Transmission Electron Microscope Tem And Scanning Electron Microscope

Transmission Electron Microscope Center For Biotechnology Scanning electron microscopy (sem) and transmission electron microscopy (tem) are the two most common types of electron microscopy. tem and sem differ in how they work and what types of images they are able to capture. this article will overview sem and tem, including what they are, how they work, and how they compare to one another.<br ><br >. In overall design, em is similar to light microscopes with some differences (refer: electron microscope vs light microscope) electron microscope was designed by knoll and ruska of germany in 1932. there are two types of electron microscopes: tem (transmission electron microscope) and sem (scanning electron microscope).
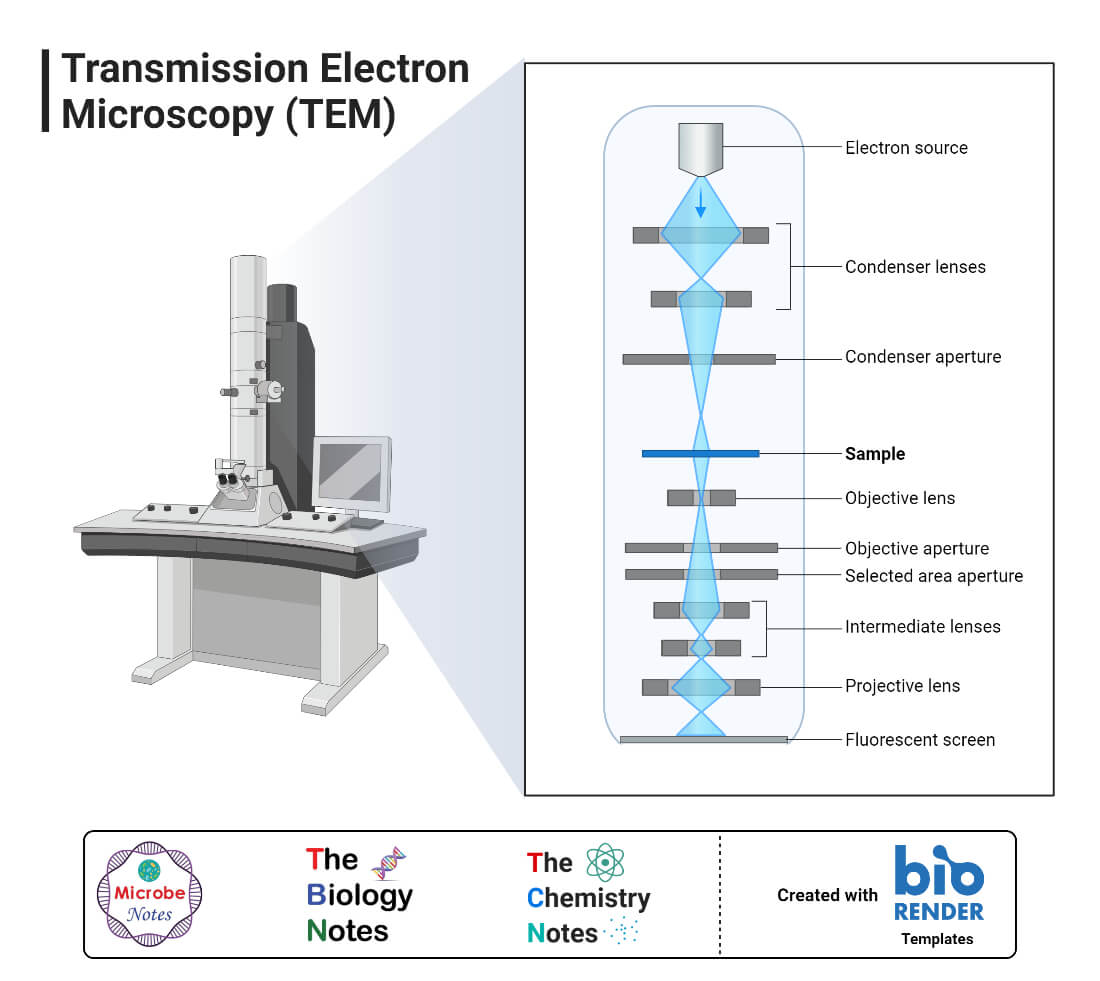
Transmission Electron Microscope Tem Definition Principle Images Tem vs sem comparison. the two most common types of electron microscopes are transmission (tem) and scanning (sem) systems, but the differences between these two instruments can be fairly nuanced. here we hope to provide a fundamental primer for individuals looking to get started with this powerful technique. scanning electron microscope (sem. Their versatility and extremely high spatial resolution render them a very valuable tool for many applications. the two main types of electron microscopes are the transmission electron microscope (tem) and the scanning electron microscope (sem). here, we briefly describe their similarities and differences. the difference between sem and tem. The working principle of the transmission electron microscope (tem) is similar to the light microscope. the major difference is that light microscopes use light rays to focus and produce an image while the tem uses a beam of electrons to focus on the specimen, to produce an image. electrons have a shorter wavelength in comparison to light which. A scanning transmission electron microscope (stem) is a type of transmission electron microscope (tem). pronunciation is [stɛm] or [ɛsti:i:ɛm]. as with a conventional transmission electron microscope (ctem), images are formed by electrons passing through a sufficiently thin specimen. however, unlike ctem, in stem the electron beam is focused.

Transmission Electron Microscopy Tem 17e The working principle of the transmission electron microscope (tem) is similar to the light microscope. the major difference is that light microscopes use light rays to focus and produce an image while the tem uses a beam of electrons to focus on the specimen, to produce an image. electrons have a shorter wavelength in comparison to light which. A scanning transmission electron microscope (stem) is a type of transmission electron microscope (tem). pronunciation is [stɛm] or [ɛsti:i:ɛm]. as with a conventional transmission electron microscope (ctem), images are formed by electrons passing through a sufficiently thin specimen. however, unlike ctem, in stem the electron beam is focused. The polio virus is 30 nm in diameter. [1] transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. the specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. an image is formed from the interaction of the electrons. This scanning mode methodology with transmitted signal collection is usually called scanning transmission electron microscopy (stem) (egerton, 2011). modern tems fitted with extra scan instrumentation can also scan a highly focused beam, enabling stem implementation at higher electron energies (keyso et al., 1998, pennycook and nellist, 2011).

Scanning Electron Microscope Sem Definition Images Uses The polio virus is 30 nm in diameter. [1] transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. the specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. an image is formed from the interaction of the electrons. This scanning mode methodology with transmitted signal collection is usually called scanning transmission electron microscopy (stem) (egerton, 2011). modern tems fitted with extra scan instrumentation can also scan a highly focused beam, enabling stem implementation at higher electron energies (keyso et al., 1998, pennycook and nellist, 2011).

Comments are closed.