The Structure Of An Antibody Molecule Represents The Dramatic
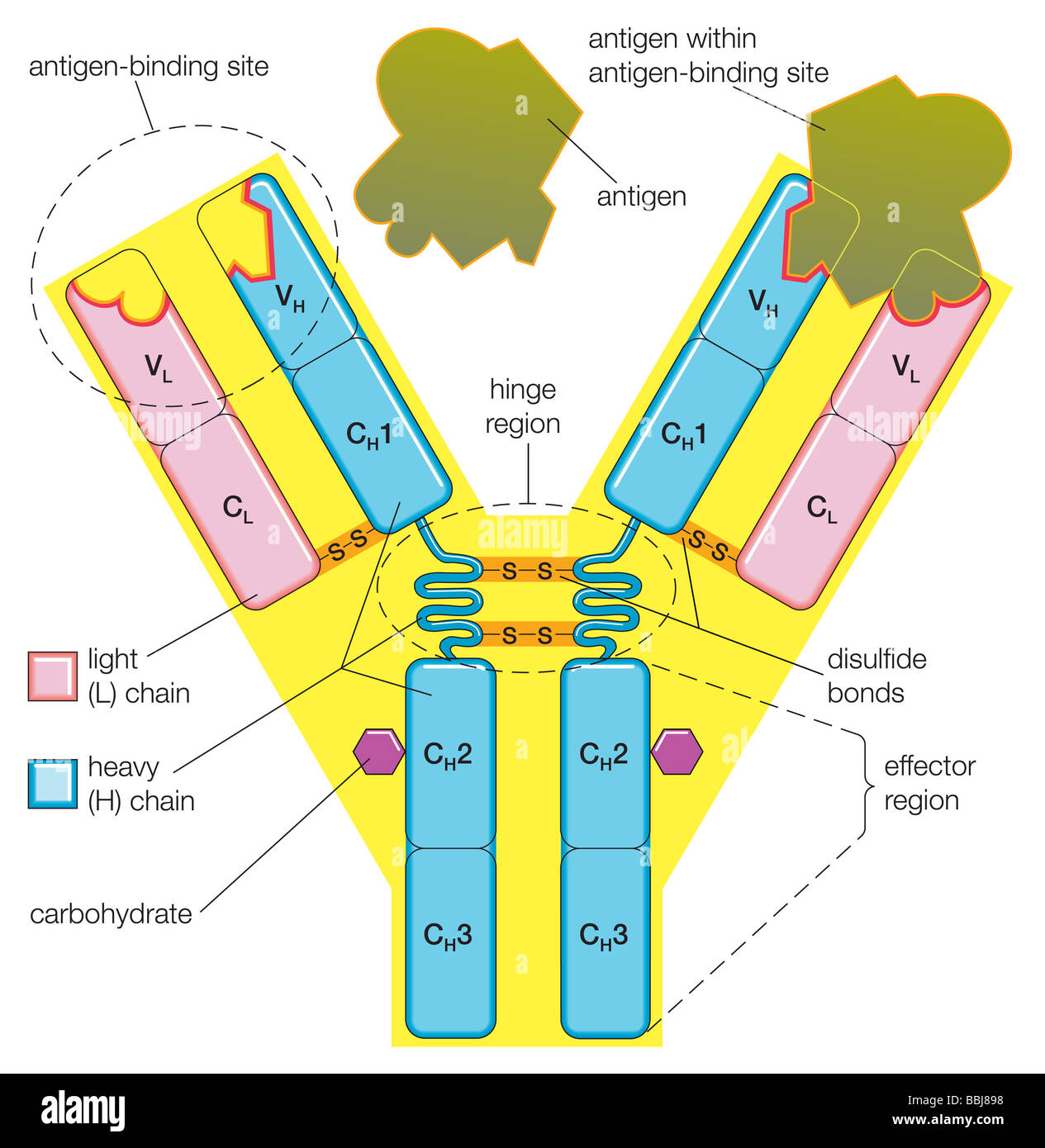
The Structure Of An Antibody Molecule Represents The Dramatic Stock The structure of a typical antibody molecule. antibodies are the secreted form of the b cell receptor. an antibody is identical to the b cell receptor of the cell that secretes it except for a small portion of the c terminus of the heavy chain constant region. in the case of the b cell receptor the c terminus is a hydrophobic membrane anchoring. The antibody is made up of variable v regions, and constant c regions. heterodimer structure of antibodies. the antibody structure was first determined by edelman who isolated it from the blood sample of multiple myeloma, using myeloma proteins. they identified two chains, with molecular weights of 20 kda (light chain) and 50 kda (heavy chain).

Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica The intact antibody molecule shown in figure 1 has three functional components, two fragment antigen binding domains (fabs) and the fragment crystallizable (fc), with the two fabs linked to the fc by a hinge region that allows the fabs a large degree of conformation flexibility relative to the fc. each of the fabs have identical antigen binding. Antibody structure. an antibody molecule is comprised of four polypeptides: two identical heavy chains (large peptide units) that are partially bound to each other in a “y” formation, which are flanked by two identical light chains (small peptide units), as illustrated in figure 42.22. bonds between the cysteine amino acids in the antibody. Antibody structure the structure of an antibody molecule represents the dramatic rearrangements of dna that occur in the immune systems of mammals. each antibody contains a light chain and a heavy chain that are encoded by different segments of dna. Discuss antibody production. an antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin (ig), is a protein that is produced by plasma cells after stimulation by an antigen. antibodies are the functional basis of humoral immunity. antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk.

