Uniform Circular Motion And Centripetal Force

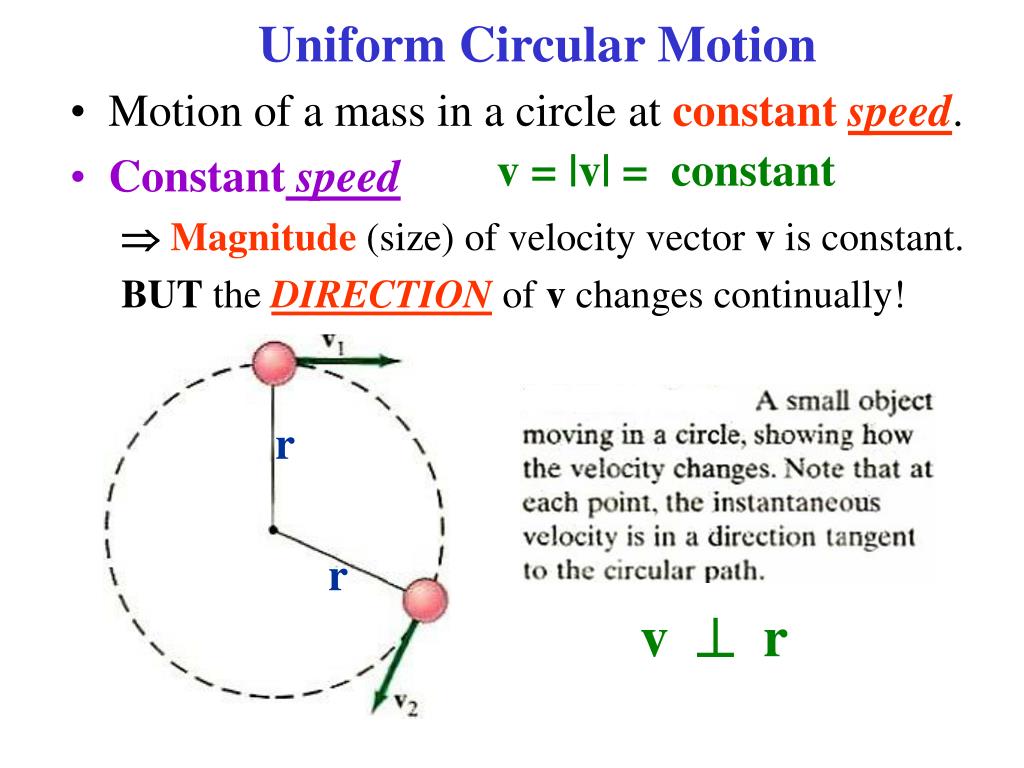
Motion Pictures 6 Centripetal force is perpendicular to tangential velocity and causes uniform circular motion. the larger the centripetal force f c, the smaller is the radius of curvature r and the sharper is the curve. the lower curve has the same velocity v, but a larger centripetal force f c produces a smaller radius r ′ r ′. Δv = v rΔr. (4.5.2) figure 4.5.1: (a) a particle is moving in a circle at a constant speed, with position and velocity vectors at times t and t Δt. (b) velocity vectors forming a triangle. the two triangles in the figure are similar. the vector Δv points toward the center of the circle in the limit Δt → 0.
Ppt Uniform Circular Motion Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): the frictional force supplies the centripetal force and is numerically equal to it. centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity and causes uniform circular motion. the larger the f c, the smaller the radius of curvature r and the sharper the curve. the second curve has the same v, but a larger f c produces a smaller. The uniform circular motion interactive is shown in the iframe below. there is a small hot spot in the lower right corner of the iframe. dragging this hot spot allows you to change the size of iframe to whatever dimensions you prefer. our uniform circular motion simulation is now available with a concept checker. do the simulation. The sum of the forces is often called the “net force” on an object, and in the specific case of uniform circular motion, that net force is sometimes called the “centripetal force” however, it is not a force in and of itself and it is always the sum of the forces that points towards the center of the circle. Figure 6.20 the frictional force supplies the centripetal force and is numerically equal to it. centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity and causes uniform circular motion. the larger the f c, f c, the smaller the radius of curvature r and the sharper the curve. the second curve has the same v, but a larger f c f c produces a smaller r′.

Two Simple Derivations Of Centripetal Acceleration Youtube The sum of the forces is often called the “net force” on an object, and in the specific case of uniform circular motion, that net force is sometimes called the “centripetal force” however, it is not a force in and of itself and it is always the sum of the forces that points towards the center of the circle. Figure 6.20 the frictional force supplies the centripetal force and is numerically equal to it. centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity and causes uniform circular motion. the larger the f c, f c, the smaller the radius of curvature r and the sharper the curve. the second curve has the same v, but a larger f c f c produces a smaller r′. Evaluate centripetal and tangential acceleration in nonuniform circular motion, and find the total acceleration vector. uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. for example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. This force maintains the circular motion of the object, preventing it from moving off its path due to inertia. centripetal force is the force that acts toward the center of a circular path. the force is always perpendicular to the direction of movement. the formula for centripetal force is f c = mv 2 r.

Comments are closed.