The Role Of Gamma Oscillations In Cognition And Schizophrenia
Ppt Schizophrenia And Gamma Oscillations Powerpoint Presentation The purpose of this article is to review recent clinical and basic science findings concerning the relationship between schizophrenia and γ band oscillations (gbos). schizophrenia is a complex and devastating neuropsychiatric disorder, which is believed to stem from a combination of genetic, developmental, and environmental factors. In addition to the role of gamma oscillations in the sharing of information, studies in the prefrontal cortex suggest that gamma oscillations may also have a role in segmenting information during a working memory task. working memory is a process in which one can keep several memory items in “mind” for a given amount of time.

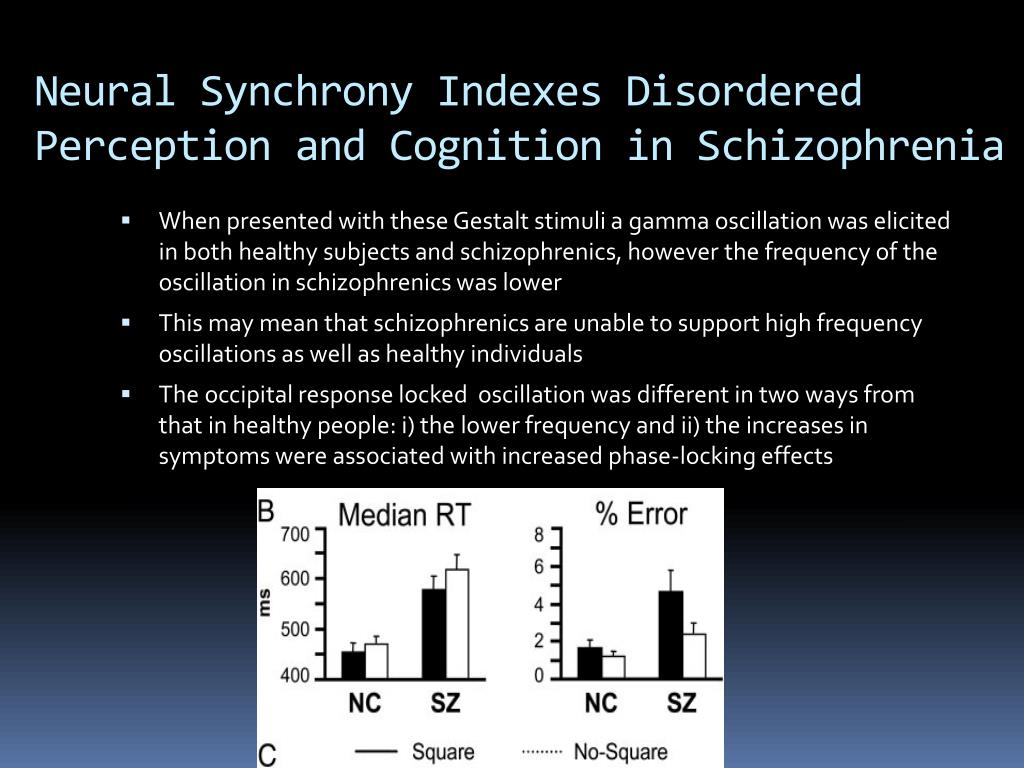
Ppt Schizophrenia And Gamma Oscillations Powerpoint Presentation Id Gamma (30 50hz) oscillations have warranted special attention due to their omnipresence in cognitive tasks. for patients with schizophrenia (scz), a disease associated with poor cognition, abnormal gamma oscillations have been reported in many experimental paradigms. the goal of this paper is to review the literature on gamma oscillations in scz. We discuss the evidence for aberrant function in schizophrenia, the role in healthy cognitive function, and their part in modulating e i balance. gamma oscillations are associated with the. Based on work reviewed herein, we propose that a potential functional role for da in modulating cognitive processes is through opposing effects on neuronal excitability, synaptic strength, and gamma oscillations mediated via d1 and d2 type da receptors (see kwon et al., 2008; andersson et al., 2012b ). Gamma oscillations (30–80 hz) have received much interest in preclinical and translational studies of sz, given their role in local and interregional information flow critical for cognition and.

Ppt Schizophrenia And Gamma Oscillations Powerpoint Presentation Based on work reviewed herein, we propose that a potential functional role for da in modulating cognitive processes is through opposing effects on neuronal excitability, synaptic strength, and gamma oscillations mediated via d1 and d2 type da receptors (see kwon et al., 2008; andersson et al., 2012b ). Gamma oscillations (30–80 hz) have received much interest in preclinical and translational studies of sz, given their role in local and interregional information flow critical for cognition and. In fact, transiently enhancing the synchrony of parvalbumin interneuron–generated gamma oscillations can lead to long lasting improvements in cognition in mice that model aspects of schizophrenia. gamma oscillations emerge from specific patterns of connections between a variety of cell types within cortical microcircuits. Gamma (30–50 hz) oscillations have warranted special attention due to their omnipresence in cognitive tasks. for patients with schizophrenia (scz), a disease associated with poor cognition, abnormal gamma oscillations have been reported in many experimental paradigms. the goal of this paper is to review the literature on gamma oscillations in.

Comments are closed.