The Structure Of A Typical Antibody Molecule Antibodies And Amino Acids Antibody structure the structure of an antibody molecule represents the dramatic rearrangements of dna that occur in the immune systems of mammals. each antibody contains a light chain and a heavy chain that are encoded by different segments of dna. Discuss antibody production. an antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin (ig), is a protein that is produced by plasma cells after stimulation by an antigen. antibodies are the functional basis of humoral immunity. antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk. Immune serum globulin. antibody, a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance, called an antigen. antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens in order to remove them from the body. a wide range of substances are regarded by the body as antigens, including disease causing organisms and. Al qaraghuli, m. m., kubiak ossowska, k. & mulheran, p. a. thinking outside the laboratory: analyses of antibody structure and dynamics within different solvent environments in molecular dynamics.
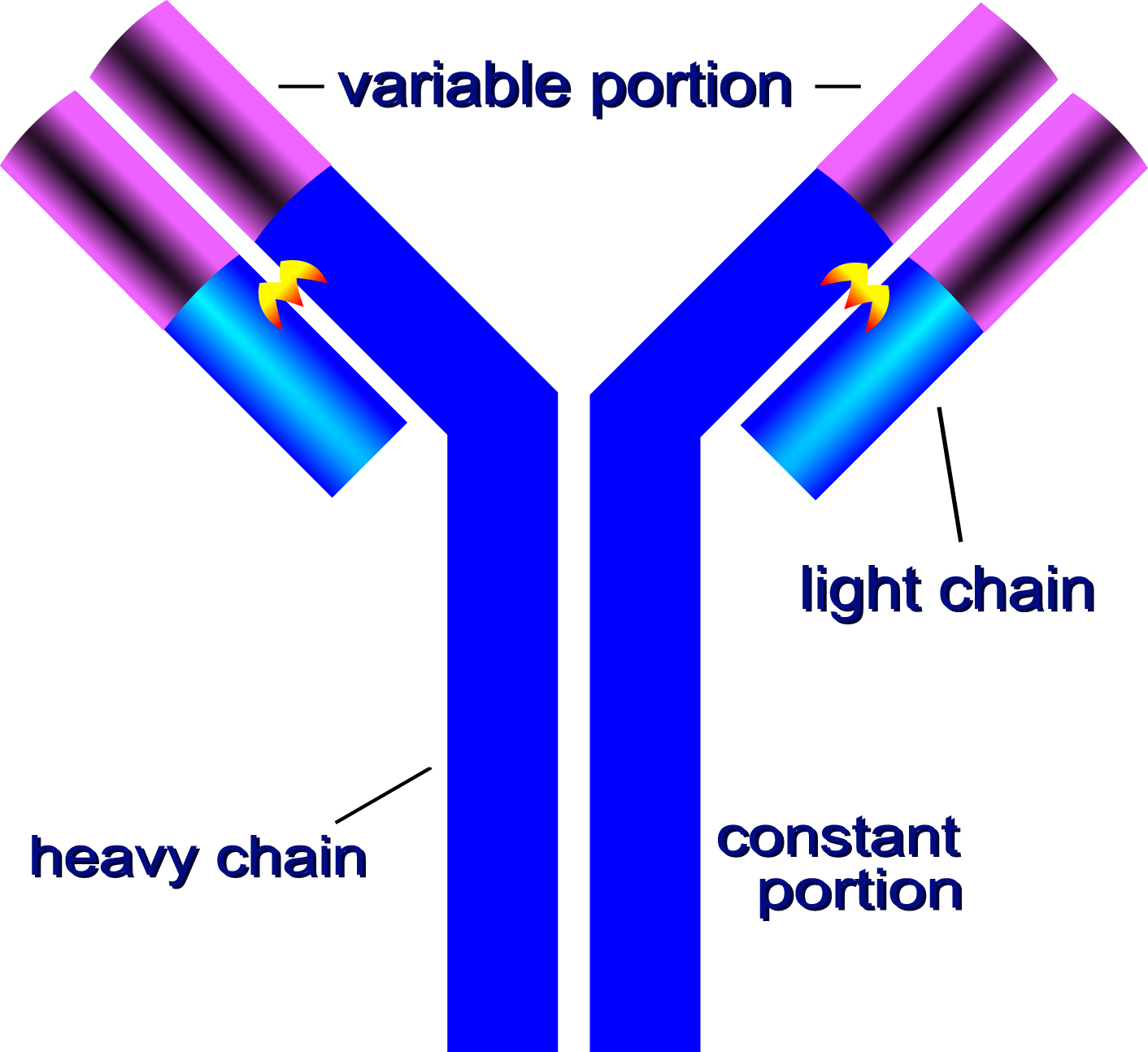
Label The Diagram Of An Antibody Structure Immune serum globulin. antibody, a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance, called an antigen. antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens in order to remove them from the body. a wide range of substances are regarded by the body as antigens, including disease causing organisms and. Al qaraghuli, m. m., kubiak ossowska, k. & mulheran, p. a. thinking outside the laboratory: analyses of antibody structure and dynamics within different solvent environments in molecular dynamics.

Comments are closed.