Why Do Our Brains Get Addicted
What Causes Addiction In The Brain The brain plays a leading role in addiction, just as it plays a role in all human behavior. the choice to try a drug is a decision that that is centered in the executive portion of the brain, the. Nora’s research has been instrumental in demonstrating that addiction is a brain disease that undermines the function of circuits that underlie reward, motivation and self control—and in identifying overlapping circuitry disruptions in obesity. find out more.

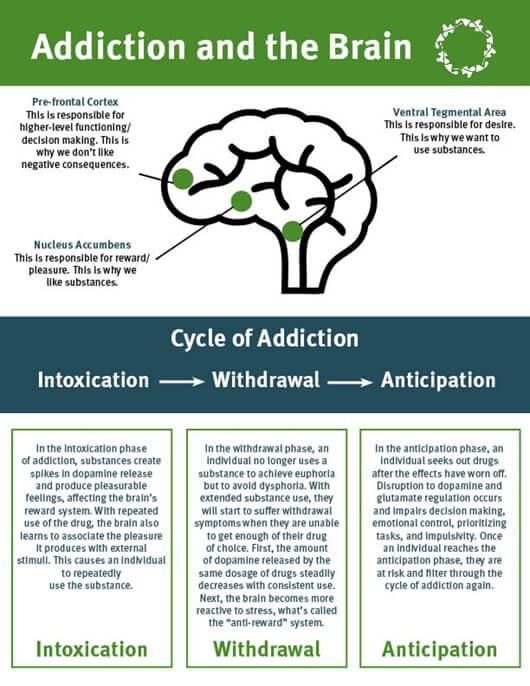
Addiction And The Brain Addiction involves craving for something intensely, loss of control over its use, and continuing involvement with it despite adverse consequences. addiction changes the brain, first by subverting the way it registers pleasure and then by corrupting other normal drives such as learning and motivation. although breaking an addiction is tough, it. When we eat foods, the reward pathways activate a chemical called dopamine, which, in turn, releases a jolt of satisfaction. this encourages you to eat again in the future. when a person develops an addiction to a substance, it’s because the brain has started to change. this happens because addictive substances trigger an outsized response. The science of addiction on drugs and the brain. the human brain is the most complex organ in the body. this three pound mass of gray and white matter sits at the center of all human activity—you need it to drive a car, to enjoy a meal, to breathe, to create an artistic masterpiece, and to enjoy everyday activities. For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction. when scientists began to study addictive behavior in the 1930s, people with an addiction were thought to be morally flawed and lacking in willpower.

Comments are closed.