Tiered Pricing Model Vs Tier Pricing Strategy Definition Examples

What Is Tiered Pricing Dealhub Tiered pricing is a pricing strategy that scales the price of a product according different thresholds of a certain metric. for example, a b2b saas company may have an entry level tier that allows one employee to access the system and a higher end tier that lets unlimited employees use it. in between there will be plans offering in between ranges. Tiered pricing examples: which saas companies use tiered pricing? if you are unsure whether to make your pricing model tier based or what to include in each tier, here are some real world examples to help guide your decision. 1. drift . the revenue acceleration platform, drift, relies heavily on a three tiered pricing strategy. they clearly.
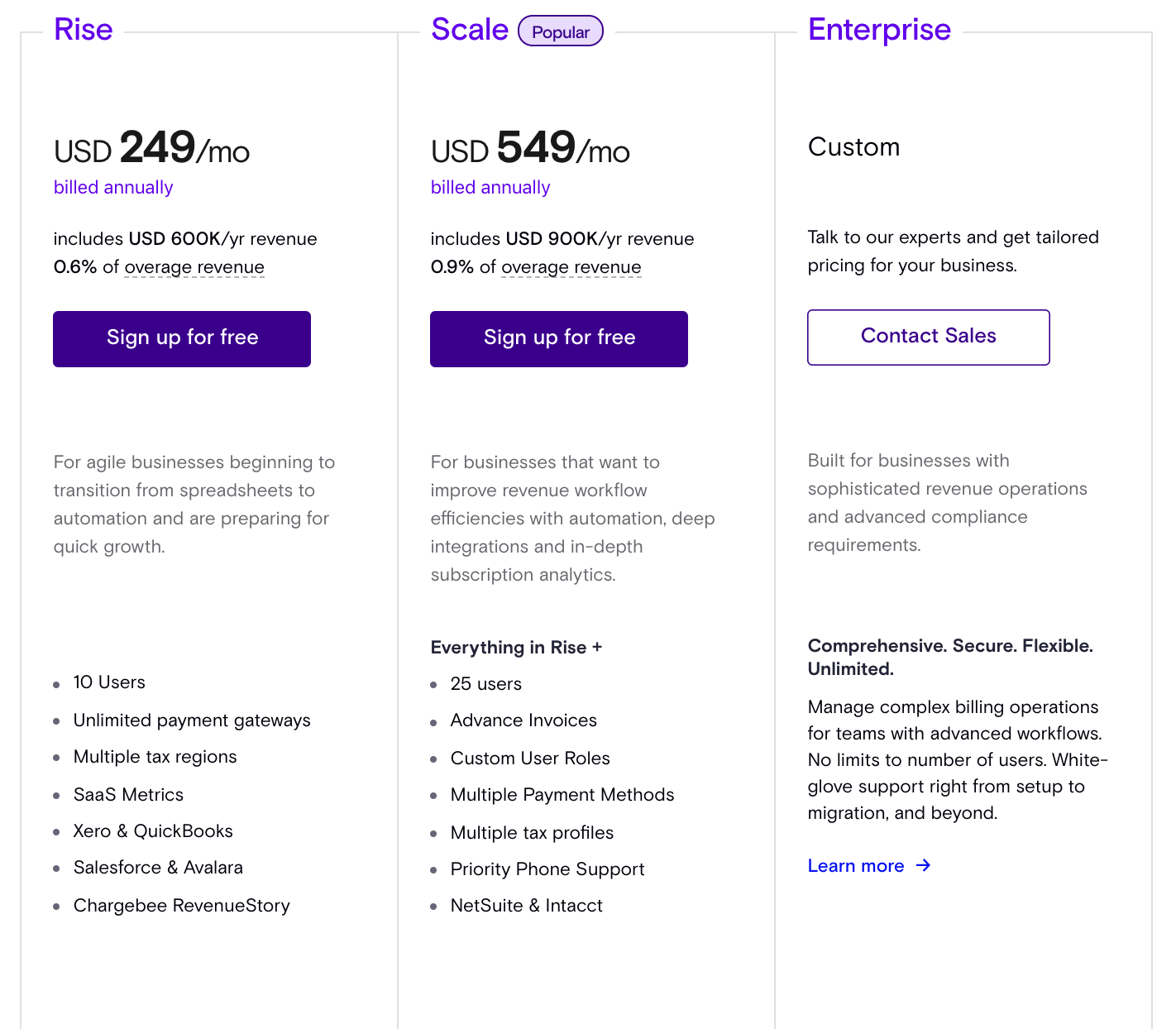
Tiered Pricing Model Vs Tier Pricing Strategy Definition Examples In a tiered pricing model, you calculate your total like this: [ ($20x10) ($10x20) ($5 x 30)] = $550. you move to the next tier only when one tier is completely filled. whereas, in a volume pricing model, the total is calculated as ($5x60) according to the total number of widgets bought which falls under the 30 100 widgets price range. Published on: november 9, 2021. tiered pricing is one of the most familiar billing strategies used today. it’s a method where companies limit or expand their offering based on pre defined tiers. the model has a wide range of applications beyond saas and is best suited to selling services, features, products, licences, etc. 3. bring in more revenue with higher volumes sales. one of the foundational pillars of tiered pricing strategy is the enhanced perceived value with each subsequent tier. while basic tiers cater to essential needs, the higher tiers, packed with advanced features and integrations, often come with a premium price tag. With tiered pricing the customer pays a different price for each usage tier. the first 5 users are in the 1 5 users tier, so they pay $10 each, totaling $50. the next 5 users fall in the 6 10 users tier, costing $9 each, totaling $45. the remaining 3 users belong to the 11 20 users tier, costing $8 each, totaling $24.
