What Is Perpendicular Bisector Theorem In Maths Defin Vrogue Co
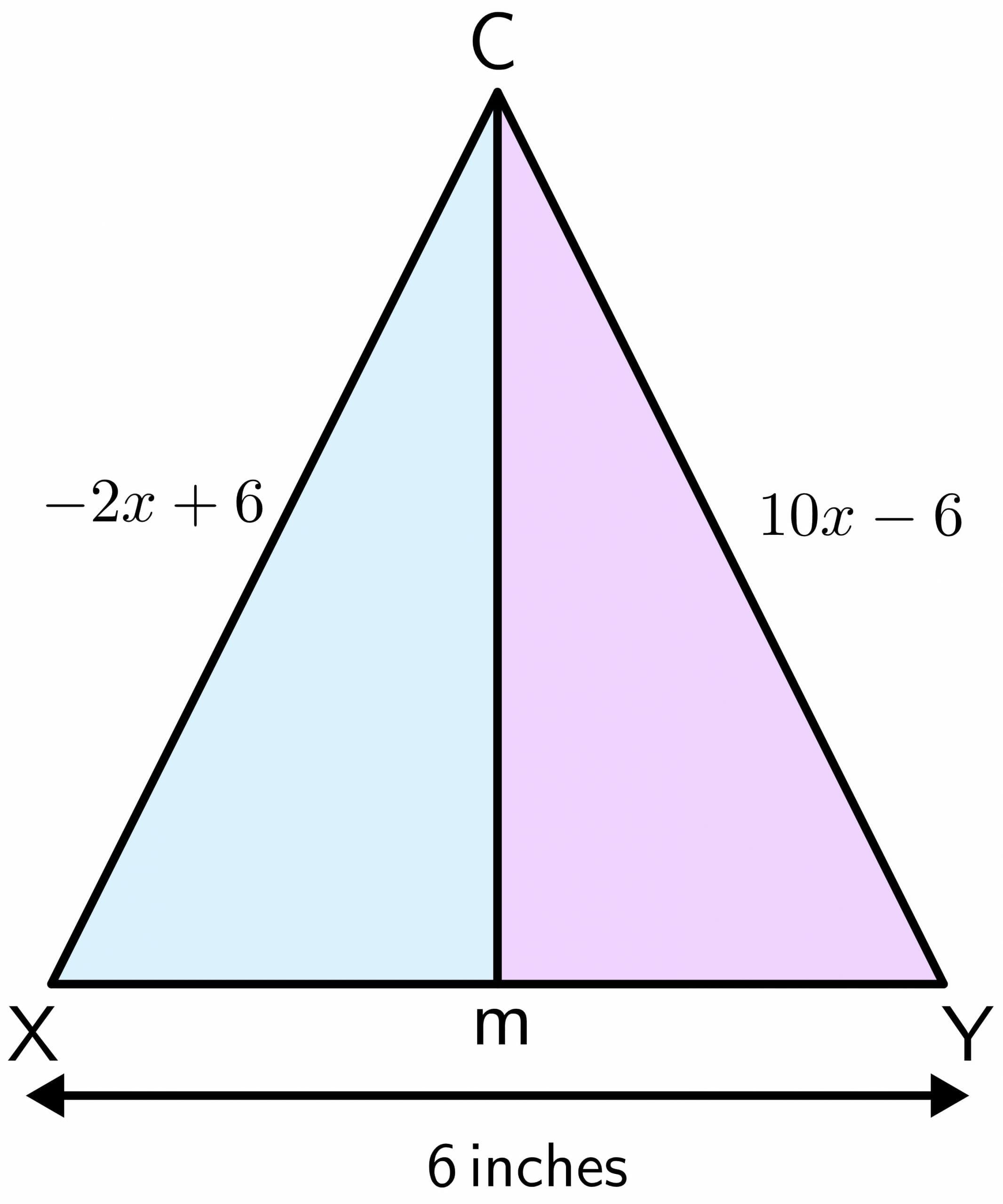
What Is Perpendicular Bisector Theorem In Maths Defin Vrogue Co Solution: according to the perpendicular bisector theorem, any point on the perpendicular bisector is equidistant from both the endpoints of the line segment on which it is drawn. we have ab = ac. 2x 10 = 18. 2x = 18 – 10. 2x = 8. x = 8 2 = 4. find the value of x if ap is the perpendicular bisector of the side bc. Solved examples on perpendicular bisector theorem. example 1: in a pyramid, line segment ad is the perpendicular bisector of triangle abc on line segment bc. if ab = 20 feet and bd= 7 feet, find the length of side ac. solution. it is given that ad is the perpendicular bisector on the line segment bc. so, by perpendicular bisector theorem, any.

What Is Perpendicular Bisector Theorem In Maths Defin Vrogue Co Behold the awesome power of the two words, "perpendicular bisector," because with only a line segment, hm, and its perpendicular bisector, wa, we can prove this theorem. perpendicular bisector theorem proof sas. we are given line segment hm and we have bisected it (divided it exactly in two) by a line wa. that line bisected hm at 90° because. Perpendicular bisector theorem. a perpendicular bisector is a line that intersects a line segment at its midpoint and is perpendicular to that line segment, as shown in the construction below. figure 4.20.1 4.20. 1. one important property related to perpendicular bisectors is that if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then. The perpendicular bisector theorem is a theorem stating that if we take any point on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment, then that point will be equidistant from both the endpoints of the line segment. this is shown in the figure below. A perpendicular bisector is a line, line segment, ray, or plane that divides a line segment into two equal pieces and intersects the bisected line segment at a right angle. examples are the.

