The Theory Of Consumer Behavior

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free Consumer theory is useful but not flawless, as it is based on a number of assumptions about human behavior. understanding consumer theory individuals have the freedom to choose between different. The review of the decision making models undertaken here highlights the complexity of consumer choices and identifies the key processes that lead to behaviour. a wide range of variables have been posited across the models, and each has evidence to justify its inclusion in attempts to explain behaviour.
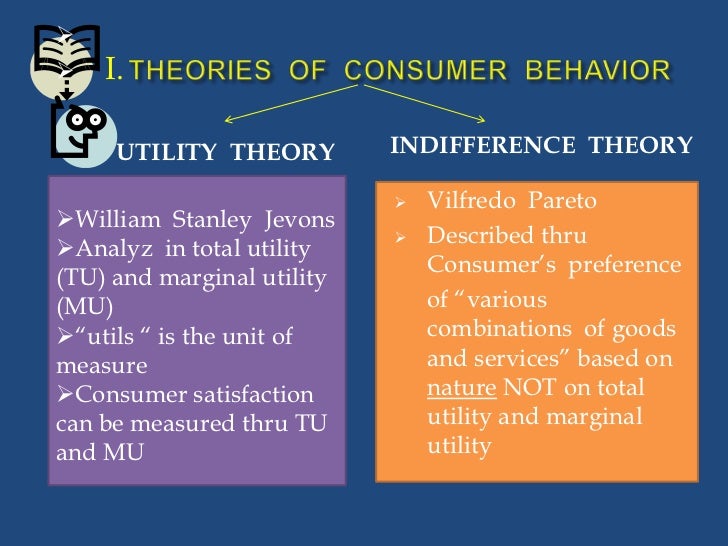
Theories Of Consumer Behavior Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organisations and all the activities associated with the purchase, use and disposal of goods and services. consumer behaviour consists of how the consumer 's emotions, attitudes, and preferences affect buying behaviour. consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub. The consumption values theory can be used to predict consumer behaviour, and more than that, this theory can also describe and explain this behaviour. so, it must be pointed out that this theory can be applied to different product categories, and it has a prediction validity regarded as excellent in more than 200 situations already analysed [ 52 ]. Unit 2: consumer theory. the second unit of the course introduces you to the analysis of consumer behavior. the decisions that individuals make about what and how much to consume are among the most important factors that shape the evolution of the overall economy, and we can analyze these decisions in terms of their underlying preferences. you. Some basic assumptions about preferences. 1. completeness: preferences are assumed to be complete. in other words, consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets. thus, for any two market baskets a and b, a consumer will prefer a to b, will prefer b to a, or will be indifferent between the two.

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free Unit 2: consumer theory. the second unit of the course introduces you to the analysis of consumer behavior. the decisions that individuals make about what and how much to consume are among the most important factors that shape the evolution of the overall economy, and we can analyze these decisions in terms of their underlying preferences. you. Some basic assumptions about preferences. 1. completeness: preferences are assumed to be complete. in other words, consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets. thus, for any two market baskets a and b, a consumer will prefer a to b, will prefer b to a, or will be indifferent between the two. Consumer attitudes and behaviors are fundamentally dynamic processes; thus, understanding consumer dynamics is crucial for truly understanding consumer behaviors and for firms to formulate appropriate actions. recent history in empirical marketing research has enjoyed increasingly richer consumer data as the result of technology and firms’ conscious data collection efforts. richer data, in. Samuelson extended georgescu roegen’s (1936) study of the pure theory of consumer behavior. later, the works of samuelson , debreu (1959, 1960), and morishima were extended by lancaster . there are three ways in which the new approach to consumer theory is different from the traditional theory of consumer behavior.

Pdf Consumer Behaviour Theory Approaches And Models Semantic Scholar Consumer attitudes and behaviors are fundamentally dynamic processes; thus, understanding consumer dynamics is crucial for truly understanding consumer behaviors and for firms to formulate appropriate actions. recent history in empirical marketing research has enjoyed increasingly richer consumer data as the result of technology and firms’ conscious data collection efforts. richer data, in. Samuelson extended georgescu roegen’s (1936) study of the pure theory of consumer behavior. later, the works of samuelson , debreu (1959, 1960), and morishima were extended by lancaster . there are three ways in which the new approach to consumer theory is different from the traditional theory of consumer behavior.

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.