Whats The Point Of Geometry Euclid Explains It Nice And Easy

What S The Point Of Geometry Euclid Explains It Nice And Easy Learn about the basics of geometry with a friendly introduction from euclid, (who invented it!)geometry lies at the root of all drawing, so it's good to know. Euclid's geometry was introduced by the father of geometry i.e. euclid and is also called euclidean geometry. geometry was originated from the need for measuring land and was studied in various forms in every ancient civilization such as egypt, babylonia, india, etc. euclid's geometry came into play when euclid accumulated all the concepts and fundamentals of geometry into a book called.

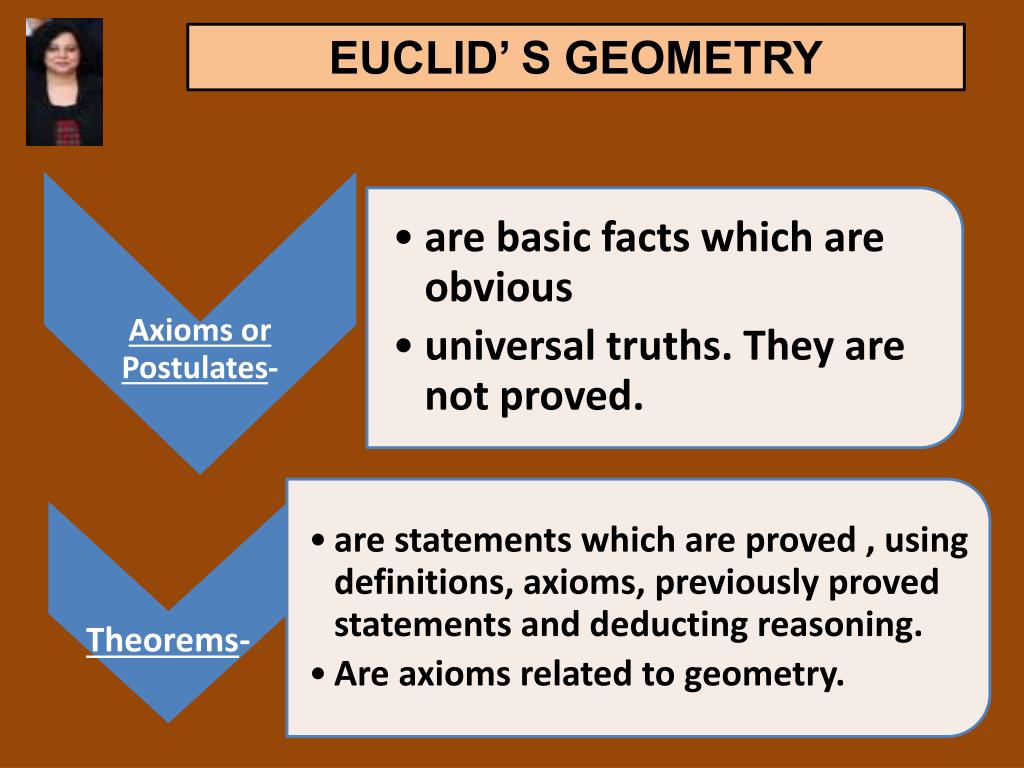
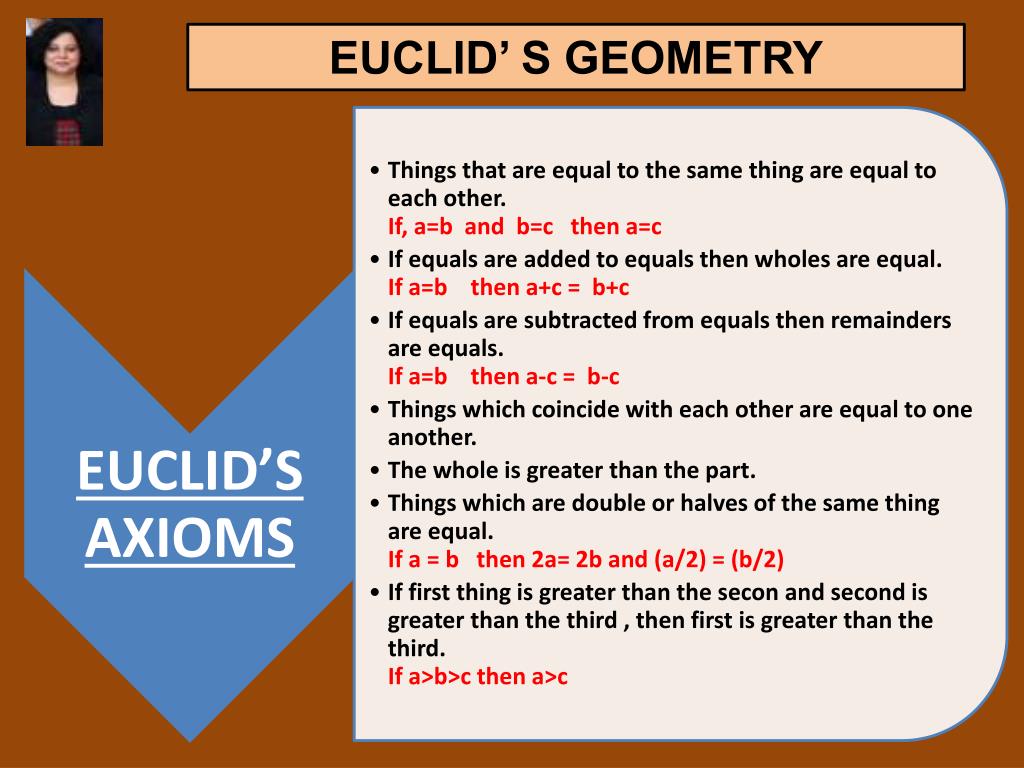
Euclid The Man Who Invented Geometry вђ Artofit Euclid’s five postulates. the five postulates of euclid’s are: euclid’s postulate 1: a straight line may be drawn from anyone point to any other point. euclid’s postulate 2: a terminated line can be produced indefinitely. euclid’s postulate 3: a circle can be drawn with any center and any radius. Euclid's five postulates. euclidean geometry, sometimes called parabolic geometry, is a geometry that follows a set of propositions that are based on euclid's five postulates. there are two types of euclidean geometry: plane geometry, which is two dimensional euclidean geometry, and solid geometry, which is three dimensional euclidean geometry. The 7 axioms of euclid are: 1) a straight line segment can be drawn between any two points. 2) a straight line segment can be extended indefinitely. 3) a circle can be drawn with any point as its center and any distance as its radius. 4) all right angles are equal to each other. Assume the figure has four sides. there are several ways to prove it's a parallelogram. the three simplest ways are: (1) prove that each side is equal in length to its opposite side; (2) prove that each angle is equal to its opposite angle; and (3) prove that opposite sides are parallel to each other.