What Is Perpendicular Bisector Theorem In Maths Defin Vrogue Co The perpendicular bisector theorem is a theorem stating that if we take any point on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment, then that point will be equidistant from both the endpoints of the line segment. this is shown in the figure below. A perpendicular bisector is a line, line segment, ray, or plane that divides a line segment into two equal pieces and intersects the bisected line segment at a right angle. examples are the. If you want to determine if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment, the perpendicular bisector theorem and its converse might come in handy. this tutorial gives a great example of how to tell if a given point is a perpendicular bisector of a segment! virtual nerd's patent pending tutorial system provides in context. Step 2. consider right triangles АОК and КОВ: АО=ОВ – КО is the perpendicular bisector; КО – the common leg. ΔАОК = ΔКОВ – by legs. according to the property of congruent triangles: due to the fact that point k is an arbitrary point, this equality will be valid for any point lying on the perpendicular bisector.
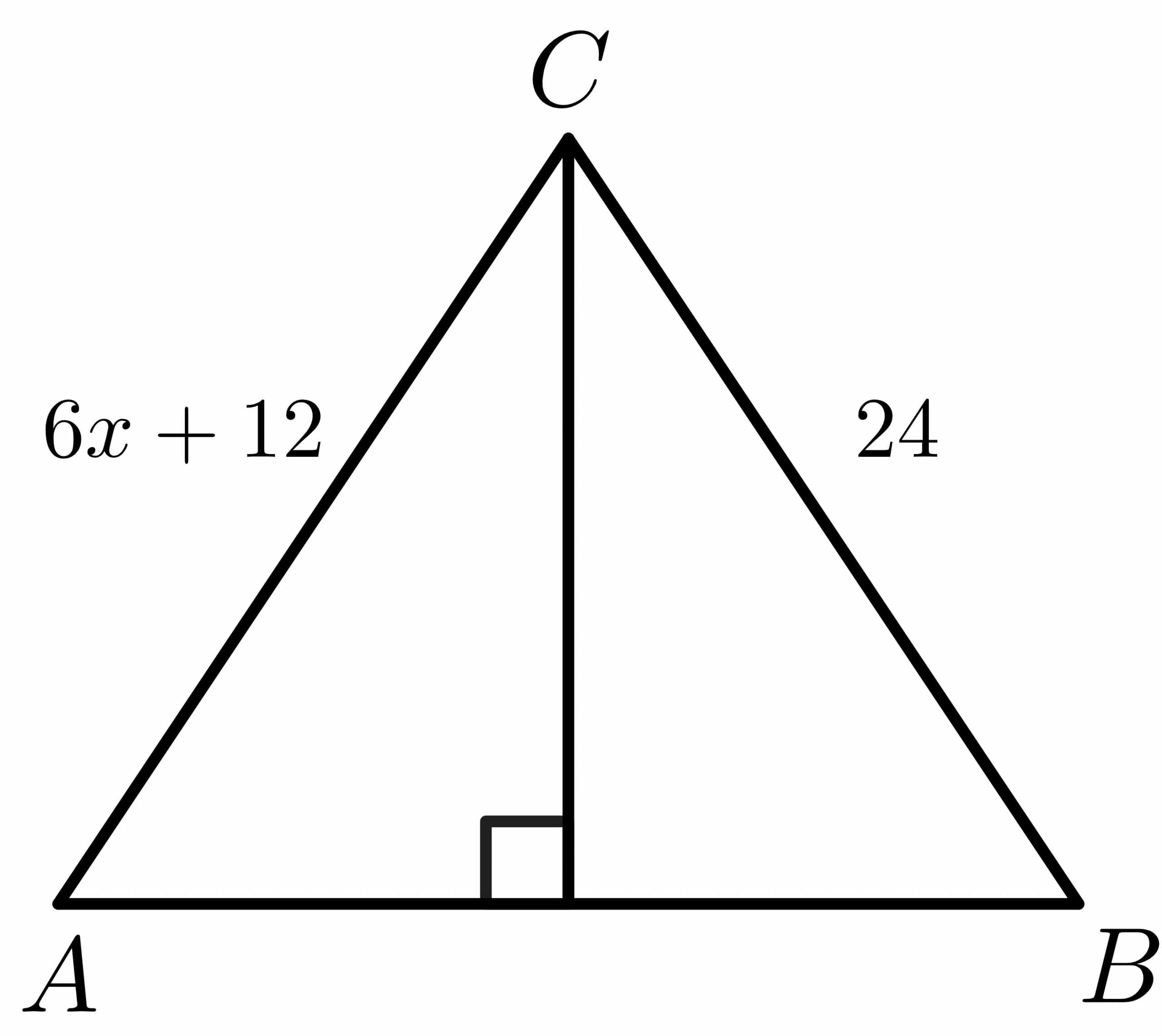
What Is Perpendicular Bisector Theorem In Maths Defin Vrogue Co If you want to determine if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment, the perpendicular bisector theorem and its converse might come in handy. this tutorial gives a great example of how to tell if a given point is a perpendicular bisector of a segment! virtual nerd's patent pending tutorial system provides in context. Step 2. consider right triangles АОК and КОВ: АО=ОВ – КО is the perpendicular bisector; КО – the common leg. ΔАОК = ΔКОВ – by legs. according to the property of congruent triangles: due to the fact that point k is an arbitrary point, this equality will be valid for any point lying on the perpendicular bisector.

Comments are closed.