Thoracentesis And Paracentesis
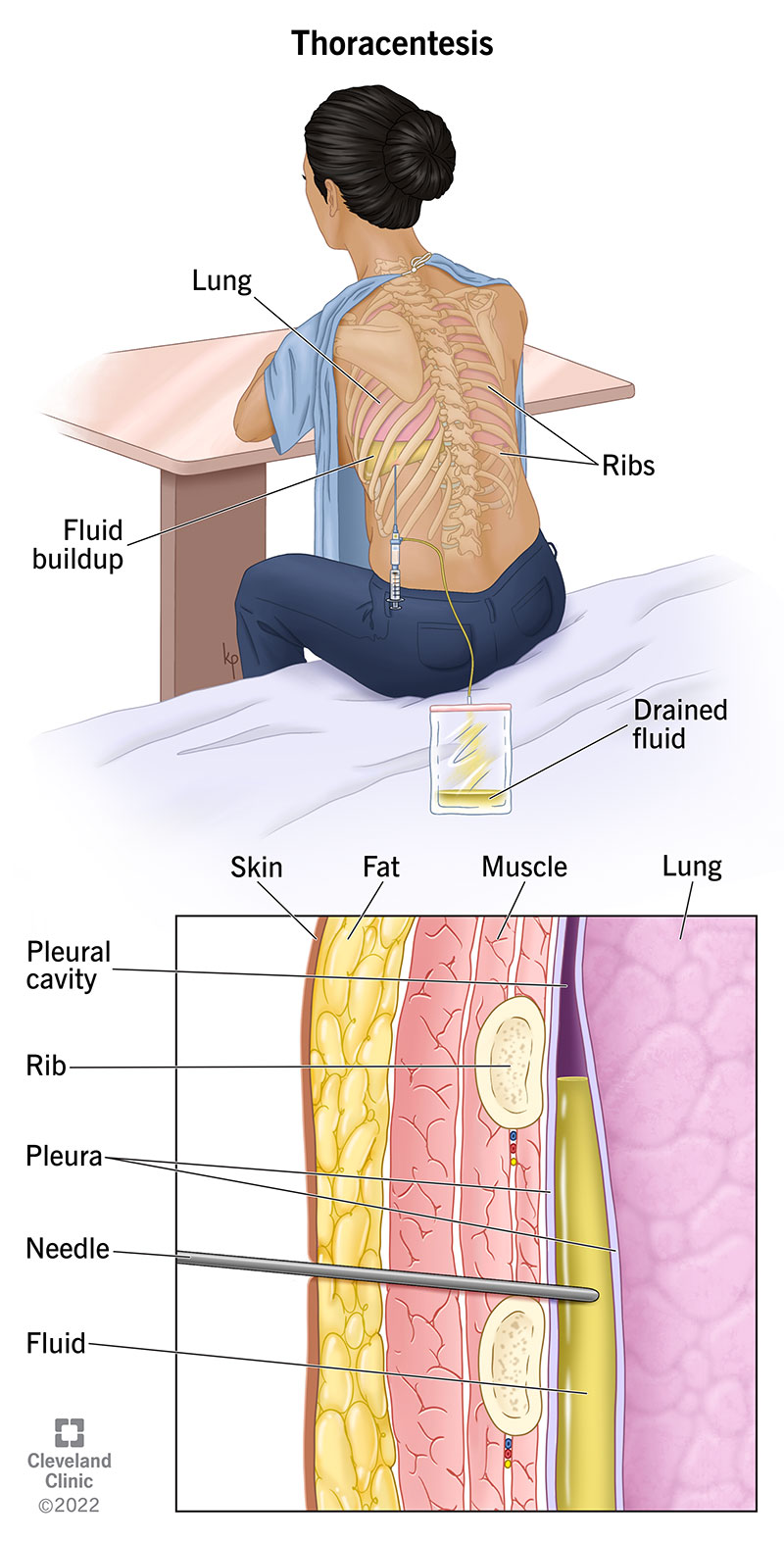
Thoracentesis Procedure Thoracentesis. thoracentesis is a procedure that a provider uses to drain extra fluid from around the lungs (pleural space) with a needle. it’s used to test the fluid for infection or other illnesses and to relieve chest pressure that makes it tough to breathe. thoracentesis is a short, low risk procedure done while you’re awake. Paracentesis is a procedure that drains excess fluid called ascites from your abdomen. ascites occur when fluid collects in a membrane called your peritoneum. your peritoneum covers your abdominal organs, including your stomach, liver, kidney and parts of your intestines. it consists of two layers.

Thoracentesis And Paracentesis вђ Infra Healthcare Paracentesis vs thoracentesis positioning. for paracentesis, a supine position with the head of the bed slightly elevated (anywhere between 45 to 90 degrees) or a lateral decubitus position is advised. for thoracentesis, a seated position with the patient leaning slightly forward is prescribed. Abdominal paracentesis is a simple bedside or clinic procedure in which a needle is inserted into the peritoneal cavity and ascitic fluid is removed [1]. diagnostic paracentesis refers to the removal of a small quantity of fluid for testing. therapeutic paracentesis refers to the removal of five liters or more of fluid to reduce intra abdominal. Similar nonrandomized data exist for paracentesis and thoracentesis . the pooled data on patients with abnormal coagulation profiles (inr > 1.5 and or platelet count < 50 × 10 9 l) indicate a very low risk of major bleeding for paracentesis (0.2%, 5 of 2,113 patients) (56,72–74) and thoracentesis (0.5%, 7 of 1,505 patients) (75–78) . Thoracentesis is a procedure that is performed to remove fluid or air from the thoracic cavity for both diagnostic and or therapeutic purposes.[1][2] thoracentesis is also known as thoracocentesis, pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression. a cannula, or hollow needle, is introduced into the thorax after administration of local anesthesia.

Comments are closed.