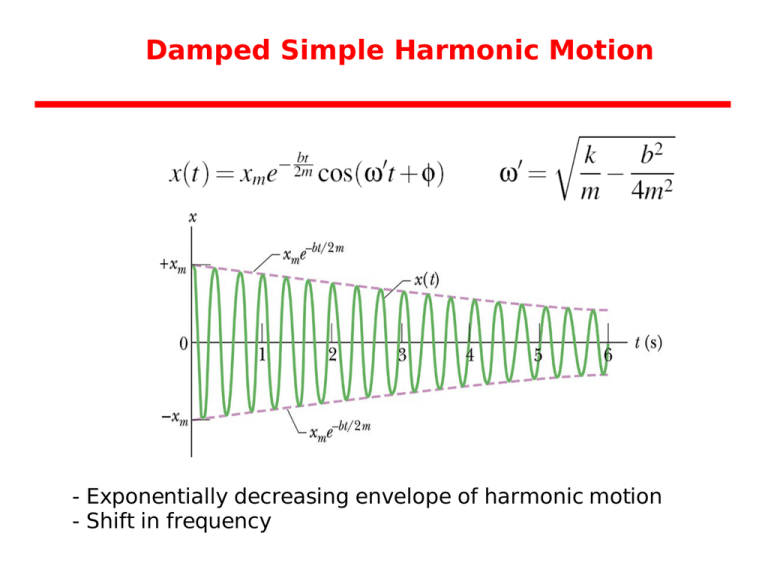
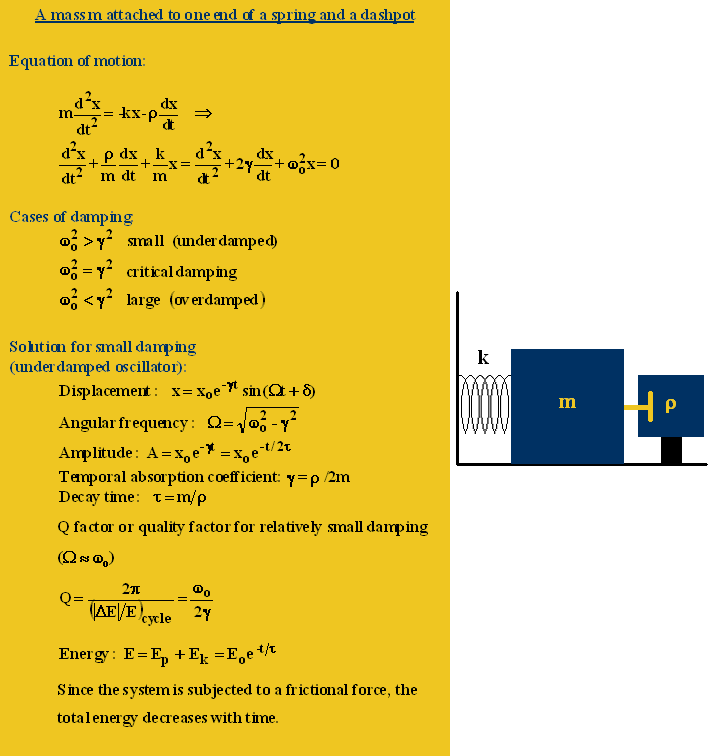
Damped Simple Harmonic Motion This page titled 16.7: damped harmonic motion is shared under a cc by 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by openstax via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. although we can often make friction and other non conservative forces negligibly small, completely undamped motion is rare. By newton’s second law, the equation of motion for the mass is therefore mx ̈ = fnet = −bx ̇ − kx, and ω2 = . eq.(4) is the desired equation of motion for harmonic motion with air drag. it models what is known as damped harmonic oscillations, and is more realistic than the case where b is assumed to be zero. If a frictional force ( damping ) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. driven harmonic oscillators are damped oscillators further affected by an externally applied force f (t). newton’s second law takes the form f(t) − kx − cdx dt = md2x dt2. These two conditions are sufficient to obey the equation of motion of the damped harmonic oscillator. show that a circuit with an inductor, capacitor, and resistor in series obeys the damped harmonic oscillator equation. a series rlc circuit, in which the resistor dissipates energy while the voltages across the capacitor and inductor oscillate [2].

Damped Harmonic Motion Equation Of Damped Harmonic Oscillations If a frictional force ( damping ) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. driven harmonic oscillators are damped oscillators further affected by an externally applied force f (t). newton’s second law takes the form f(t) − kx − cdx dt = md2x dt2. These two conditions are sufficient to obey the equation of motion of the damped harmonic oscillator. show that a circuit with an inductor, capacitor, and resistor in series obeys the damped harmonic oscillator equation. a series rlc circuit, in which the resistor dissipates energy while the voltages across the capacitor and inductor oscillate [2]. When a damped oscillator is underdamped, it approaches zero faster than in the case of critical damping, but oscillates about that zero. the equation is that of an exponentially decaying sinusoid. the damping coefficient is less than the undamped resonant frequency . the sinusoid frequency is given by. but the motion is not strictly periodic. To determine the solution to this equation, consider the plot of position versus time shown in (figure). the curve resembles a cosine curve oscillating in the envelope of an exponential function a0e−αt a 0 e − α t where α = b 2m α = b 2 m. the solution is. x(t)= a0e− b 2mtcos(ωt φ). x (t) = a 0 e − b 2 m t cos (ω t φ).
Simple Harmonic Motion And Damped Oscillator When a damped oscillator is underdamped, it approaches zero faster than in the case of critical damping, but oscillates about that zero. the equation is that of an exponentially decaying sinusoid. the damping coefficient is less than the undamped resonant frequency . the sinusoid frequency is given by. but the motion is not strictly periodic. To determine the solution to this equation, consider the plot of position versus time shown in (figure). the curve resembles a cosine curve oscillating in the envelope of an exponential function a0e−αt a 0 e − α t where α = b 2m α = b 2 m. the solution is. x(t)= a0e− b 2mtcos(ωt φ). x (t) = a 0 e − b 2 m t cos (ω t φ).

Damped Simple Harmonic Motion Definition Expression Example Video

Comments are closed.