The Structure Of Electric Power Systems Generation Distribution And
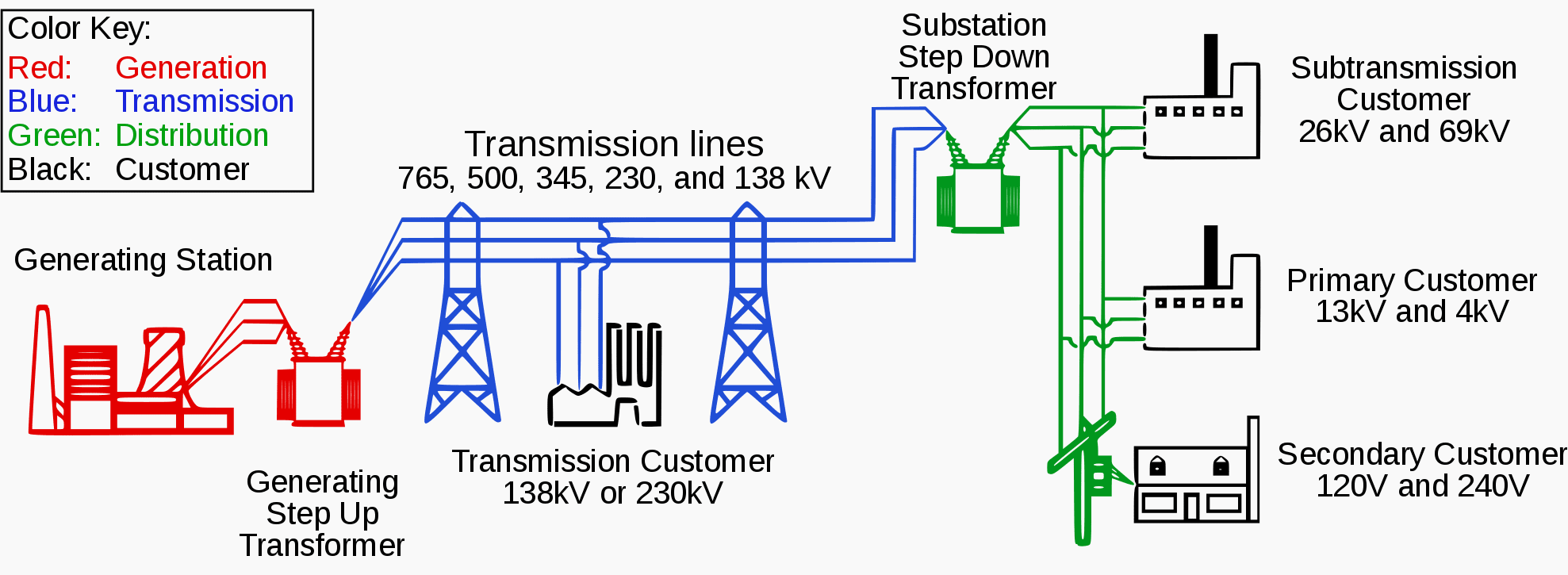
The Structure Of Electric Power Systems Generation Distribution And Power generation. power plants convert the energy stored in the fuel (mainly coal, oil, natural gas, enriched uranium) or renewable energies (water, wind, solar) into electric energy. conventional modern generators produce electricity at a frequency that is a multiple of the rotation speed of the machine. voltage is usually no more than 6 to 40 kv. Spring 2012. a.h. mohsenian‐rad (u of t) networking and distributed systems 1. the four main elements in power systems: power production generation. power transmission. power distribution. power consumption load. of course, we also need monitoring and control systems. power production:.
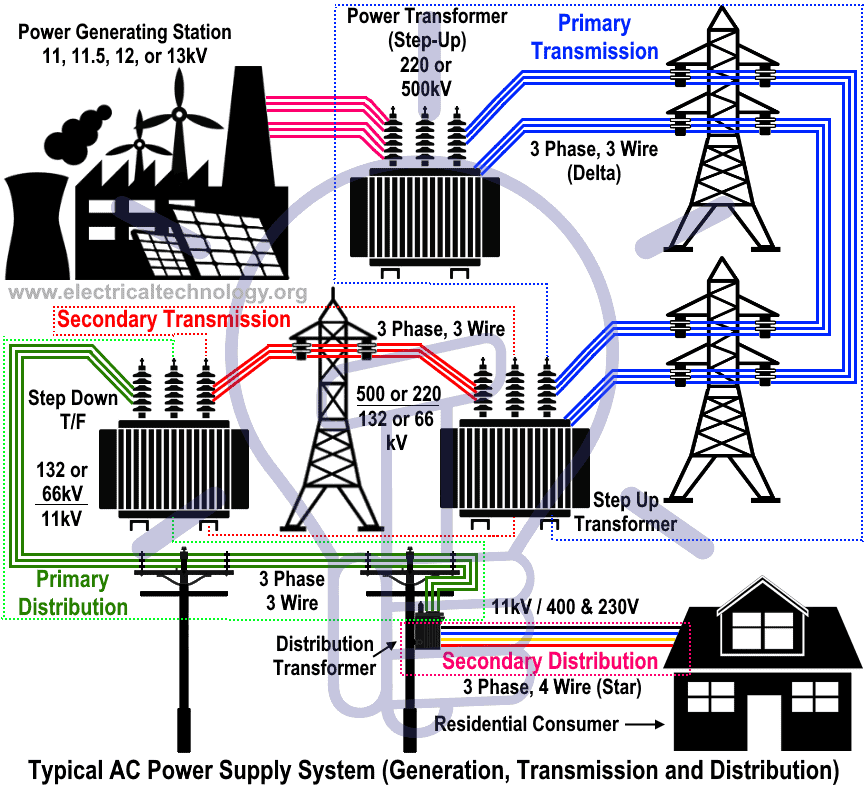
Electric Power System Generation Transmission Distribution Of Fig 2: typical ac electric power supply systems scheme (generation, transmission & distribution) after these five levels, the energy must be available as the stated form in terms of voltage magnitudes, frequency and consistency. generation means the conversion of a form of energy into electrical energy. A combination of all these systems is collectively known as an electric power system. a power system is a combination of central generating stations, electric power transmission system, distribution and utilization system. each one of these systems is explained in detail in the next sections. fig. 1: basic structure of an electric power system. Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electricity. electricity is carried from the transmission system to individual consumers. distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kv and 33 kv with the use of transformers. [1]. An electric power system is defined as a network of electrical components used to supply, transfer, and consume electric power. the supply is done through some form of generation (e.g. a power plant), the transfer is done through a transmission (via a transmission line) and distribution system, and the consumption can be through residential.

Comments are closed.