Understand Domain And Range
What Is Domain And Range Example #1: find the domain and range of a graph. for our first example, we are given the graph of the function f (x)=x^2 and we are tasked with finding the domain and the range (note that our answers must be in interval notation). figure 08: find the domain and range of the graph of y=x^2. The range also excludes negative numbers because the square root of a positive number x is defined to be positive, even though the square of the negative number − √x also gives us x. figure 3.3.20: cube root function f(x) = 3√x. for the cube root function f(x) = 3√x, the domain and range include all real numbers.
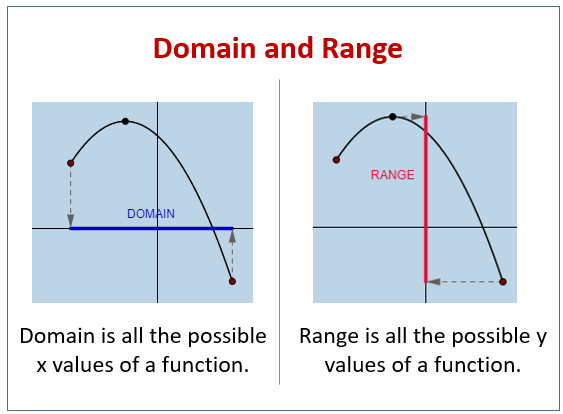
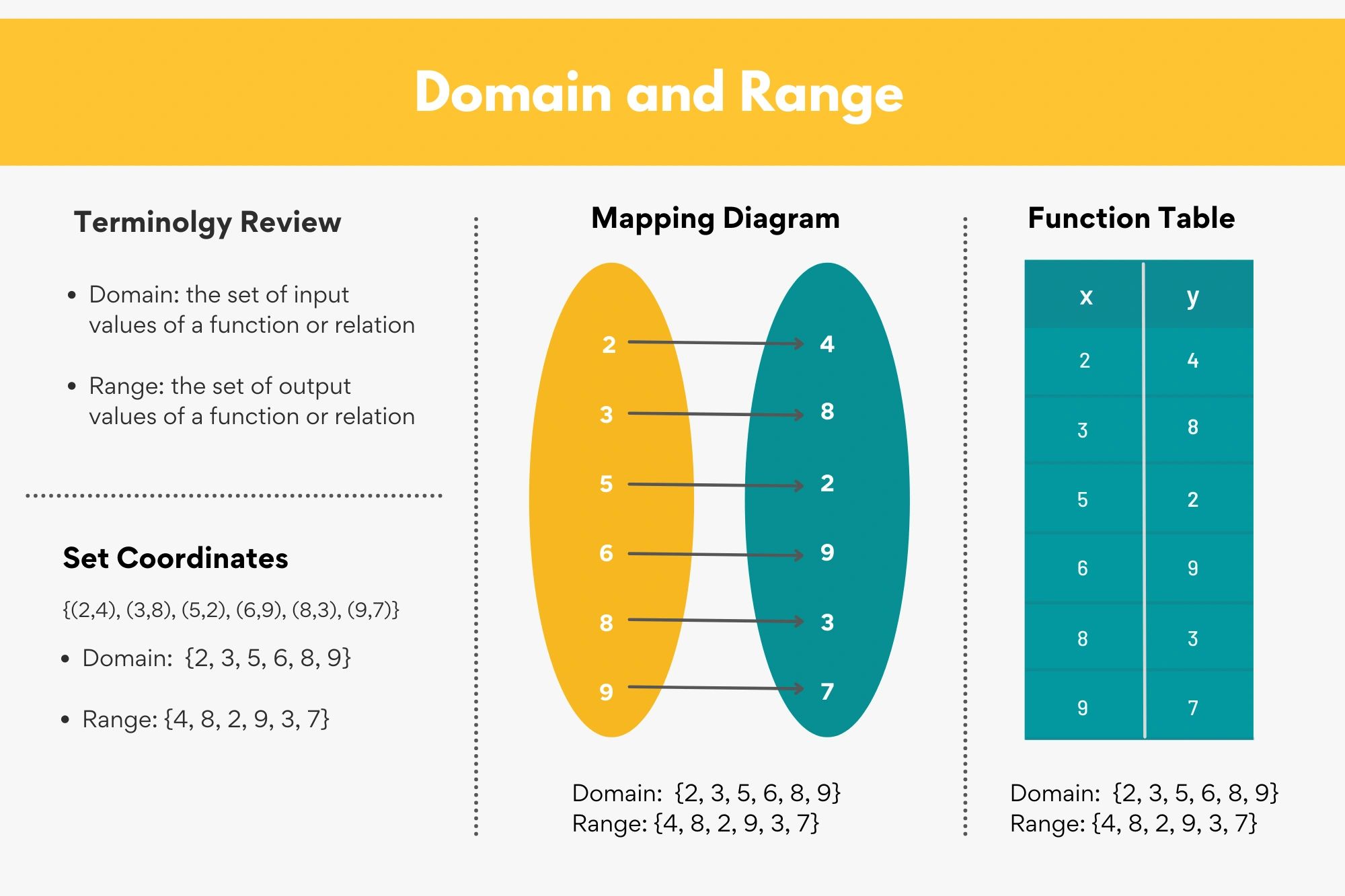
Domain And Range Of Functions Video Lessons Examples Solutions Understanding domain and range: a comprehensive guide. jerri de la cruz. april 11, 2023 ∙ 5 minutes read. domain and range are fundamental concepts in mathematics, particularly in studying functions. understanding the domain and range of a function is crucial for solving problems in calculus, algebra, and other branches of mathematics. Finding domain and range from graphs. another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x axis. the range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y axis. keep in mind. The codomain is actually part of the definition of the function. and the range is the set of values that actually do come out. example: we can define a function f (x)=2x with a domain and codomain of integers (because we say so). but by thinking about it we can see that the range (actual output values) is just the even integers. The domain and range of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable, x, for which y is defined. the range of a function is all the possible values of the dependent variable y. in other words, the domain is the set of values that we can plug into a function that will result in a real y value; the range is the set of values.

Comments are closed.