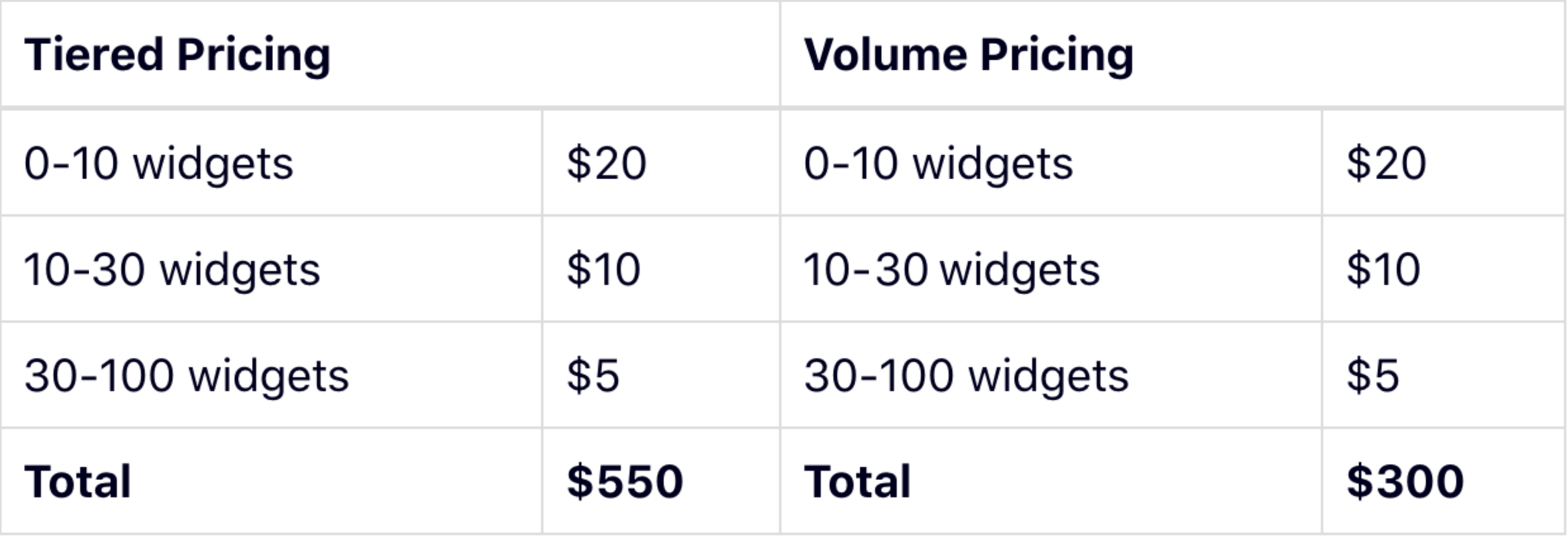
Tiered Pricing Model Vs Tier Pricing Strategy Definition Examples 3. bring in more revenue with higher volumes sales. one of the foundational pillars of tiered pricing strategy is the enhanced perceived value with each subsequent tier. while basic tiers cater to essential needs, the higher tiers, packed with advanced features and integrations, often come with a premium price tag. With tiered pricing the customer pays a different price for each usage tier. the first 5 users are in the 1 5 users tier, so they pay $10 each, totaling $50. the next 5 users fall in the 6 10 users tier, costing $9 each, totaling $45. the remaining 3 users belong to the 11 20 users tier, costing $8 each, totaling $24. Tiered pricing is a strategy that businesses use to set the costs of products or services based on the different levels or quantities that customers purchase. the more a customer buys, the less they pay per unit. this structure, which is common across industries, is a way for businesses to reward customers for making larger purchases. Tiered pricing: the complete guide. a one size fits all approach generally isn’t as appealing as a personalized experience. this can be true for the merchant as well as the consumer. if you are selling tickets to a concert, for instance, having a cheaper general admission ticket and a more expensive vip treatment ticket would probably suit.
