Trauma Brain Diagram

Infographic Trauma Brain Of Processing With so many changes taking place in the brain, along with stress hormones circulating through your system on a regular basis, you may experience several symptoms of ptsd. according to the. Understanding how trauma works in the brain and body is the first step to beginning a process of healing that can lead to lasting change. but don't try to do it all on your own. seek the help of a.

How Trauma Affects The Brain Long term effects of trauma on the brain can be visualized through trauma and brain diagrams, which often show marked differences compared to healthy brain images. one of the most notable changes is a persistent hyperactivity in the amygdala, leading to an exaggerated fear response even in safe situations. Traumatic stress can be associated with lasting changes in these brain areas. traumatic stress is associated with increased cortisol and norepinephrine responses to subsequent stressors. antidepressants have effets on the hippocampus that counteract the effects of stress. findings from animal studies have been extended to patients with post. Forensic experiential trauma interviewing (feti) techniques. purpose is to collect as much forensic physiological evidence as possible. step 1: genuine empathy. step 2: “help me understand what you are able to remember about the experience.”. step 3: listen. acknowledge the difficulty of the situation. focus on what can be remembered. Introduction. traumatic brain injury (tbi) occurs when a traumatic event causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, leading to damage. as illustrated in the poster (panel a), the event can be classified as either impact or non impact, depending on whether the head makes direct contact with an object (impact) or encounters a non impact force such as blast waves or rapid acceleration and.
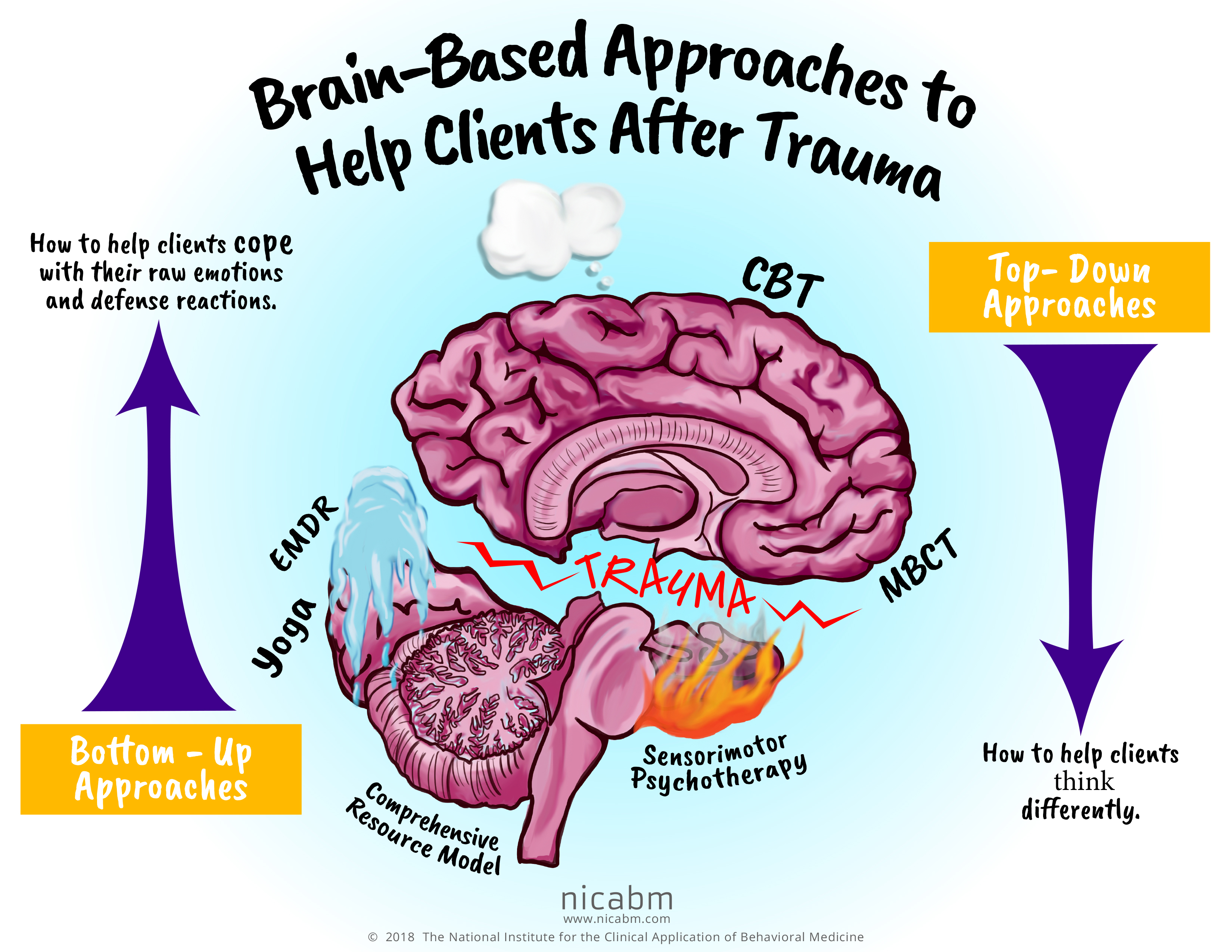
Infographic Brain Based Approaches To Help Clients After Trauma Forensic experiential trauma interviewing (feti) techniques. purpose is to collect as much forensic physiological evidence as possible. step 1: genuine empathy. step 2: “help me understand what you are able to remember about the experience.”. step 3: listen. acknowledge the difficulty of the situation. focus on what can be remembered. Introduction. traumatic brain injury (tbi) occurs when a traumatic event causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, leading to damage. as illustrated in the poster (panel a), the event can be classified as either impact or non impact, depending on whether the head makes direct contact with an object (impact) or encounters a non impact force such as blast waves or rapid acceleration and. When a traumatic event occurs, the hippocampus: creates and stores the memory. retrieves the memory. calms the amygdala alarm circuit. effects after traumatic stress. signs and symptoms of ptsd associated with the hippocampus are: confusion. disorientation. recurring thoughts, nightmares, and or flashbacks. The following regions of the brain are the most likely to change following a traumatic event. the amygdala is designed to detect and react to people, places, and things in the environment that could be dangerous. this is important for safety and survival. after trauma, the amygdala can become even more highly attuned to potential threats in the.

Comments are closed.