Euclid Geometry Presentation The 7 axioms of euclid are: 1) a straight line segment can be drawn between any two points. 2) a straight line segment can be extended indefinitely. 3) a circle can be drawn with any point as its center and any distance as its radius. 4) all right angles are equal to each other. Assume the figure has four sides. there are several ways to prove it's a parallelogram. the three simplest ways are: (1) prove that each side is equal in length to its opposite side; (2) prove that each angle is equal to its opposite angle; and (3) prove that opposite sides are parallel to each other. Euclidean geometry is the study of 2 dimensional geometrical shapes and figures. euclidean geometry is based on different axioms and theorems. the word geometry is derived from the greek words ‘geo’ meaning earth and ‘metrein’ meaning ‘to measure’. thus, geometry is the measure of the earth or various shapes present on the earth. Question 1: euclid’s fifth postulate is. the whole is greater than the part. a circle may be described with any radius and any centre. all right angles are equal to one another. if a straight line falling on two straight lines makes the interior angles on the same side of it, taken together = less than two right angles (<1800), then the two.
Ppt юааeuclidюабтащ S юааgeometryюаб Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Euclidean geometry is the study of 2 dimensional geometrical shapes and figures. euclidean geometry is based on different axioms and theorems. the word geometry is derived from the greek words ‘geo’ meaning earth and ‘metrein’ meaning ‘to measure’. thus, geometry is the measure of the earth or various shapes present on the earth. Question 1: euclid’s fifth postulate is. the whole is greater than the part. a circle may be described with any radius and any centre. all right angles are equal to one another. if a straight line falling on two straight lines makes the interior angles on the same side of it, taken together = less than two right angles (<1800), then the two.
Ppt юааeuclidюабтащ S юааgeometryюаб Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Comments are closed.