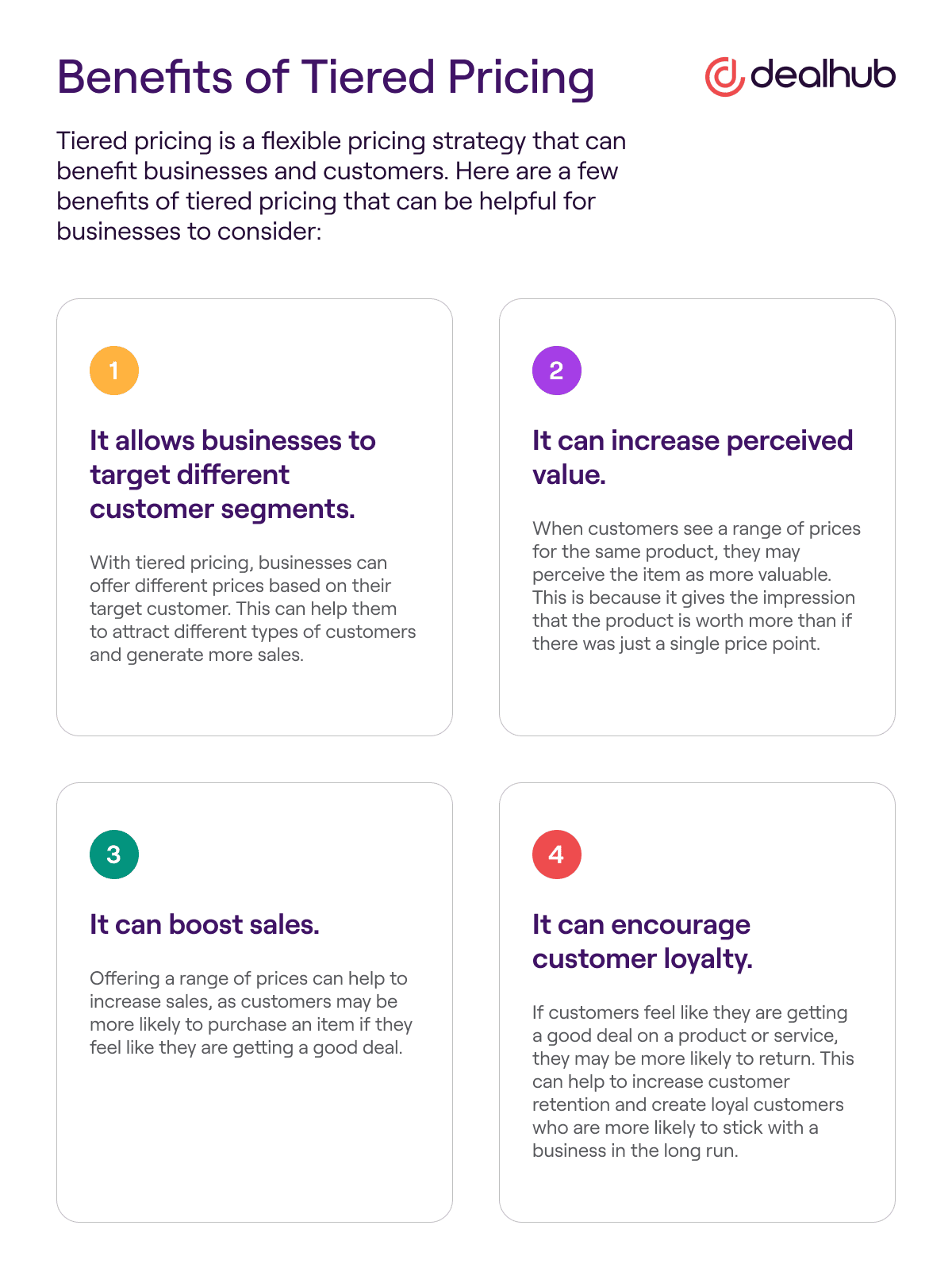
Tiered Pricing Strategy Definition Examples Benefits 52 Off Tiered pricing is a strategy that businesses use to set the costs of products or services based on the different levels or quantities that customers purchase. the more a customer buys, the less they pay per unit. this structure, which is common across industries, is a way for businesses to reward customers for making larger purchases. Tiered pricing: the complete guide. a one size fits all approach generally isn’t as appealing as a personalized experience. this can be true for the merchant as well as the consumer. if you are selling tickets to a concert, for instance, having a cheaper general admission ticket and a more expensive vip treatment ticket would probably suit.

Comments are closed.