What Is A Line Graph Understand Graphs Data 6 8 27

What Is A Line Graph Understand Graphs Data 6 8 27 Youtube More lessons: mathandscience twitter: twitter jasongibsonmath in this lesson, you will learn what a line graph is and how to read. Line graph. line graph: graph is an essential topic in schools as a graph represents the data in the form of visualization which makes the raw data understandable in an easy way. examples of graphs are bar graphs, histograms, pie charts, line graphs, etc. here in this article, we will learn about line graphs including its definition, types, and.
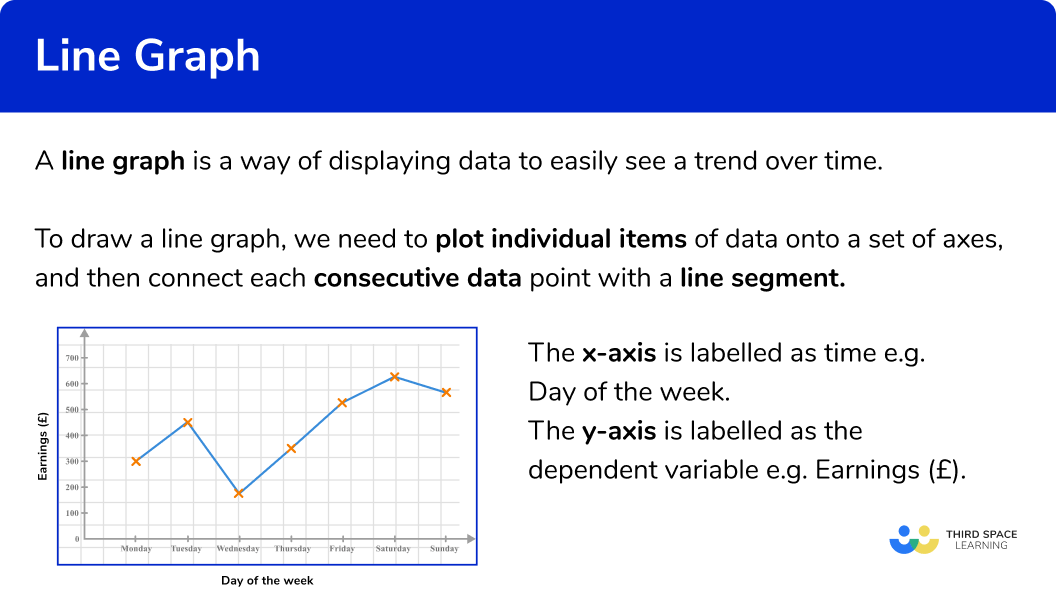
Line Graph Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Also sometimes called a line chart, line graphs are a type of graph that demonstrates how data points trend over a continuous interval. in a line graph, you plot data points on a set of axes and then draw a line to connect these points. the graph shows how the dependent variable changes with any deviations in the independent variable. Line charts typically require a continuous variable for the y axis and a continuous, time, or categorical variable for the x axis. to learn about other graphs, read my guide to data types and how to graph them. example line chart. a school tracks its enrollment over time and uses a line chart to display the long term trends. A line graph, also known as a line chart or a line plot, is commonly drawn to show information that changes over time. you can plot it by using several points linked by straight lines. it comprises two axes called the “ x axis ” and the “ y axis “. the horizontal axis is called the x axis. the vertical axis is called the y axis. Line graphs are used to represent quantitative data collected over a specific subject and a specific time interval. all the data points are connected by a line. data points represent the observations that are collected on a survey or research. learn about a line graph, its parts, reading and creating them, advantages and disadvantages along with solved examples.

Line Graph Figure With Examples Teachoo Reading Line Graph A line graph, also known as a line chart or a line plot, is commonly drawn to show information that changes over time. you can plot it by using several points linked by straight lines. it comprises two axes called the “ x axis ” and the “ y axis “. the horizontal axis is called the x axis. the vertical axis is called the y axis. Line graphs are used to represent quantitative data collected over a specific subject and a specific time interval. all the data points are connected by a line. data points represent the observations that are collected on a survey or research. learn about a line graph, its parts, reading and creating them, advantages and disadvantages along with solved examples. Varieties of line graphs. there are two primary categories of line graphs based on the number of data series depicted: single line graph. as the name suggests, a single line graph plots just one dataset’s performance over intervals against the axes. it is suitable for monitoring simple metrics like monthly temperature or daily stock price. Plot the points on the graph, connect them, and make sure it forms a straight line. look at the graph to see if it passes through the origin. if it does, go to step 3. if it goes through the origin, find the common ratio (unit rate) in the form of \, \cfrac{\textbf{y}}{\textbf{x}} \, . explain what the common ratio (unit rate) means on the graph.

Line Graphs Solved Examples Data Cuemath Varieties of line graphs. there are two primary categories of line graphs based on the number of data series depicted: single line graph. as the name suggests, a single line graph plots just one dataset’s performance over intervals against the axes. it is suitable for monitoring simple metrics like monthly temperature or daily stock price. Plot the points on the graph, connect them, and make sure it forms a straight line. look at the graph to see if it passes through the origin. if it does, go to step 3. if it goes through the origin, find the common ratio (unit rate) in the form of \, \cfrac{\textbf{y}}{\textbf{x}} \, . explain what the common ratio (unit rate) means on the graph.

Comments are closed.