Why Square Root Of 50 Is Not A Rational Number

Why Square Root Of 50 Is Not A Rational Number Youtube The square root of 50 is not a whole number, or even a rational number. it is an irrational number, but you can simplify it or find rational approximations for it. first note that. 50 = 2 × 5 × 5. contains a square factor 52. we can use this to simplify the square root: √50 = √52 ⋅ 2 = √52 ⋅ √2 = 5√2. apart from simplifying it. First, not all square roots are irrational. for example, sqrt(9) has the perfectly rational solution of 3 before we go on, let's review what it means to have an irrational number it has to be a value that goes on forever in decimal form and is not a pattern, like pi. and since it has a never ending value that does not follow a pattern, it cannot be written as a fraction. for example, 1 3.

Which Square Roots Are Not Rational Numbers Youtube Example: 1.5 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 3 2. example: 7 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 7 1. example 0.317 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 317 1000. but some numbers cannot be written as a ratio! they are called irrational (meaning "not rational" instead of "crazy!"). Check to see if it can be expressed as a fraction, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. if it can’t, then it’s an irrational number. for example, √2 (the square root of 2) is irrational. when expressed as a decimal, it becomes the number 1.41421356237…, which cannot be made into a simple fraction. Difference between rational and irrational numbers. as you can see from the examples, the primary difference between rational and irrational numbers is rational numbers can be written as fractions, irrational numbers can not. numbers in the form of decimals and square roots can be classified as rational and irrational numbers, so we have to be. A) 25 · 64 = 5 · 8 · 5 · 8 = 40 · 40. b) 16 · 49 = 4 · 7 · 4 · 7 = 28 · 28. c) 4 · 9 · 25 = 2 · 3 · 5 · 2 · 3 · 5 = 30 · 30. rational and irrational numbers. a rational number is any number of arithmetic: any whole number, fraction, mixed number, or decimal; together with its negative image. a rational number has the same.
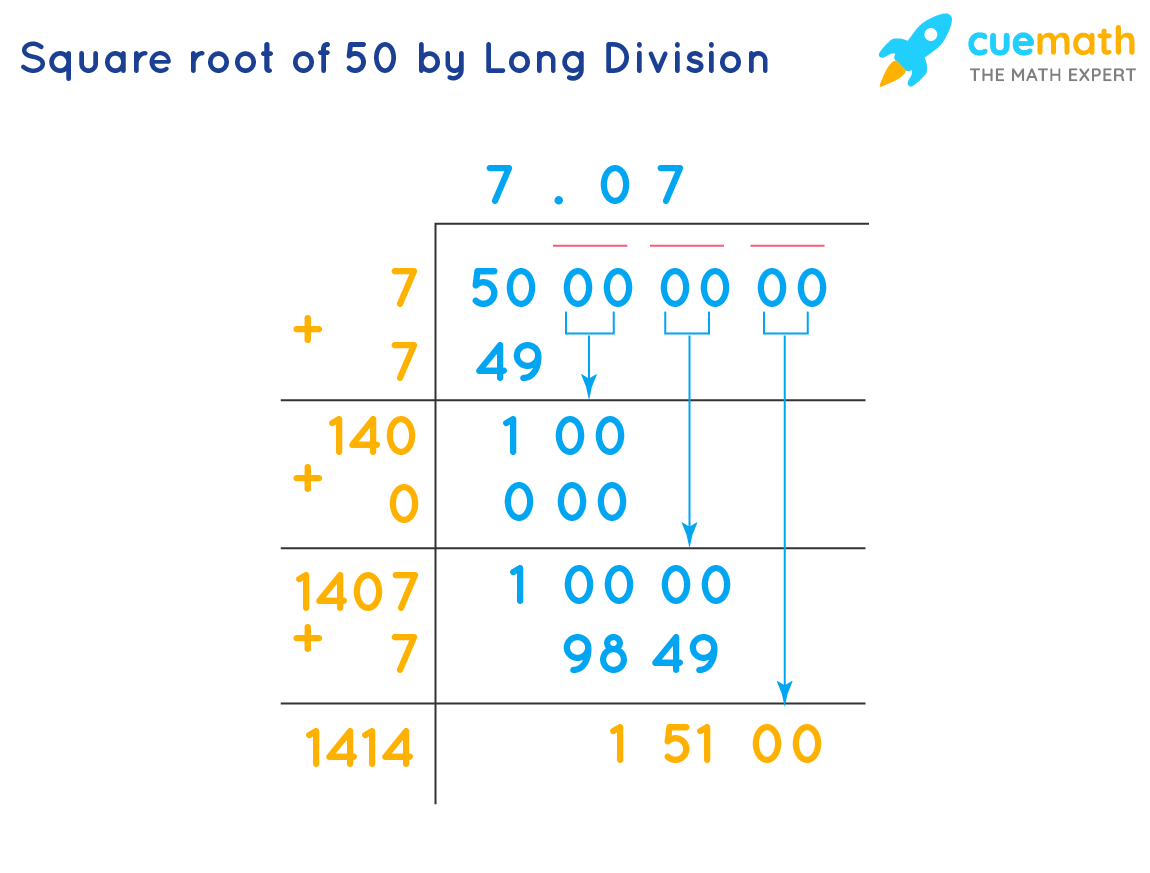
Is The Square Root Of 50 A Rational Number Difference between rational and irrational numbers. as you can see from the examples, the primary difference between rational and irrational numbers is rational numbers can be written as fractions, irrational numbers can not. numbers in the form of decimals and square roots can be classified as rational and irrational numbers, so we have to be. A) 25 · 64 = 5 · 8 · 5 · 8 = 40 · 40. b) 16 · 49 = 4 · 7 · 4 · 7 = 28 · 28. c) 4 · 9 · 25 = 2 · 3 · 5 · 2 · 3 · 5 = 30 · 30. rational and irrational numbers. a rational number is any number of arithmetic: any whole number, fraction, mixed number, or decimal; together with its negative image. a rational number has the same. If the decimal representation of a number does not terminate or form a repeating decimal, that number is not a rational number. one class of numbers that is not rational is the square roots of integers or rational numbers that are not perfect squares, such as 10 10 and 25 6 25 6. more generally, the number b b is the square root of the number a. Rational numbers. a rational number can be made by dividing an integer by an integer. (an integer itself has no fractional part.) example: 1.5 is a rational number because 1.5 = 3 2 (3 and 2 are both integers).

Simplifying The Square Root Of 50 Lesson Study If the decimal representation of a number does not terminate or form a repeating decimal, that number is not a rational number. one class of numbers that is not rational is the square roots of integers or rational numbers that are not perfect squares, such as 10 10 and 25 6 25 6. more generally, the number b b is the square root of the number a. Rational numbers. a rational number can be made by dividing an integer by an integer. (an integer itself has no fractional part.) example: 1.5 is a rational number because 1.5 = 3 2 (3 and 2 are both integers).

Chapter 8 Section Ppt Download

Comments are closed.