What Is Entropy Definition Meaning Formula And Examples

What Is Entropy Definition And Examples Definition and examples. entropy is defined as a measure of a system’s disorder or the energy unavailable to do work. entropy is a key concept in physics and chemistry, with application in other disciplines, including cosmology, biology, and economics. in physics, it is part of thermodynamics. in chemistry, it is part of physical chemistry. Entropy means the amount of disorder or randomness of a system. it is a measure of thermal energy per unit of the system which is unavailable for doing work. entropy is represented by s and its formula is given as s = kb ln Ω. learn more about entropy, its meaning, properties and formulas in this article.
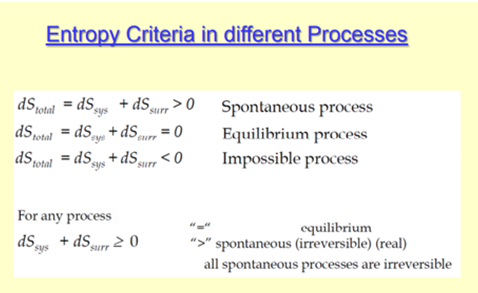
Entropy Equation Definition Summary Examples Units Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. because work is obtained from ordered molecular motion, the amount of entropy is also a measure of the molecular disorder, or randomness, of a system. the concept of entropy provides deep insight into the direction of spontaneous. Definition of entropy. the concept of entropy of a system is directly related to the number of possible microstates in a system. it is defined by the formula s = k*ln (Ω) where Ω is the number of microstates in the system, k is the boltzmann constant, and ln is the natural logarithm. this equation, as well as a great deal of the field of. Entropy is a scientific concept that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. the term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. Entropy is the measure of the disorder of a system. it is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of matter present. in equations, entropy is usually denoted by the letter s and has units of joules per kelvin (j⋅k −1) or kg⋅m 2 ⋅s −2 ⋅k −1. a highly ordered system has low.

Comments are closed.