Updated Guidance For People With Type 2 Diabetes Planning To Fast

Updated Guidance For People With Type 2 Diabetes Planning To Fast Based on the latest scientific research and clinical trials, the standards of care includes vital new and updated practice guidelines to care for people with diabetes and prediabetes, including for the diagnosis and treatment of youth and adults with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes; strategies for the prevention or delay of type 2. Management in type 2 diabetes provides an aid for healthcare professionals (hcps) while proposing and making management decisions for muslim patients with type 2 diabetes who are planning to fast during ramadan (figure 1). this has been adopted and modified specifi cally for ramadan based on the ada easd consensus recommendations 2018.
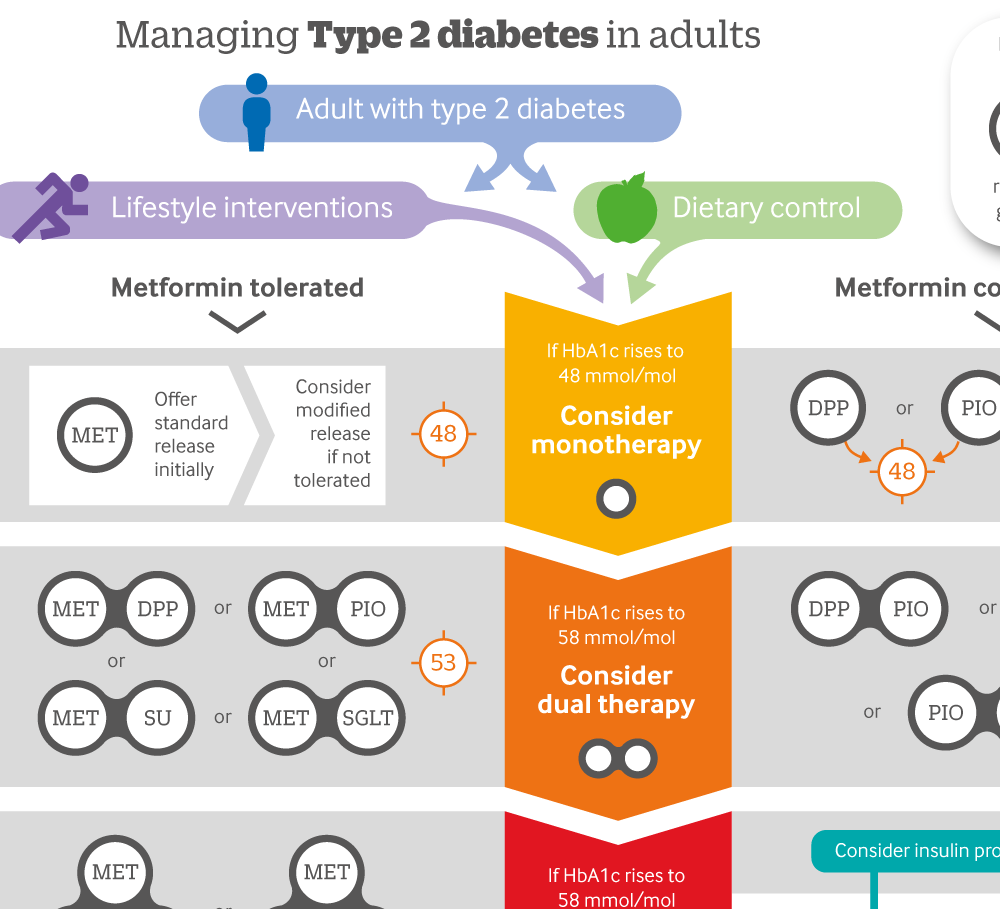
Management Of Type 2 Diabetes In Adults Summary Of Updated Nice Full guidance on individual antidiabetic drugs for people with t2dm that fast during ramadan is available in the full version of the idf dar diabetes and ramadan practical guidelines 2021. the recommended use of antidiabetic drugs during ramadan have been summarised in table 5. antidiabetic medications. The new guidance applies the principles of the american diabetes association (ada) and the european association for the study of diabetes (easd) consensus recommendations of 2018 and its update in 2019 to the management of people with type 2 diabetes during ramadan including the use of sglt2i and glp1 ra, two medicines that improve glycaemic. The largest dataset is the recent epidiar study , which showed that fasting during ramadan increased the risk of severe hypoglycemia (defined as hospitalization due to hypoglycemia) some 4.7 fold in patients with type 1 diabetes (from 3 to 14 events · 100 people −1 · month −1) and 7.5 fold in patients with type 2 diabetes (from 0.4 to 3. One mixed effects meta analysis model has estimated a 43% diabetes remission rate (95% ci 34%, 53%) following metabolic surgery in people with type 2 diabetes and a bmi <30 kg m 2 , significantly higher than that achieved with traditional medical management . however, there is a strong association between duration of diabetes and the likelihood.
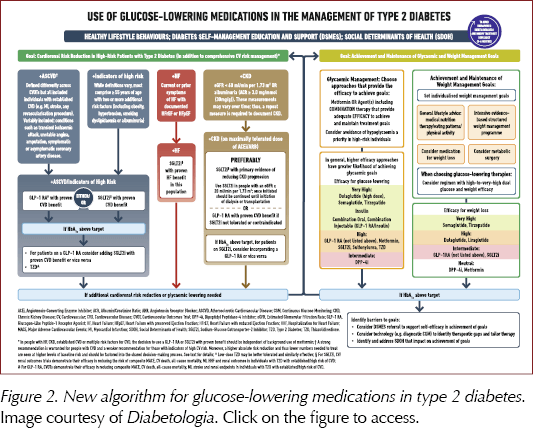
Easd 2022 Updated Ada Easd Type 2 Diabetes Consensus Published The largest dataset is the recent epidiar study , which showed that fasting during ramadan increased the risk of severe hypoglycemia (defined as hospitalization due to hypoglycemia) some 4.7 fold in patients with type 1 diabetes (from 3 to 14 events · 100 people −1 · month −1) and 7.5 fold in patients with type 2 diabetes (from 0.4 to 3. One mixed effects meta analysis model has estimated a 43% diabetes remission rate (95% ci 34%, 53%) following metabolic surgery in people with type 2 diabetes and a bmi <30 kg m 2 , significantly higher than that achieved with traditional medical management . however, there is a strong association between duration of diabetes and the likelihood. The landmark epidemiology of diabetes and ramadan (epidiar) study found that as many as 42.8% of the 1080 patients with t1 diabetes and 78.7% of the 11,173 patients with t2 diabetes reported fasting for at least 15 days during ramadan , leading to an estimation that approximately 120 million people with diabetes worldwide fast during ramadan. The cardiovascular risk score qrisk2 is recommended in current nice guidance 2 for assessing cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes and is used widely in practice. however, qrisk2 does not reflect lifetime cardiovascular risk; therefore, additional risk factors should be considered for people aged under 40 years with type 2 diabetes.

Comments are closed.