Turbofan Engines Display From Gm Parts

Turbofan Engine Diagram Small size, big energy. 😁#turbofanengines #engines #aerospaceparts #aerospacemanufacturing #aerospaceengineering #leanmanufacturing #rapidprototyping #massp. Figure 3: a turbofan engine, viewed from the front, with the fan visible 1. air intake ingestion the fan is responsible for producing the majority of the thrust generated by a turbofan engine and is easily visible when looking at the front of the engine, as seen in figure 3. the fan is directly connected to the low pressure.

Turbine Engine Exploded Parts Diagram Gm Th400 Automatic Transmission Fuel injector. the fuel injector is responsible for injecting fuel into the turbofan. like with other combustion engines, turbofans require a mixture of fuel and air. they get air from the inlet and fan, and turbofans get fuel from the fuel injector. the fuel injector sprays fuel into the turbofan where it mixes with air before being burned. Innovation brings challenge and opportunity, and we’re suiting up for both. because when it comes to the evolving maintenance, repair, collision and powertrain needs of chevrolet, buick, gmc and cadillac vehicles, only gm genuine parts and acdelco original equipment parts offer true gm original equipment built for what’s next. A turbofan engine is a modified type of jet engine that uses a combination of bypass air and jet core efflux to create thrust. bypass air is blown through a ducted fan. the jet core drives this ducted fan. the turbofan engine is also known as a bypass or fanjet engine. the term “turbofan” stands for “turbine” and “fan,” the. To accommodate the higher flight speeds, the blades are scimitar shaped with swept back leading edges at the blade tips. engines featuring such propellers are called propfans. picture of turboprop engine. turbofans. a turbofan engine has a large fan at the front, which sucks in air. most of the air flows around the outside of the engine, making.

Turbofan Engine Diagram A turbofan engine is a modified type of jet engine that uses a combination of bypass air and jet core efflux to create thrust. bypass air is blown through a ducted fan. the jet core drives this ducted fan. the turbofan engine is also known as a bypass or fanjet engine. the term “turbofan” stands for “turbine” and “fan,” the. To accommodate the higher flight speeds, the blades are scimitar shaped with swept back leading edges at the blade tips. engines featuring such propellers are called propfans. picture of turboprop engine. turbofans. a turbofan engine has a large fan at the front, which sucks in air. most of the air flows around the outside of the engine, making. Rated at 94,000 lbs. of thrust, the ge90 94b engine builds on the proven success of the early ge90 engine models to power the boeing 777 200 and 777 300 aircraft. ge90 115b engine after being selected by boeing to develop an engine with 110,000 to 115,000 lbs. of thrust, ge aerospace delivered the ge90 115b engine, which now powers the longer. Turbofan engines, as mentioned earlier, have bypass ratios of up to 12:1. this bypass air has a lower velocity and averages out the hot section high velocity air, causing a lower noise profile than a turbofan engine. maintenance. because the turbofan has more components than a turbojet engine, it adds more mechanical complexity to the engine.

What Is A Turbofan Engine How Does A Turbofan Work Rated at 94,000 lbs. of thrust, the ge90 94b engine builds on the proven success of the early ge90 engine models to power the boeing 777 200 and 777 300 aircraft. ge90 115b engine after being selected by boeing to develop an engine with 110,000 to 115,000 lbs. of thrust, ge aerospace delivered the ge90 115b engine, which now powers the longer. Turbofan engines, as mentioned earlier, have bypass ratios of up to 12:1. this bypass air has a lower velocity and averages out the hot section high velocity air, causing a lower noise profile than a turbofan engine. maintenance. because the turbofan has more components than a turbojet engine, it adds more mechanical complexity to the engine.
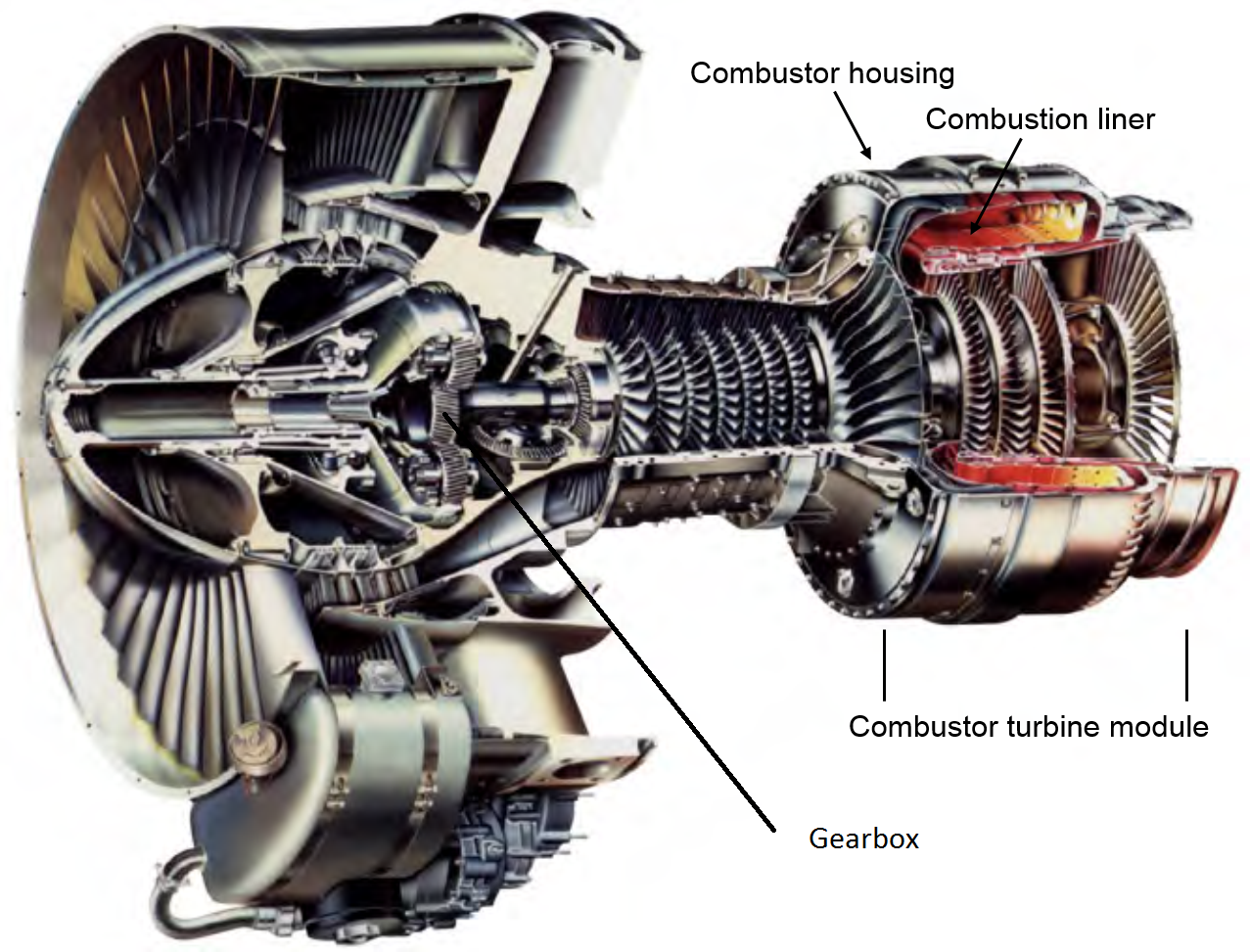
General Electric Turbofan Engines

Comments are closed.