Updrafts And Thunderstorms

Thunderstorm Definition Types Structure Facts Britannica Updrafts and downdrafts also occur as part of the turbulence that is created when air passes over topographic barriers such as mountains. thunderstorm microburst (left) the air that forms the microburst is initially “dammed” aloft by the strength of the storm's updraft then cascades downward in a high velocity, narrow column (less than 4 km, or 2.5 miles, in diameter). Thunderstorm updrafts, downdrafts, air masses: the motion of a thunderstorm across the land is determined primarily by the interactions of its updrafts and downdrafts with steering winds in the middle layers of the atmosphere in which the storm develops. the speed of isolated storms is typically about 20 km (12 miles) per hour, but some storms move much faster. in extreme circumstances, a.

The Importance Of Rotating Updrafts In Severe Weather Fox21 News Colorado Thunderstorm: structure when the atmosphere becomes unstable enough to form large powerful updrafts and downdrafts (as indicated by the red and blue arrows), a towering thundercloud is built up. at times the updrafts are strong enough to extend the top of the cloud into the tropopause, the boundary between the troposphere (or lowest layer of the atmosphere) and the stratosphere. Multi cell line (squall line) sometimes thunderstorms will form in a line that can extend laterally for hundreds of miles. these "squall lines" can persist for many hours and produce damaging winds and hail. updrafts, and therefore new cells, continually re form at the leading edge of the system, with rain and hail following behind. The dissipating stage. when the downdrafts in the cloud become stronger than the updrafts, the storm starts to weaken. since warm moist air can no longer rise, cloud droplets can no longer form. the storm dies out with light rain as the cloud disappears from bottom to top. the whole process takes about one hour for an ordinary thunderstorm. A multi cell storm is a common, garden variety thunderstorm in which new updrafts form along the leading edge of rain cooled air (the gust front). individual cells usually last 30 to 60 minutes, while the system as a whole may last for many hours. multicell storms may produce hail, strong winds, brief tornadoes, and or flooding.
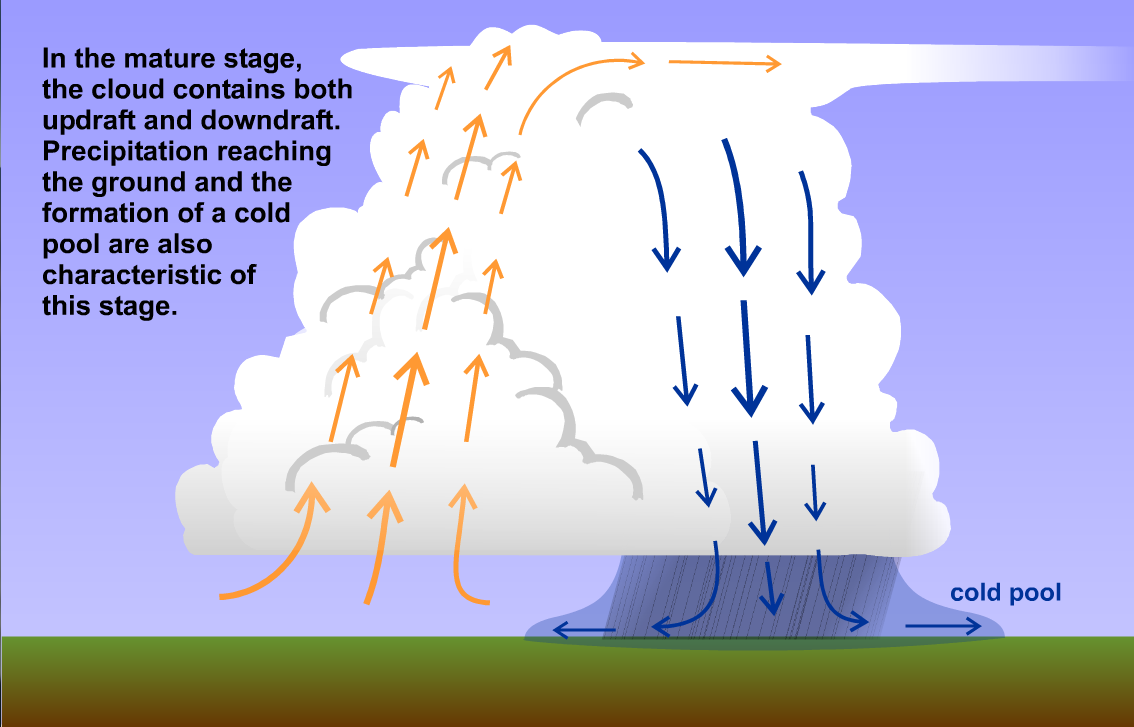
Single Cell Thunderstorms Meteo 3 Introductory Meteorology The dissipating stage. when the downdrafts in the cloud become stronger than the updrafts, the storm starts to weaken. since warm moist air can no longer rise, cloud droplets can no longer form. the storm dies out with light rain as the cloud disappears from bottom to top. the whole process takes about one hour for an ordinary thunderstorm. A multi cell storm is a common, garden variety thunderstorm in which new updrafts form along the leading edge of rain cooled air (the gust front). individual cells usually last 30 to 60 minutes, while the system as a whole may last for many hours. multicell storms may produce hail, strong winds, brief tornadoes, and or flooding. This thunderstorm has violent updrafts, which is why aircraft would avoid flying through it. this page titled 14.4: instability, cape and updrafts is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by roland stull via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. In the mature stage (fig. 14.7), the thunderstorm has an anvil, both updrafts and downdrafts, and heavy precipitation of large size drops. this often is the most violent time during the storm, with possible lightning, strong turbulence and winds.

Comments are closed.