Variability Of Eye Coloration In Humans And Animals On Biology
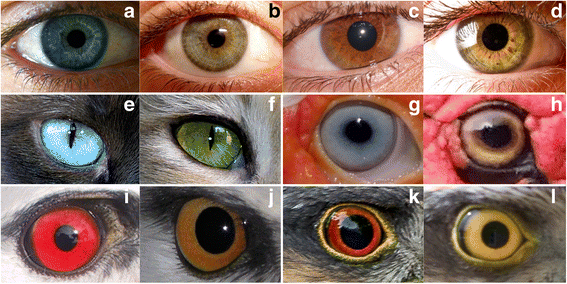
Variability Of Eye Coloration In Humans And Animals On Biology Curiously enough, eye color variants for humans may have also started very recently (about 8,000 years ago), concurrent with sedentarism and domestication of plants and animals, and only (or mainly) in europe. as of today, eye color variation in humans may be described as continuous, with numerous shades from very light blues to very dark browns. Kobayashi and kohshima’s seminal studies 1,2 brought attention to the dramatic variation present in primate eye colour and morphology that was further explored by others 3,4,5,6,7 (fig. 1.

Variability Of Eye Coloration In Humans And Animals On Biology Background human populations and breeds of domestic animals are composed of individuals with a multiplicity of eye (= iris) colorations. some wild birds and mammals may have intraspecific eye color variability, but this variation seems to be due to the developmental stage of the individual, its breeding status, and or sexual dimorphism. in other words, eye colour tends to be a species specific. A three single nucleotide polymorphism haplotype in intron 1 of oca2 explains most human eye color variation. am j hum genet. 2007;80:241–52. article cas pubmed google scholar. Birds display a rainbow of eye colours, but this trait has been little studied compared with plumage coloration. avian eye colour variation occurs at all phylogenetic scales: it can be conserved throughout whole families or vary within one species, yet the evolutionary importance of this eye colour variation is under studied. Background: human populations and breeds of domestic animals are composed of individuals with a multiplicity of eye (= iris) colorations. some wild birds and mammals may have intraspecific eye.

On Biology Variability Of Eye Coloration In Humans And Animals Birds display a rainbow of eye colours, but this trait has been little studied compared with plumage coloration. avian eye colour variation occurs at all phylogenetic scales: it can be conserved throughout whole families or vary within one species, yet the evolutionary importance of this eye colour variation is under studied. Background: human populations and breeds of domestic animals are composed of individuals with a multiplicity of eye (= iris) colorations. some wild birds and mammals may have intraspecific eye. 2) humans and domestic animal populations, on the contrary, have eyes of multiple colors. sexual selection has been invoked for eye color variation in humans, but this selection mode does not easily apply in domestic animals, where matings are controlled by the human breeder. testing the hypothesis: eye coloration is polygenic in humans. we. Mammalian colors and color patterns are some of the most diverse and conspicuous traits found in nature and have been widely studied from genetic developmental and evolutionary perspectives. in this review we first discuss the proximate causes underlying variation in pigment type (i.e., color) and pigment distribution (i.e., color pattern) and highlight both processes as having a distinct.

Comments are closed.