What Is Operant Conditioning And How Does It Work
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
Operant Conditioning How Does It Work Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a learning method that employs rewards and punishments for behavior. through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence (whether negative or positive) for that behavior. for example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light. Operant conditioning, sometimes called instrumental conditioning or skinnerian conditioning, is a method of learning that uses rewards and punishment to modify behavior. through operant.
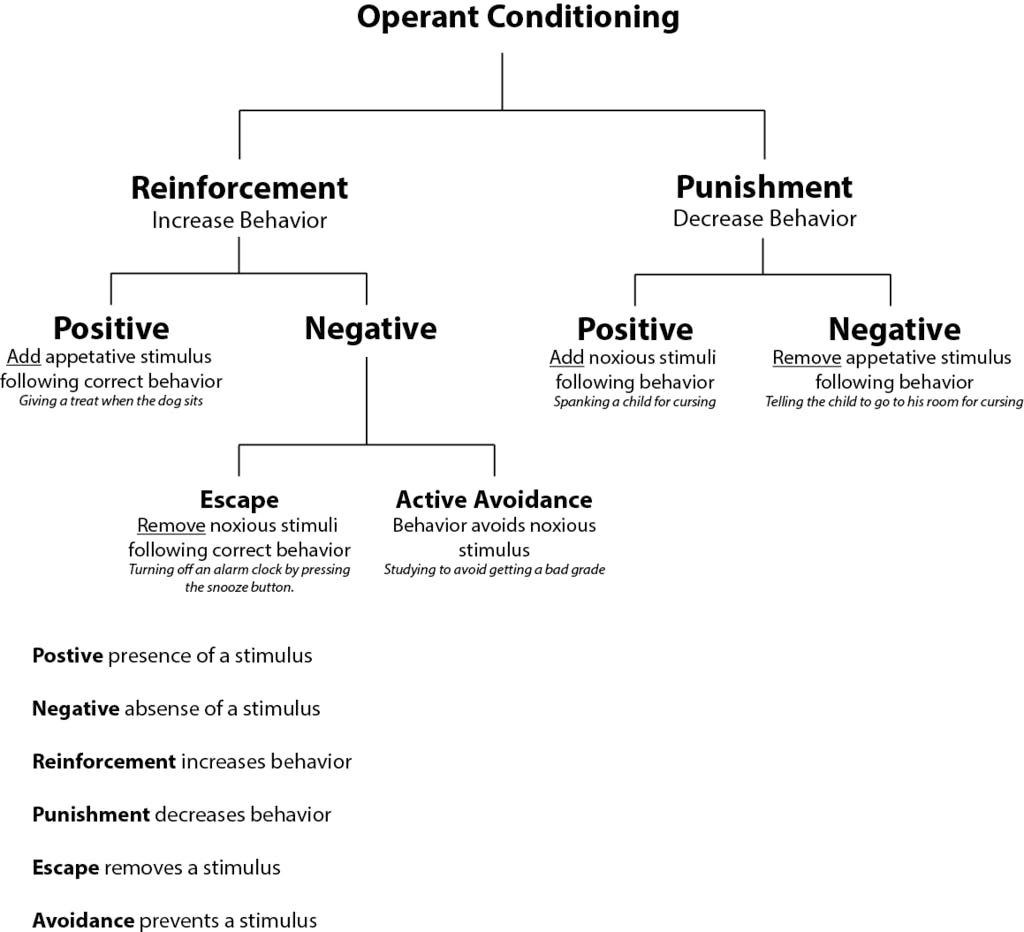
Operant Conditioning Research Operant Conditioning Theory What It Is Operant conditioning, or instrumental conditioning, is a theory of learning where behavior is influenced by its consequences. behavior that is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior that is punished will occur less frequently. by the 1920s, john b. watson had left academic psychology, and other behaviorists were becoming. Operant conditioning is a fundamental concept in psychology. it describes the process where behavior changes depending on the consequences of the behavior (american psychological association, 2023). for example, if a behavior is rewarded (positively reinforced), the likelihood of it being repeated increases. and if it’s punished, the. Put forward by b.f. skinner in the 1930s, operant conditioning is a learning theory that describes how behavior can be shaped by specific consequences called reinforcers and punishers. essentially. Key takeaways: operant conditioning. operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment. in operant conditioning, behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences of that behavior. operant conditioning was defined and studied by behavioral psychologist b.f. skinner.

