The Science Of Goosebumps

The Science Of Goosebumps Youtube Researchers discovered a new role for goosebumps: the muscle and nerve cells involved in this response to cold trigger new hair growth by activating stem cells. these mechanisms may have implications for reversing hair loss and understanding wound healing in the skin. researchers think they may have figured out the reasons for goosebumps. The connection between the sympathetic nerve and the muscle has been well known, since they are the cellular basis behind goosebumps: the cold triggers sympathetic neurons to send a nerve signal, and the muscle reacts by contracting and causing the hair to stand on end. however, when examining the skin under extremely high resolution using.

The Science Of Goosebumps And Music Chills Simple Education The real reason behind goosebumps. july 20, 2020. harvard scientists find that the same cell types that cause goosebumps are responsible for controlling hair growth. the hair follicle under the microscope, with the sympathetic nerve in green and the muscle in magenta. credit: hsu laboratory, harvard university. New research suggests an answer: regulating stem cells that control hair follicles and hair growth. in a detailed analysis of mice, scientists found that the specific muscles that contract when goosebumps appear are connected to the sympathetic nervous system. when low temperatures are sensed, these muscles bridge the gap between sympathetic. In people this reaction is useless because we do not have a hair coat, but goosebumps persist nevertheless. on supporting science journalism if you're enjoying this article, consider supporting. Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose pimples[1] (also called chill bumps[citation needed]) are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal. [2][3] the formation of goose bumps in humans under stress is.

The Science Behind Goosebumps Why Do We Have Them In 2023 In people this reaction is useless because we do not have a hair coat, but goosebumps persist nevertheless. on supporting science journalism if you're enjoying this article, consider supporting. Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose pimples[1] (also called chill bumps[citation needed]) are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal. [2][3] the formation of goose bumps in humans under stress is. Goosebumps are an automatic response to hormone surges caused by temperature change or emotion. they aren’t beneficial because we’ve evolved to be less hairy. there isn’t much science to. Goosebumps, also called gooseflesh, are small bumps on the skin that cause it to appear raised. they are caused by muscles contracting around the hair follicles in your skin. when blood flow to.
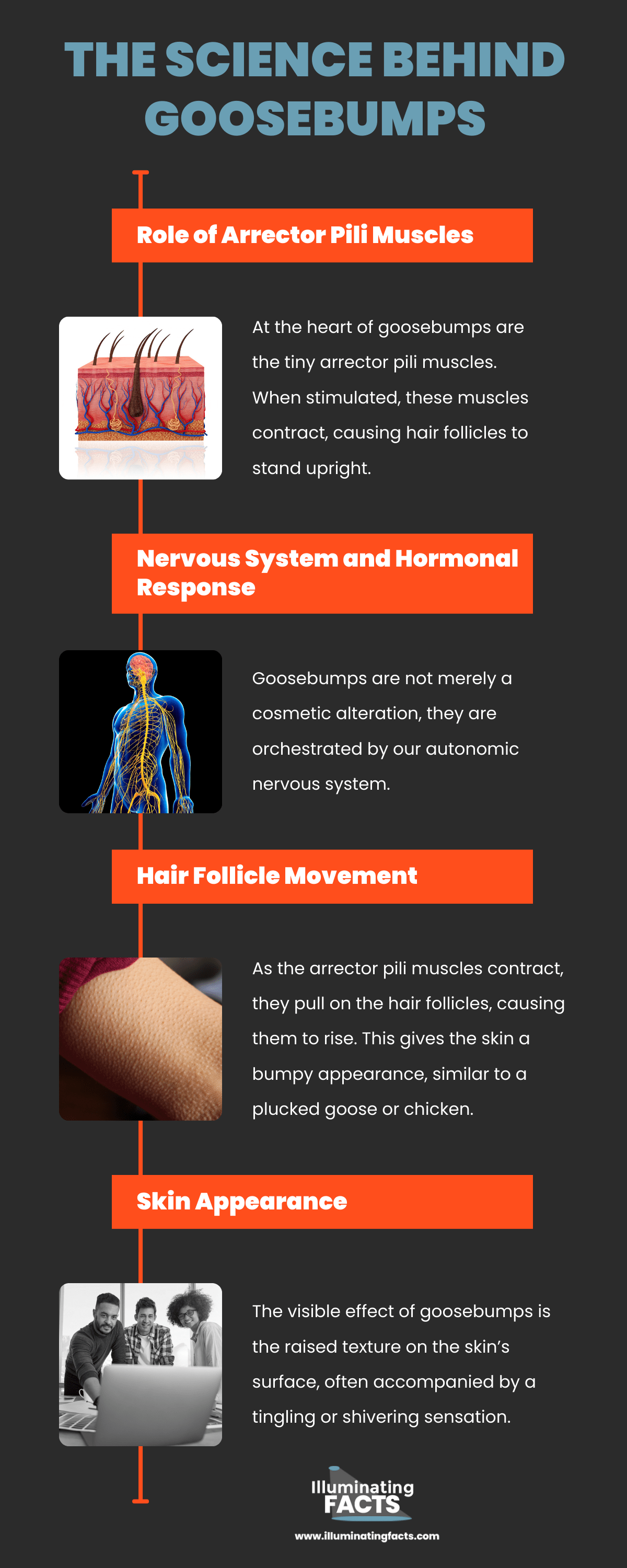
What Happens When You Experience Goosebumps Illuminating Facts Goosebumps are an automatic response to hormone surges caused by temperature change or emotion. they aren’t beneficial because we’ve evolved to be less hairy. there isn’t much science to. Goosebumps, also called gooseflesh, are small bumps on the skin that cause it to appear raised. they are caused by muscles contracting around the hair follicles in your skin. when blood flow to.

Comments are closed.