Water Special Issue Flood Risk Management And Resilience Volume
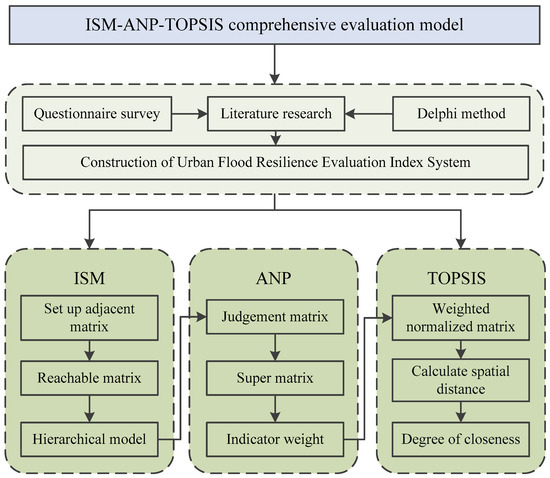
Water Special Issue Flood Risk Management And Resilience Volume Ii Dear colleagues, the first highly successful volume of this special issue, called flood risk management and resilience vol 1, included 18 papers on a range of contemporary themes and issues linked to resilience. these included papers on topics, such as community response and perspectives, impact on farmers, vulnerability assessment, climate. The aim of this special issue is to draw together the latest multi and interdisciplinary research in the domain of resilience to flood risk, drawing on a wide range of expertise and applications (as captured in the keywords below) to provide a state of the art collection of research connected to improving our understanding and approaches to.
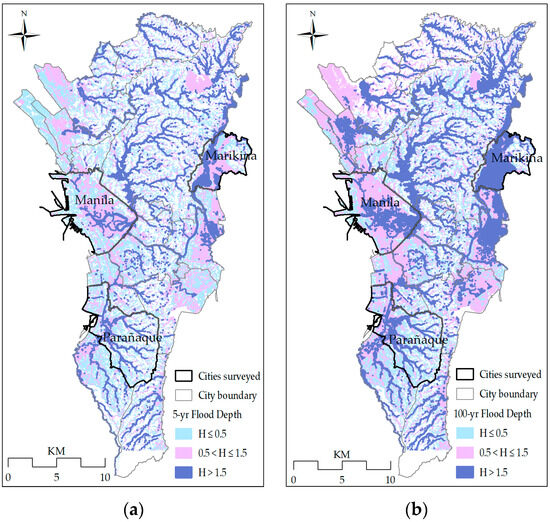
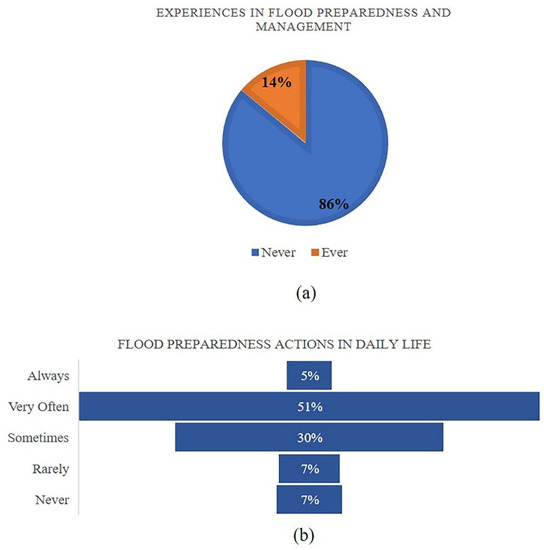
Water Special Issue Flood Risk Management And Resilience Volume Ii This special issue will provide a platform for researchers and engineers to share and discuss state of the art scientific knowledge and best practices in flood management. this special issue aims to address key challenges towards a more flood resilient future, encompassing not only both flood risk and resilience, but also their intersections. Journal of flood risk management provides an international platform for knowledge sharing in all areas related to flood risk. we publish flood related research with content ranging from leading edge academic papers to innovative applied content with the practitioner in mind. our readers and authors come from a wide background and share an. Beyond water—flood risk and resilience management and governance must integrate ci more into its existing concepts, since spill overs from floods such as secondary hazards, secondary or cascading effects can aggravate the damages and impacts, by triggering blackouts, road blockages or other interruptions way beyond the water perimeter or. The debate on flood resilience is linked to the paradigm shift from flood protection to risk management, which started in europe after the major river flood events in 1993 and 1995 along the river rhine (hartmann, 2012), and has developed over the past decades—pushed by further major fluvial and pluvial flood events (begum, stive, & hall.
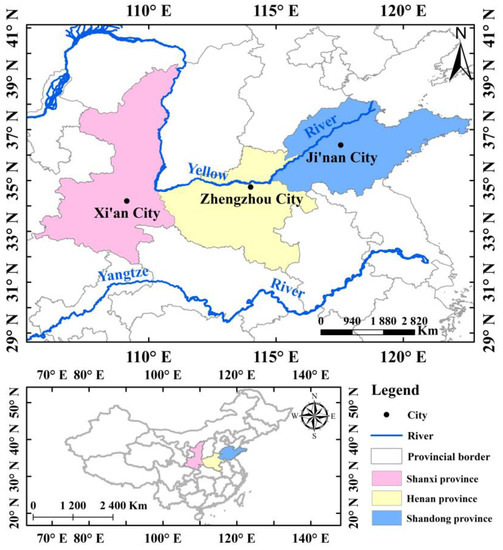
Water Special Issue Flood Risk Management And Resilience Beyond water—flood risk and resilience management and governance must integrate ci more into its existing concepts, since spill overs from floods such as secondary hazards, secondary or cascading effects can aggravate the damages and impacts, by triggering blackouts, road blockages or other interruptions way beyond the water perimeter or. The debate on flood resilience is linked to the paradigm shift from flood protection to risk management, which started in europe after the major river flood events in 1993 and 1995 along the river rhine (hartmann, 2012), and has developed over the past decades—pushed by further major fluvial and pluvial flood events (begum, stive, & hall. Fig. 1: adopting a resilience lens by operationalizing the four elements into an integrated flood risk management approach. a welfare and recovery capacity (element 1 and 2): different effects of. Flooding is one of the most severe climate related disasters worldwide, and associated with profound societal and environmental challenges 1.by 2050, current 100 year flood events are projected to.
Water Special Issue Flood Risk Management And Resilience Volume Ii Fig. 1: adopting a resilience lens by operationalizing the four elements into an integrated flood risk management approach. a welfare and recovery capacity (element 1 and 2): different effects of. Flooding is one of the most severe climate related disasters worldwide, and associated with profound societal and environmental challenges 1.by 2050, current 100 year flood events are projected to.

Comments are closed.