Vector Vs Raster Data Gis Explained

Difference Between Raster And Vector Explained Imanikruwpark Vectors are points, lines, and polygons. vector data is not made up of a grid of pixels. instead, vector graphics are comprised of vertices and paths. the three basic symbol types for vector data are points, lines, and polygons (areas). because cartographers use these symbols to represent real world features in maps, they often have to decide. Raster and vector data models differ in several ways, including: 1. data structure. raster data models are grid based, where each cell stores a value representing the attribute of interest. vector data models are based on points, lines, and polygons, where each feature is associated with a set of attribute data.

Raster Vs Vector What S The Difference And When To Use Which As you can see, vector and raster data are very different. most of the time vector data uses x and y coordinates to mark the location of the points, lines, and polygons. these points, lines, and polygons declare the location of objects such as fire hydrants, roads, walkways, and more. raster data uses squares, which are known as pixels or cells. Advantages of vector data. precision and accuracy: vector data can be very precise, representing boundaries and features with a high degree of accuracy. scalability: unlike raster data, vector data can be scaled up or down without losing quality. efficient storage: for many types of geographical data, vector formats require less storage space. Images: caitlin dempsey. vector data is the most common type of gis data. most data loaded into a gis software program tends to be in vector data. vector data represents geographic data symbolized as points, lines, or polygons. raster data represents geographic data as a matrix of cells that each contains an attribute value. This pic gives a good idea of raster vs. vector representation of data. in rastor, the area under consideration is divided into equal squares and a characteristic assigned to it. so if you consider creating a data structure for rastor it would be a 2d array, each x,y co ordinate refer a square in the are and it can have a certain predefined characteristic e.g. building, road, vegetation,.
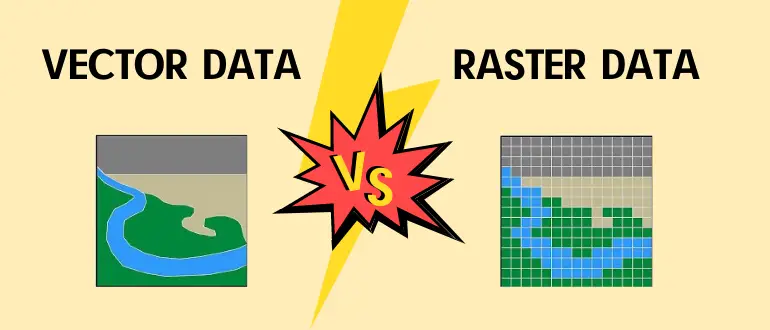
Raster Versus Vector Gis Images: caitlin dempsey. vector data is the most common type of gis data. most data loaded into a gis software program tends to be in vector data. vector data represents geographic data symbolized as points, lines, or polygons. raster data represents geographic data as a matrix of cells that each contains an attribute value. This pic gives a good idea of raster vs. vector representation of data. in rastor, the area under consideration is divided into equal squares and a characteristic assigned to it. so if you consider creating a data structure for rastor it would be a 2d array, each x,y co ordinate refer a square in the are and it can have a certain predefined characteristic e.g. building, road, vegetation,. A vector gis works by storing three types of geography. points (a power pole), lines (a power line) and polygons (a power utility service area) in a geographical database, and their attributes are stored in a separate database. raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. In gis, vector and raster are two different ways of representing spatial data. however, the distinction between vector and raster data types is not unique to gis: here is an example from the graphic design world which might be clearer. raster data is made up of pixels (or cells), and each pixel has an associated value. simplifying slightly, a.

Remote Sensing Gis Maps Vector Data Vs Raster Data A vector gis works by storing three types of geography. points (a power pole), lines (a power line) and polygons (a power utility service area) in a geographical database, and their attributes are stored in a separate database. raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. In gis, vector and raster are two different ways of representing spatial data. however, the distinction between vector and raster data types is not unique to gis: here is an example from the graphic design world which might be clearer. raster data is made up of pixels (or cells), and each pixel has an associated value. simplifying slightly, a.

Difference Between Raster And Vector Gemsplora

Comments are closed.