What Is Operant Conditioning And How Does It Work Docslib Put forward by b.f. skinner in the 1930s, operant conditioning is a learning theory that describes how behavior can be shaped by specific consequences called reinforcers and punishers. essentially. Key takeaways: operant conditioning. operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment. in operant conditioning, behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences of that behavior. operant conditioning was defined and studied by behavioral psychologist b.f. skinner. Operant conditioning is a system of learning that happens by changing external variables called 'punishments' and 'rewards.'. throughout time and repetition, learning happens when an association is created between a certain behavior and the consequence of that behavior (good or bad). you might also hear this concept as “instrumental. Operant conditioning, in psychology and the study of human and animal behaviour, a mechanism of learning through which humans and animals come to perform or to avoid performing certain behaviours in response to the presence or absence of certain environmental stimuli. the behaviours are voluntary—that is, the human or animal subjects decide.
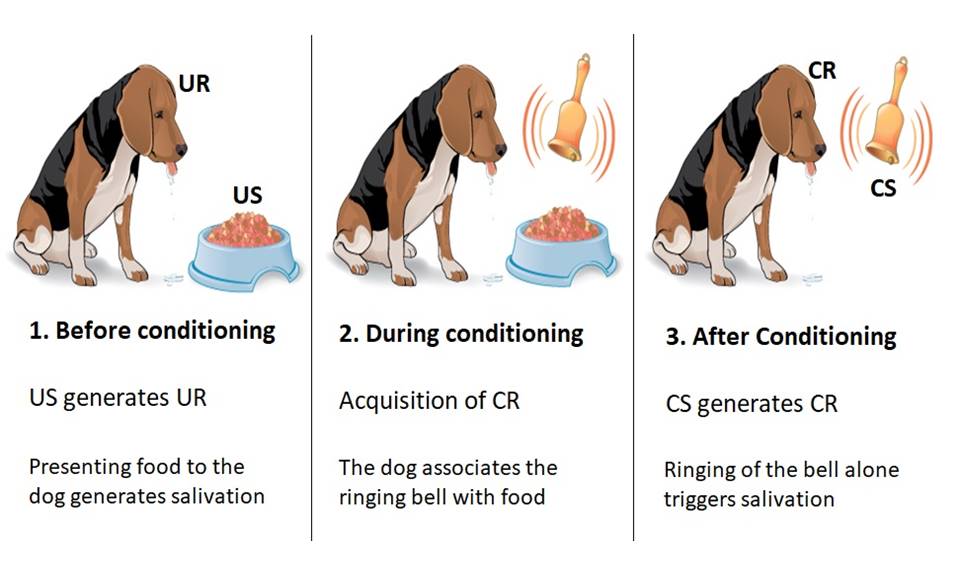
A Simple Explanation Of Classical And Operant Conditioning Operant conditioning is a system of learning that happens by changing external variables called 'punishments' and 'rewards.'. throughout time and repetition, learning happens when an association is created between a certain behavior and the consequence of that behavior (good or bad). you might also hear this concept as “instrumental. Operant conditioning, in psychology and the study of human and animal behaviour, a mechanism of learning through which humans and animals come to perform or to avoid performing certain behaviours in response to the presence or absence of certain environmental stimuli. the behaviours are voluntary—that is, the human or animal subjects decide.

Operant Conditioning Examples Alisen Berde

Comments are closed.