Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia U Vin Histopathology

Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia U Vin Histopathology Youtube Introduction. vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin) is widely accepted as the precursor lesion of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (vscc) [].vscc arises via either a human papilloma virus (hpv) associated pathway, or more commonly, via a mechanism independent of hpv, often being linked to chronic inflammatory conditions such as lichen sclerosus (ls) [1, 2]. Introduction. vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin), the precursor of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (vscc), is categorized into hpv associated high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (hsil) and low grade sil (lsil), and hpv independent vin. 1 hpv associated sil occurs mainly in younger women and is treated by imiquimod, excision, or laserevaporiazation. 2, 3 hpv independent vin, often.
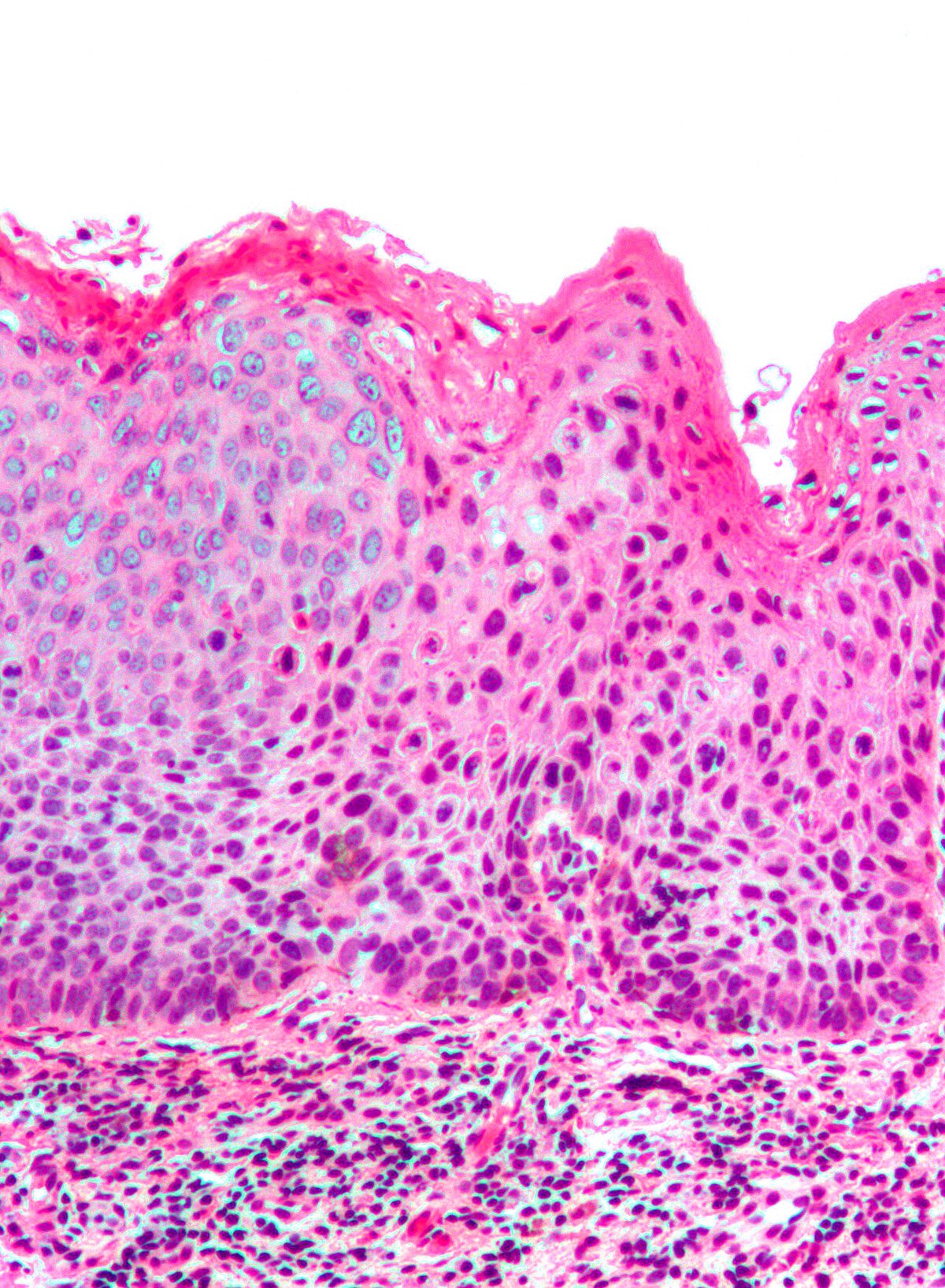
Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia Wikipedia Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin) is a noninvasive squamous lesion and precursor of squamous cell carcinoma (scc) of the vulva. because there is no screening test for vin, careful examination and biopsy of its various clinical lesions are essential. vin lesions can be raised, flat, white, gray, or pigmented; diagnosis is made clinically and confirmed with a biopsy.[1]. 2. classification. vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin) has come under different names since it was first described almost 100 years ago. the current lower anogenital squamous terminology (last) classification developed by the international society for the study of vulvar diseases (issvd) relating to human papillomavirus (hpv) associated squamous lesions of the anogenital tract [1, 2. There are 2 types of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin), both immediate precursors to vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (scc). high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (hsil, usual vin), is human papillomavirus (hpv)–related, usually shows warty basaloid morphology, and comprises more than 80% of vin but less than 50% of scc. 1–6 differentiated vin (dvin) is hpv independent and usually. Vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions (sil), previously referred to as vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (vin), are a group of premalignant conditions of the vulva. there are no routine screening methods for vulvar sil or vulvar carcinoma. in this topic, we will discuss the classification, manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of vulvar sil.

Comments are closed.